Create HTTP Load Balancer
Objective
This guide provides instructions on how to create an HTTP load balancer in F5® Distributed Cloud Console (Console) using guided configuration. This includes configuring the required objects for the virtual host. To learn more about virtual hosts, see Virtual Host.
Using guided creation for HTTP load balancer, you can create the following types of load balancers:
- HTTP load balancer
- HTTPS load balancer with your own TLS certificate
- HTTPS load balancer with automatic TLS certificate (minted by F5® Distributed Cloud Services)
Using the instructions provided in this guide, you can perform the following:
- Create and advertise an HTTP load balancer
- Create and advertise an HTTPS load balancer with your TLS certificate or with the certificate minted by Distributed Cloud Services
Note: Distributed Cloud Services support automatic certificate generation and management. You can either let Distributed Cloud Services DNS manage your zone (see Create Primary Zone), or you can add the CNAME record to your DNS records. See Automatic Certificate Generation for certificates managed by Distributed Cloud Services.
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites apply:
-
A Distributed Cloud Services Account. If you do not have an account, see Getting Started with Console.
-
A valid DNS domain managed by Distributed Cloud DNS in case you want Distributed Cloud Services to act as domain name server (DNS) or a CNAME entry in your DNS zone file. For instructions on how to set up Distributed Cloud DNS for your domain to Distributed Cloud Services, see Create Primary Zone.
-
A Distributed Cloud Services Customer Edge (CE) site in case of deploying your applications. If you do not have a site, create a site using the instructions provided in the Site Management guides. See the vK8s Deployment guide for deploying your applications on the Distributed Cloud Services network cloud or edge cloud.
Configuration
The configuration option to create the HTTP load balancer guides you through the steps for required configuration. This document covers each guided step and explains the required actions to be performed for each step.
Step 1: Log into Console and create new load balancer.
-
Log into Console.
-
Click
Multi-Cloud App Connect.
Figure: Console Homepage
- Select
Manage>Load Balancers>HTTP Load Balancers.
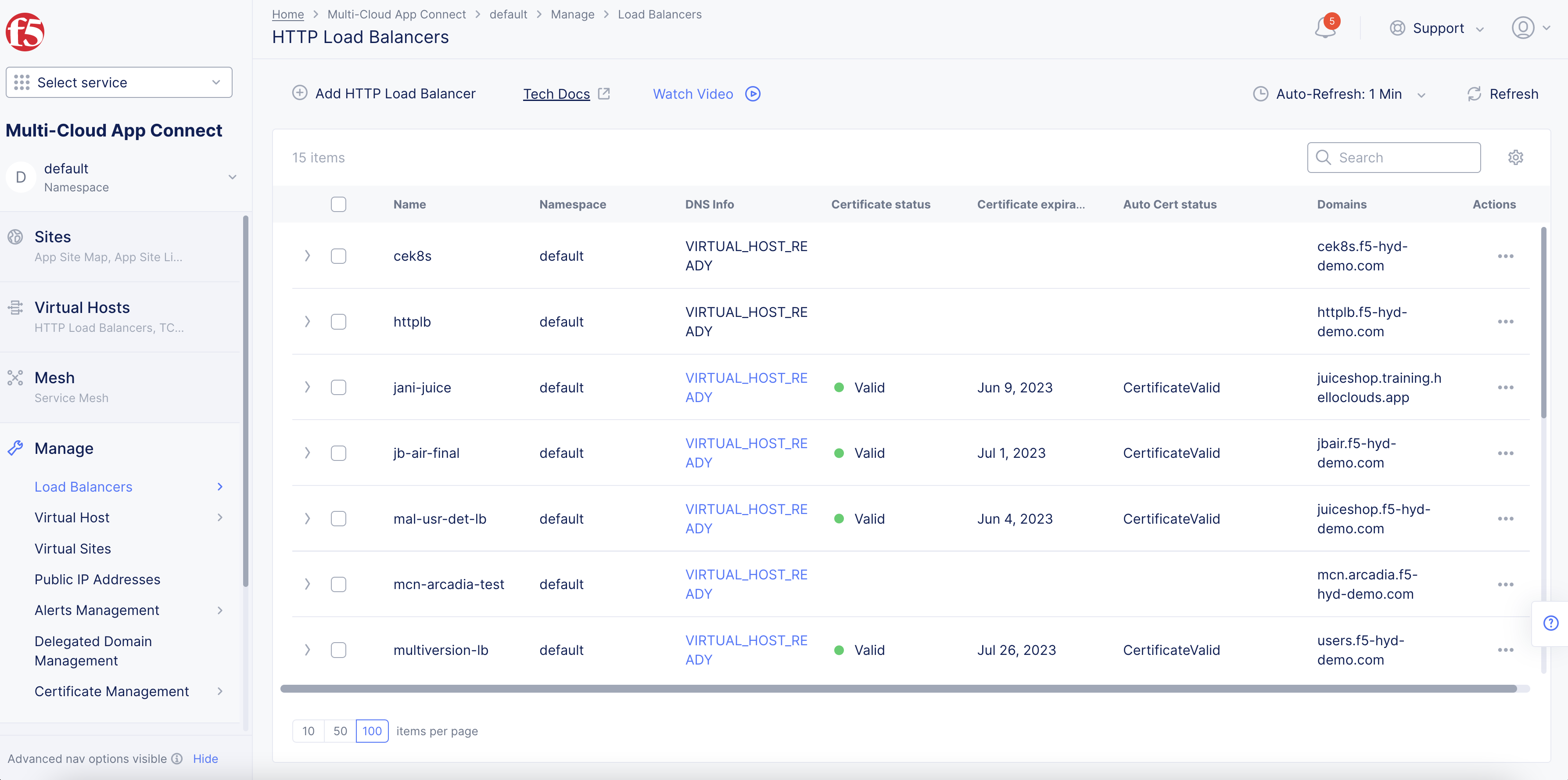
Figure: Load Balancers
-
Confirm the correct namespace is selected.
-
Click
Add HTTP Load Balancer.
Step 2: Configure metadata, domains, and load balancer type.
-
In the
Namefield, enter a name for the new load balancer. -
Optionally, select a label and enter a description.
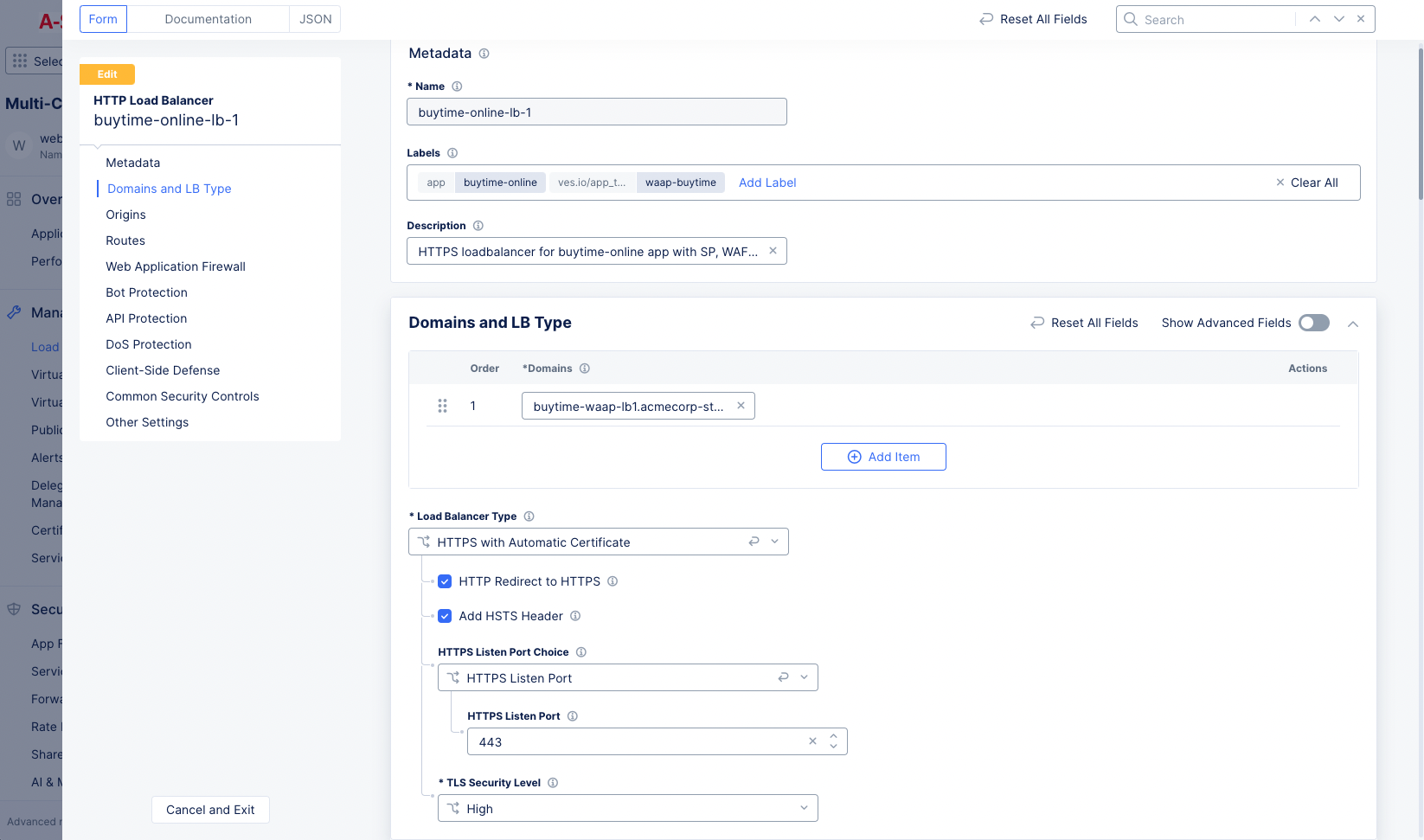
Figure: Load Balancer Form
-
In the
Domainsfield, enter a domain name. You can use wildcards to catch prefixes and suffixes. -
Click
Add itemto add more domains, if needed. -
From the
Load Balancer Typedrop-down menu, select an option. The following options are supported:-
Select
HTTPto create the HTTP load balancer. -
Select
HTTPS with Automatic Certificateto create the HTTPS load balancer with an automatic TLS certificate. -
Select
HTTPS with Custom Certificateto create the HTTPS load balancer with your custom TLS certificate.
-
Note: Do not add both wildcard and top level domains (for example,
*.example.comandexample.com) if you are using an automatic certificate for different load balancers.
Note: When looking at the
StatusorGlobal Statusfor a load balancer,statusObjectis visible only when the certificate is of type automatic certification.
-
If you select
HTTP, then select whether to have Distributed Cloud Services manage your DNS records withAutomatically Manage DNS Records. This option requires you to have a primary zone set up in Distributed Cloud DNS. -
If you select
HTTPS with Automatic CertificateorHTTPS with Custom Certificate, then optionally, selectHTTP Redirect to HTTPSandAdd HSTS Headercheckboxes. -
For all load balancer types, use the
HTTP Listen Port Choiceto select between using a single port or a range of ports, and then enter the port number(s). For a range of ports, enter a list of non-overlapping port ranges with a maximum of 64 ports in the list, e.g.443,100-120,8080,9080-9089. -
If you are using
HTTPS with Automatic Certificate, use theTLS Security Leveldrop-down menu to select the TLS level you want to use. -
If you are using the
HTTPS with Custom Certificateoption:-
Use the
TLS Configurationdrop-down menu to choose betweenTLS CertificatesorInline Certificate (legacy)options, and then clickConfigure. -
From the
TLS Security Leveldrop-down menu, select the desired level. -
For each certificate you want to add, select
Add Itemfrom theCertificatesdrop-down menu to see theTLS Certificateform.

Figure: TLS Certificate Form
-
Enter a name and optionally labels and a description.
-
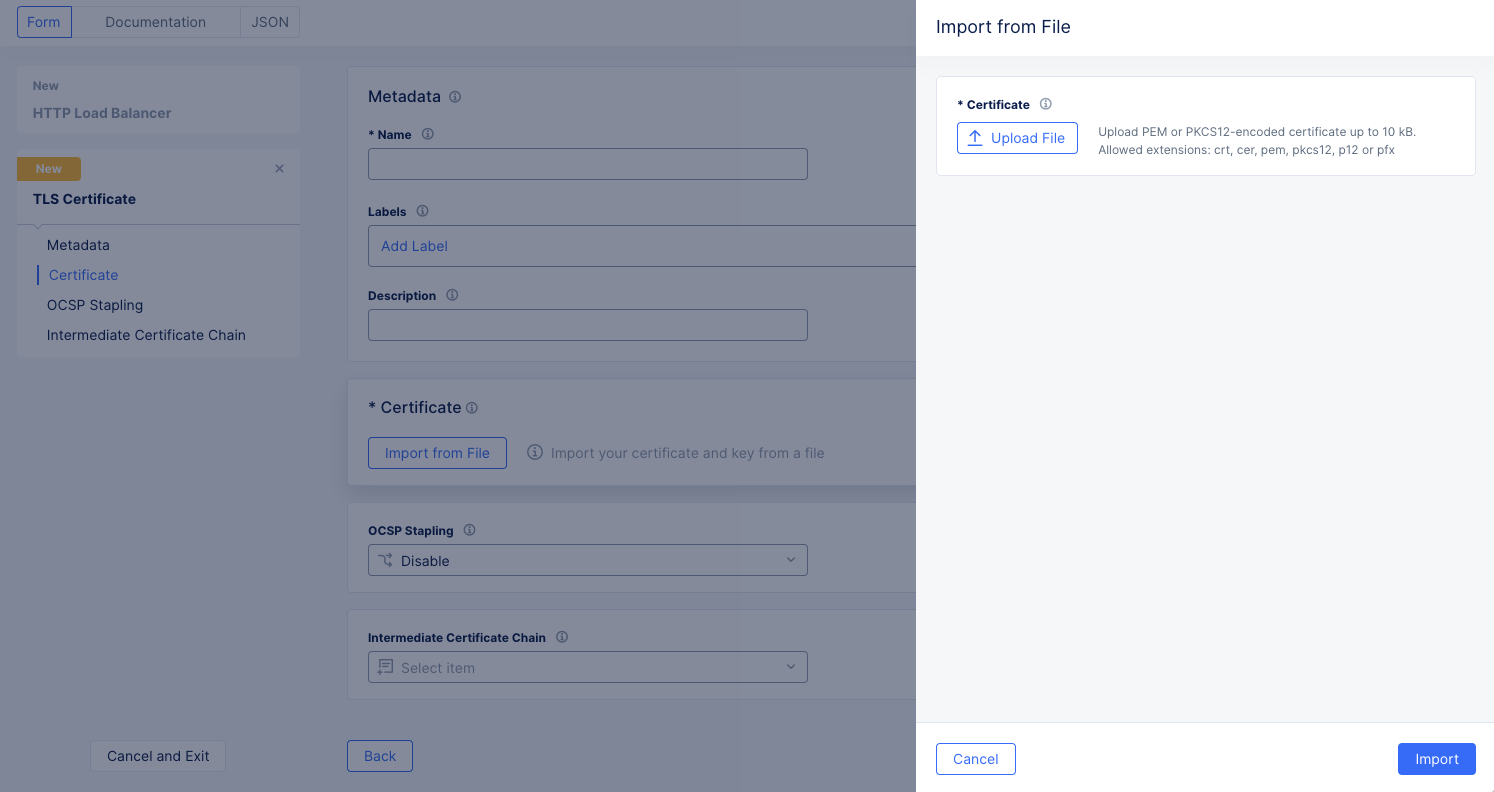
Click
Import from Fileto see the sliding import panel. ClickUpload Fileand select your file using the system file browser. Then clickImport.
Note: If you would prefer to paste your certificate in rather than import from file, see Enable TLS on a Load Balancer.
-
From the
OCSP Staplingchoice drop-down menu, select an OCSP stapling choice. -
If you have an intermediate chain, select
Add Itemfrom theIntermediate Certificate Chaindrop-down menu. Then upload the intermediate chain the same way you uploaded the certificate.
Note: You can add more than one certificate using the
Add Itemoption. However, only one certificate per encryption type (such as RSA and EC-DSA) is supported. -
-
If you are using the
HTTPS with Automatic Certificateoption:
Note: If you created a DNS Zone for a domain for a deployed AWS customer edge (CE) site, and advertise that site using a virtual IP address (Internet VIP), an automatic certificate is generated. This is not available on other types of deployed sites.
-
Enable the
Show Advanced Fieldsoption. -
From the
Mutual TLSdrop-down menu, selectEnableorDisablefor mutual TLS encryption:-
Copy the CA certificate information into the Box using the
PEMorBase64option. -
Check the
Client Certificate Optionalcheckbox if you want the client certificate check to be optional. If the client certificate is available, it will be verified and the connection will be terminated if verification fails. If the client certificate is absent, the connection is accepted. -
From the
Verify client certificate with CRmenu, selectCRLto have the client certificate verified against the CRL, and then select theCRL. -
From the
Add X-Forwarded-Client-Cert Headermenu, enable the adding of an X-Forwarded-Client-Cert (XFCC) proxy header to send client certificate details to the origin. You can choose to send the entire certificate, a single field, or multiple fields using the following:By,Hash,Cert,Chain,Subject,URI, andDNS.
-
-
From the
Server Response Headerdrop-down menu, select an option for the server response header. The following options are supported:-
Default: Specifies that the response header name isserver, and the value isvolt-adc. -
Modify header value: Specifies that a custom value be added to the existing server header. This will overwrite existing values, if any, in the server header. -
Append header value: Specifies that a custom value be added to the server header if no value is present. If there is an existing server header value, this option does not overwrite the value. Enter a header value in theAppend header valuefield. -
Do not modify: Specifies that the existing server header is passed as is. If no server header is present, a new header is not appended.
-
-
From the
Path Normalizationmenu, select an option.
Step 3: Configure origin pools.
-
In the
Originssection, clickAdd Itemto create an origin pool. -
From the
Select Origin Pool Methodmenu, select an option for a simple origin pool or a custom cluster:-
Origin Pool: From theOrigin Pooldrop-down menu, select an origin pool. To create a new origin pool, clickAdd Item. Follow the instructions at Origin Pools. -
Custom Cluster: From theCustom Clustermenu, select the cluster to use.
-
-
In the
Weightfield, set the numeric value. -
In the
Priorityfield, set the numeric value. -
Click
Apply.
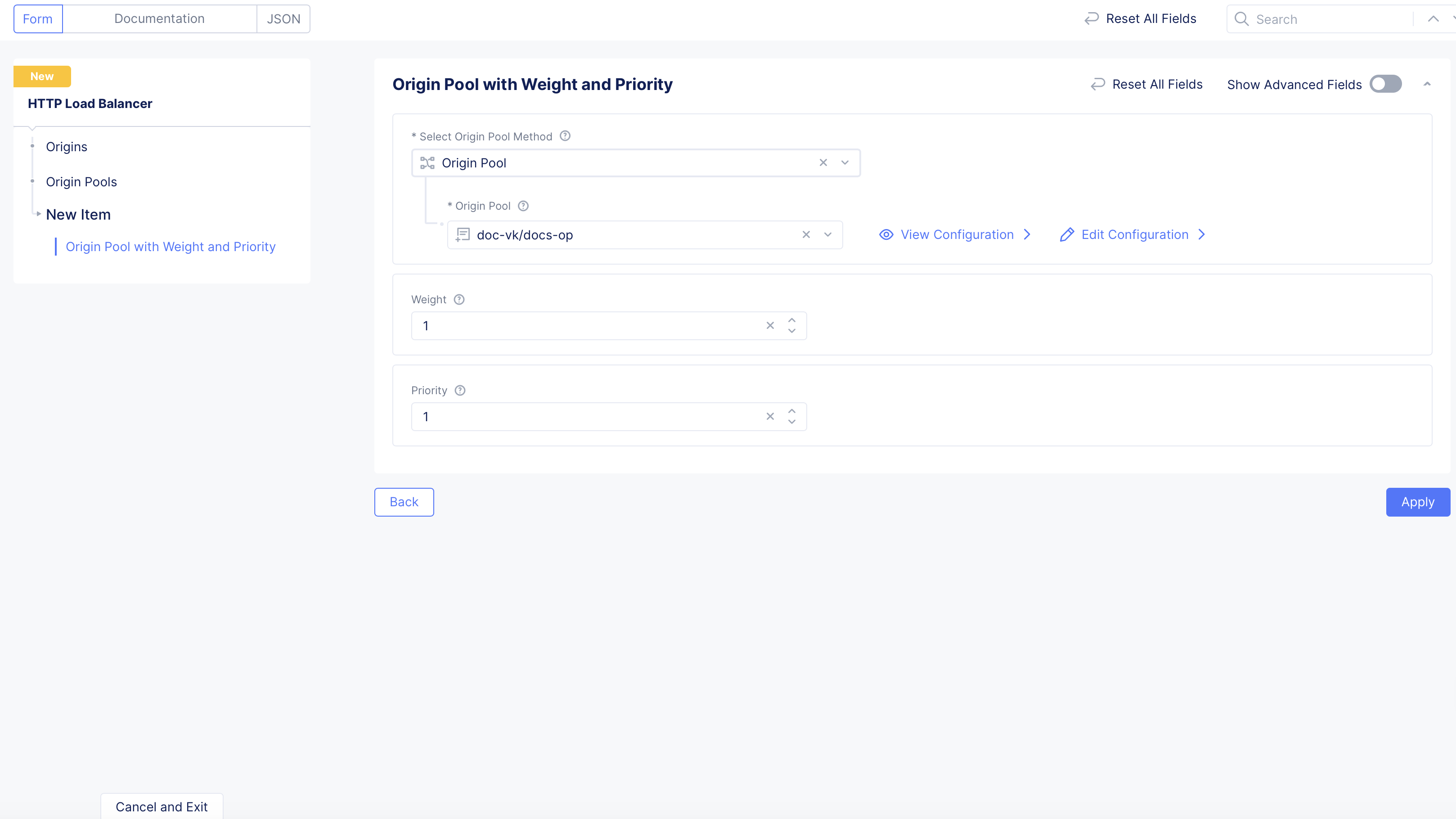
Figure: Origin Pool Configuration
Step 3.1: Optionally, configure origin server subset rules.
Origin server subset rules provide the ability to create match conditions on incoming source traffic to the HTTP load balancer using country, ASN, regional edge (RE), IP address, or client label selectors for subset selection of destination (origin servers).
As prerequisites, (1) create a label (key-value pair), (2) in origin pool configuration, add labels to one or more origin servers, (3) and then in the Other Settings subsection, select Enable Subset Load Balancing. Add one or more keys to origin server subset classes. Choose a setting for subset fallback policy. The default option is to select any origin server.
-
Enable the
Show Advanced Fieldsoption. -
Under
Origin Server Subset Rules, clickConfigure.
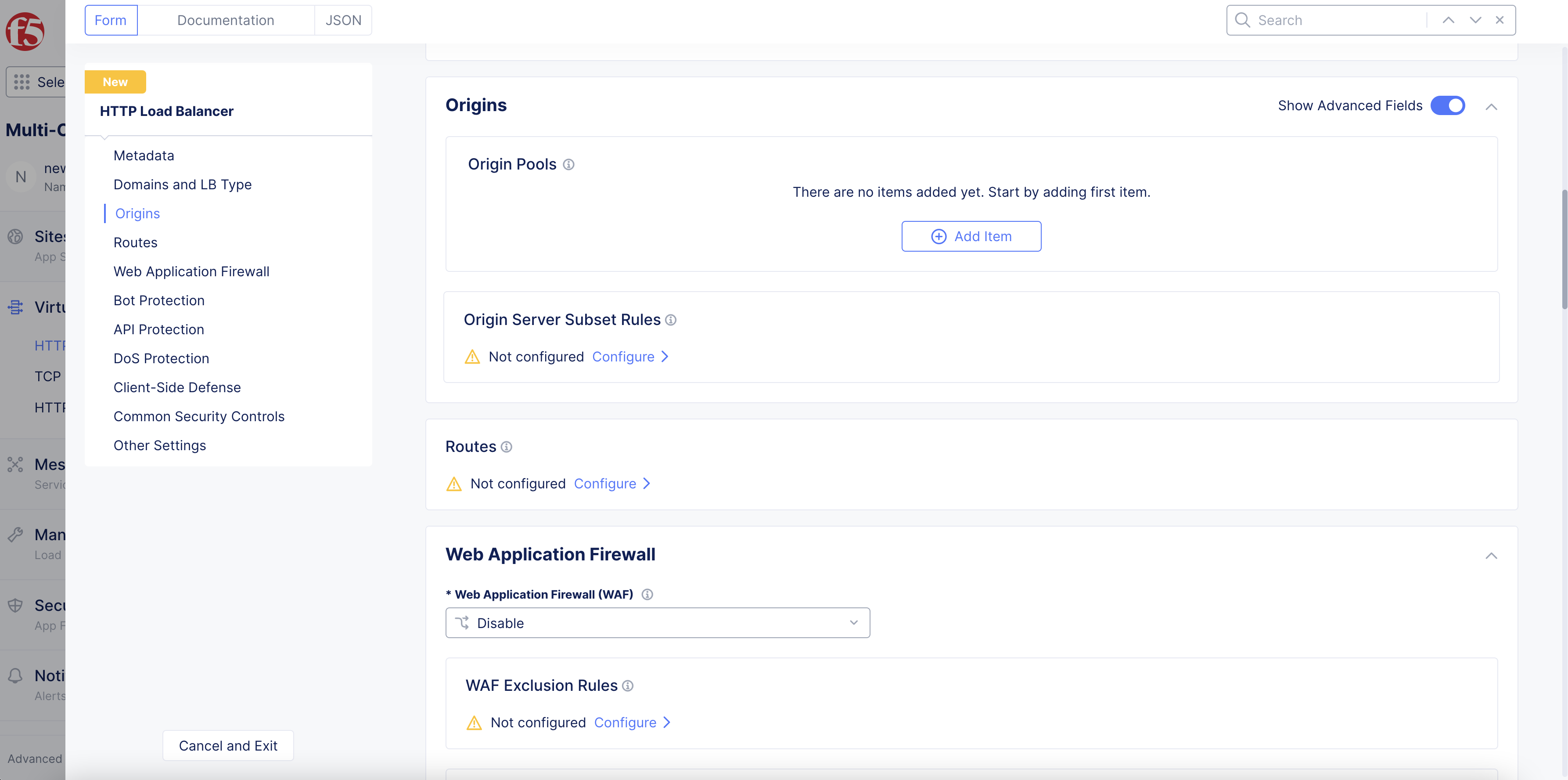
Figure: Origin Server Subset
-
Click
Add Item. -
In the
Namefield, enter a name for the rule.
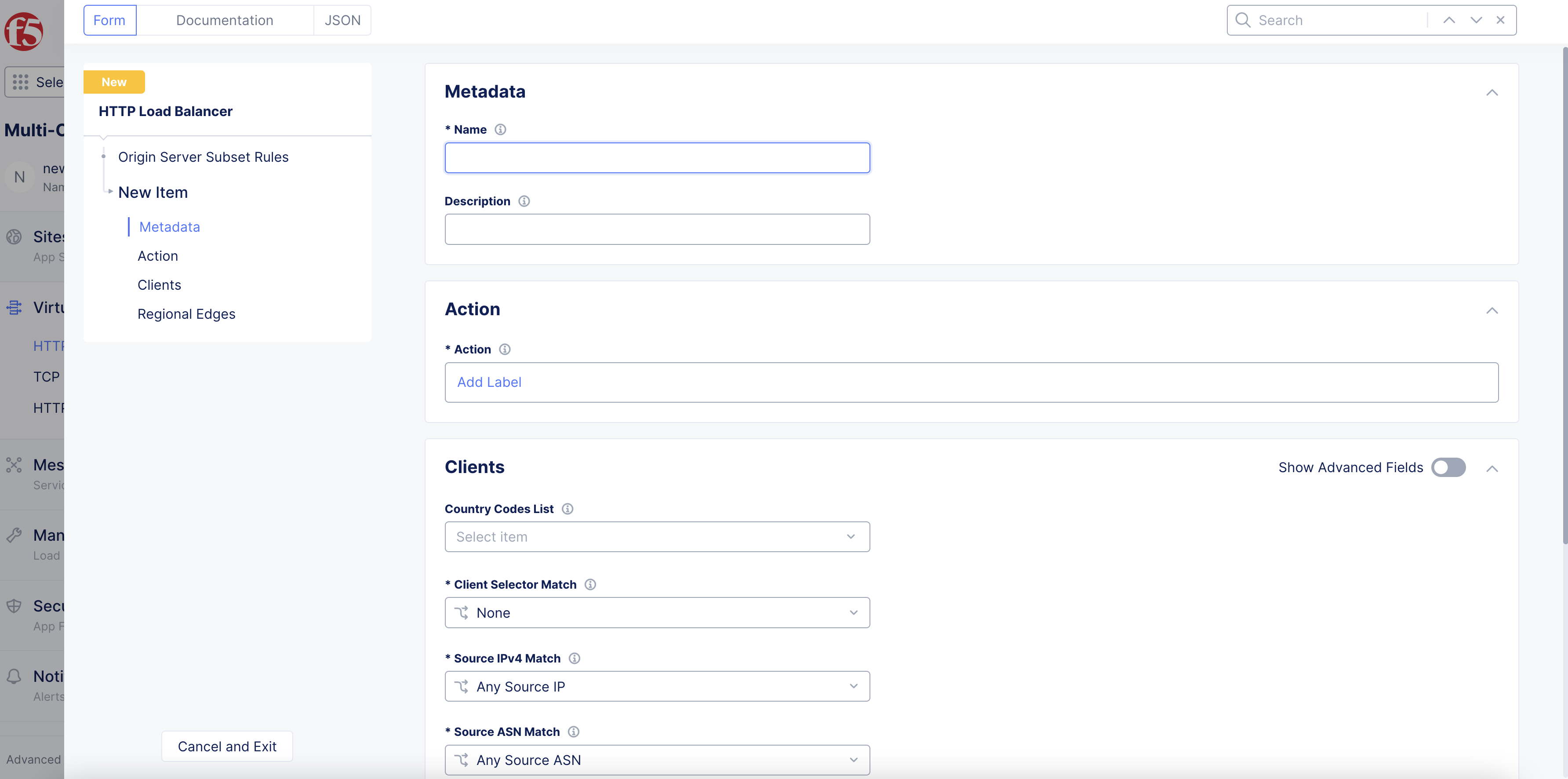
Figure: Origin Server Subset Rule Configuration
-
From the
Actionfield, clickAdd Labeland select the same label(s) that you assigned to origin servers in the origin pool configuration. -
Optionally, select a country from the
Country Codes Listmenu. -
From the
Client Selector Matchmenu, select an option to match on label selectors. -
From the
Source IPv4 Matchmenu, select an option to match on client IP address. -
From the
Source ASN Matchmenu, select an option to match on client ASN. -
In the
Regions Edgessection, clickAdd Itemto select an RE to match traffic to. -
After you finish, click
Apply.
Step 4: Configure Routes.
-
In the
Routessection, clickConfigure. -
Click
Add Item.
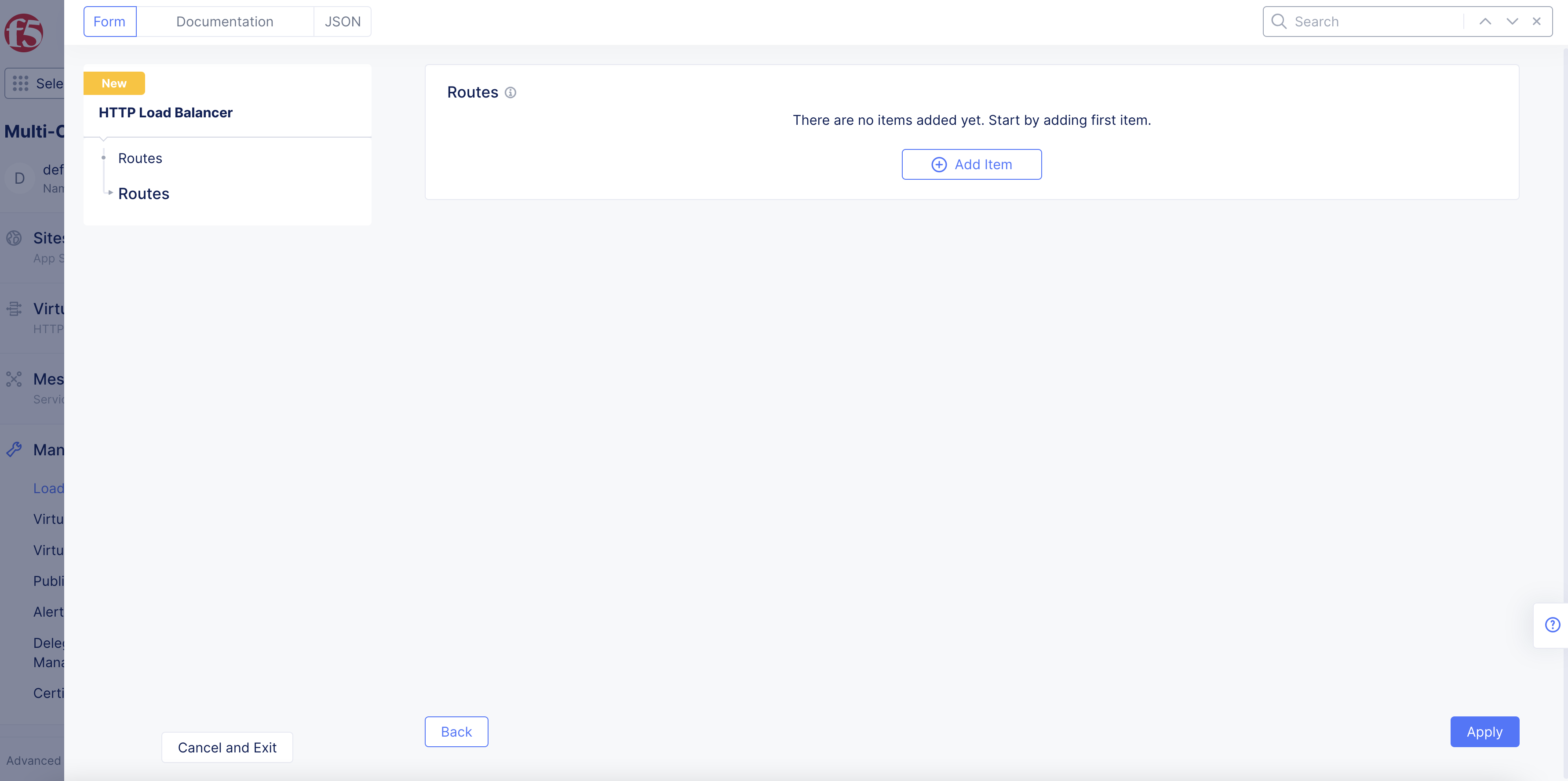
Figure: Optional Routes Configuration
-
From the
Select Type of Routemenu, select an option. -
Simple Route: matches a path and/or HTTP methods to forward the matching traffic to origin pools configured:-
Select a method for
HTTP Method. -
Select the type of path match for the
Path Matchfield. -
Add a path prefix in the
Prefixfield. You can also configure specific origin pools and/or headers for this using theAdd Itemoptions in theOrigin PoolsandHeaderssections. -
From the
Select Host Rewrite Methodmenu, select an option to specify how the host header can be modified during forwarding. -
Select an option from the
Query Parametersdrop-down menu. -
In the
Advanced Optionsfield, clickConfigureto configure advanced settings for each route.
-
Note: One of the advanced options is the Retry Policy, which allows you to specify when and how to retry based on the response code. You can select any of the following policies in the Select Retry Policy drop-down:
- Use Default Retry Policy: The default Retry Policy is
1 retrydone on the condition of5xx, which means one retry will be performed if the upstream server responds with any 5xx response code or if it fails to respond (timeout, disconnect, and more).- Do not retry: Select this option if you do not want to configure a retry policy.
- Custom Retry Policy: Select this option to configure a custom retry policy by providing values to the following fields:
- Retry Condition: Specifies the condition when a retry must occur. You can select multiple conditions from the drop-down. For more information on the retry conditions, see Retry Policies.
- Number of Retries: Specifies the allowed number of retries.
- Per Try Timeout: Specifies the timeout for the retry in milliseconds.
- Status Code to Retry: Specifies the HTTP status codes that must trigger a retry in addition to those specified by the retry conditions.
- Base Retry Interval: Specifies the base time interval between retries.
- Maximum Retry Interval: Specifies the maximum time interval between retries in milliseconds. This is an optional parameter. However, if you configure a value, ensure that it is greater than or equal to the Base Retry Interval. The default value is 10 times of the Base Retry Interval.
Ensure that the Per Try Timeout is greater than or equal to the max response time for an HTTP request, and the Routes Timeout is greater than or equal to No of Retries.
When only
retriable-status-codesis specified inRetry Condition, the retry will be done only when the origin server returns any of the response codes configured underretriable-status-codes. If the origin server does not respond and timeout happens after thePer Try Timeout, then the retry is not attempted, as there is no response code from the origin server.
-
Redirect Route: matches a path and/or HTTP methods to redirect the matching traffic to another URL:-
Select method for
HTTP Methodand a path for thePath Matchfield. -
Add a path prefix in the
Prefixfield. -
Configure the
Redirect ParametersforProtocol,Host,Redirect Pathfor redirect URL, andResponse Code. -
Select an option from the
Query Parametersdrop-down menu.
-
-
Direct Response Route: matches a path and/or HTTP methods to send the response directly to the matching traffic:-
Select method for
HTTP Methodand a path for thePath Matchfield. -
Add a path prefix in the
Prefixfield. -
Click the
Configureoption in theDirect Responsefield. Enter a response code, enter response body, and then clickApply.
-
-
Custom Route Object: uses an existing custom route object:- Select a route object in the
Reference to Custom Routedrop-down menu. For information on how to create a custom route, see How to setup path-based routing or application load balancing.
- Select a route object in the
-
To configure additional options per route:
-
Under
Advanced Options, clickConfigure. -
From the
Hash Policy Choicemenu, select an option to configure. -
Optionally, configure
Origin Servers Subsetsoption. -
Under
CSRF Policy, clickConfigure. From theAllowed Domains (Source Origin)menu, select an option. ForSpecified domains, enter the specific domain name. ClickApply.
-
-
Click
Applyto add the route.
Note: You can click
Add Itemto add more routes per your requirements.
- To set up path-based routing, see How to Set Up Custom Routing.
Step 5: Configure WAF and corresponding security features.
You can choose to disable WAF application (default setting) or you can select a WAF that was previously created, configured, and apply it in your load balancer security settings. In addition, you can also create and enable a new WAF and have your load balancer configured to exclude specific WAF rules from processing certain requests.
-
Go to the
Web Application Firewallsection. -
From the
Web Application Firewall (WAF)drop-down menu, select whether to enable the WAF for this HTTP load balancer.Disableis the default value. -
If you select
Enable, use theEnabledrop-down menu to select your WAF to apply to this load balancer.
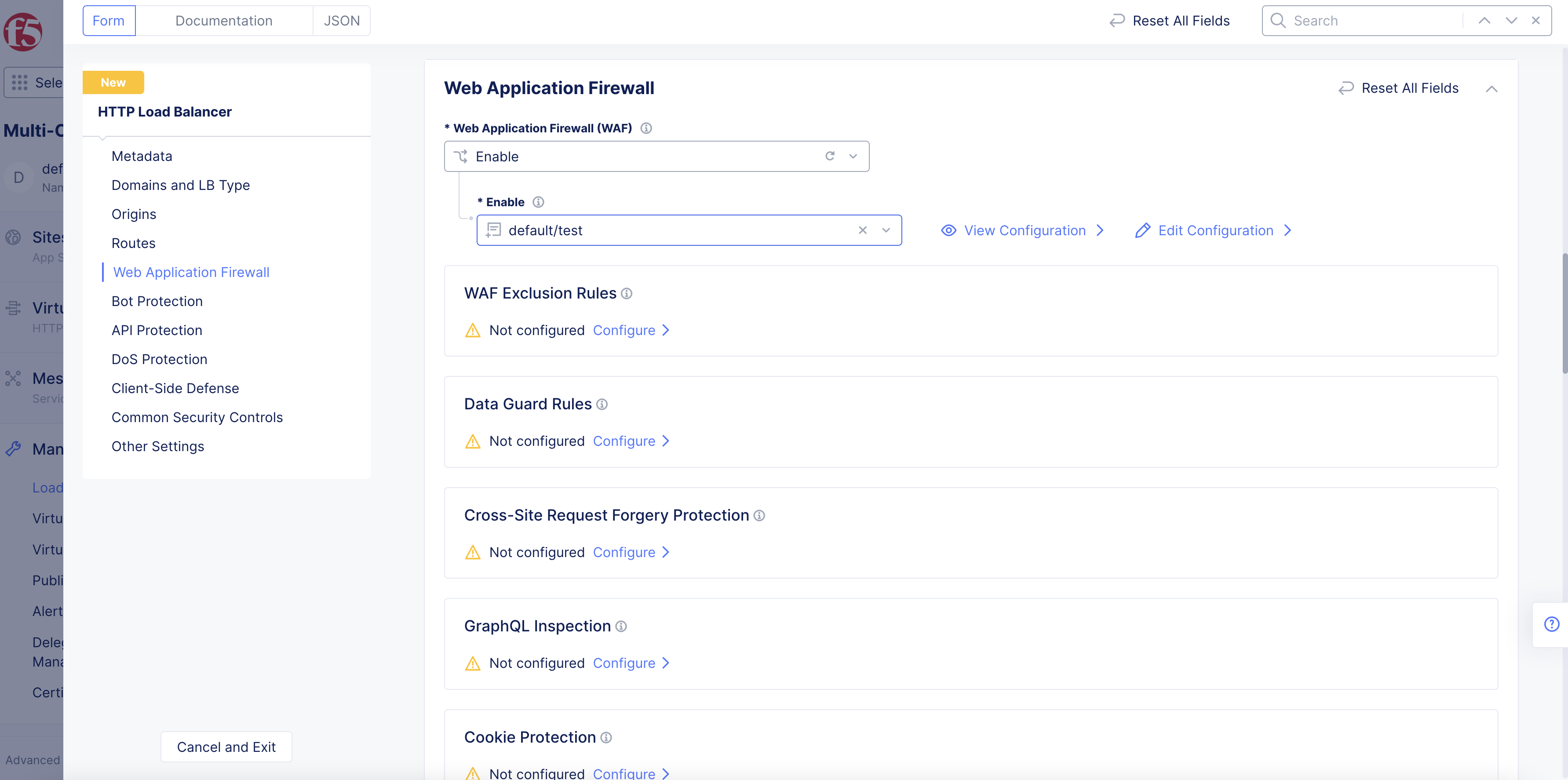
Figure: Add App Firewall
Note: You can also add App Firewall per route. In the route configuration, for
Simple Route, go to advanced options configuration, go to security section, and selectApp Firewallfor theWeb Application Firewall (WAF)field. Select an App Firewall object. By default, the route inherits the App Firewall configured for the load balancer.
-
To add exclusion rules for the WAF, follow the instructions at Create WAF Exclusion Rules.
-
Select
Configurein theData Guard Rulessection and follow the instructions listed in Configure Data Guard to set data guard rules. -
Select
Configurefor theCross-Site Request Forgery Protectionoption. Specify allowed domains in theAllowed Domains (Source Origin)field in the CSRF protection page, and selectApply. You can either configure to allow all load balancer domains or set specific domains to the allow list.
Note: You can verify the CSRF mitigation in the load balancer security monitoring page. The CSRF mitigation event is displayed as a
Service Policyevent. Expand the security event's JSON view. Thesec_event_namefield with valueCSRF Policy Violationindicates that CSRF mitigation is active. For more information on load balancer monitoring, see Monitor HTTP Load Balancer.
-
To configure the settings for GraphQL inspection, perform the following:
-
Under the
GraphQL Inspectionsection, clickConfigure. -
Click
Add Item. -
In the
Namefield, enter a name for this rule. -
From the
Domaindrop-down menu, select an option that corresponds to your domain setting. Default value isAny Domain. You can choose an option match byExact ValueorSuffix Value. -
From the
Pathdrop-down menu, select an option for the location of your GraphQL server endpoint. Default value is/graphql. -
From the
HTTP Methoddrop-down menu, select an option that specifies the method used to access the GraphQL endpoint server. -
In the
GraphQL Settingssection, perform the following:-
From the
Maximum Total Lengthmenu, enter a value to specify the maximum total length in bytes for a query. -
From the
Maximum Structure Depthmenu, enter a value to specify the maximum depth for a query. -
From the
Maximum Batched Queriesmenu, enter a value to specify the maximum number of single batch queries. -
From the
Introspection Queriesmenu, select whether to enable introspection of GraphQL schema.
-
-
Click
Applyto save settings. -
Click
Applyto apply settings to load balancer configuration.
-
-
Optionally, in the
Cookie Protectionfield, clickConfigureto add attributes to an HTTP Response cookie that is sent to the client:-
Click
Add Item. -
In the
Cookie Namefield, enter a name for this cookie.
-
Note: Wildcards and regular expressions (regex) are not supported. You must use the exact cookie name.
-
From the
SameSitemenu, select if or how the new cookie is sent with same-site and cross-site requests. You can select from the following:IgnoreStrictLaxNone
-
From the
Securemenu, select whether this new cookie is sent only over an HTTPS encrypted connection to the server. Default option isIgnore. -
From the
HttpOnlymenu, select whether this new cookie is inaccessible to JavaScript Document.cookie API. Default option isIgnore. SelectAddto ensure the cookie is inaccessible. -
Select
Enablefor theCookie Tampering Protectionfield to enable cookie tampering protection. This prevents attackers from modifying the values of session cookies. -
Click
Applyto save settings. -
Click
Applyto apply settings to load balancer configuration.
Step 6: Configure Bot Protection.
Note: You need to have
Bot Defenseenabled in your tenant as a service prior to configuring it for your load balancer.
-
Go to the
Bot Protectionsection. From theBot Defensemenu, select an option to configure bot defense. The following options are available:-
Disable: No bot defense configuration is applied to the load balancer. -
Enable: Specifies a bot defense configuration for you to apply to the load balancer. Follow the instructions listed in the Configure Bot Defense guide to set Bot defense protection for your load balancer.
-
Step 7: Configure API protection.
TheAPI Protection section provides a number of different API protection capabilities.
Step 7.1: API Definition.
-
From the
API Definitionmenu, select whether to use an API definition. The default value isDisable, meaning an API definition is not used for this load balancer. -
If you select
Enable:-
From the
API Definitionmenu, select the API definition. -
To create a new definition, click
Add item.
-
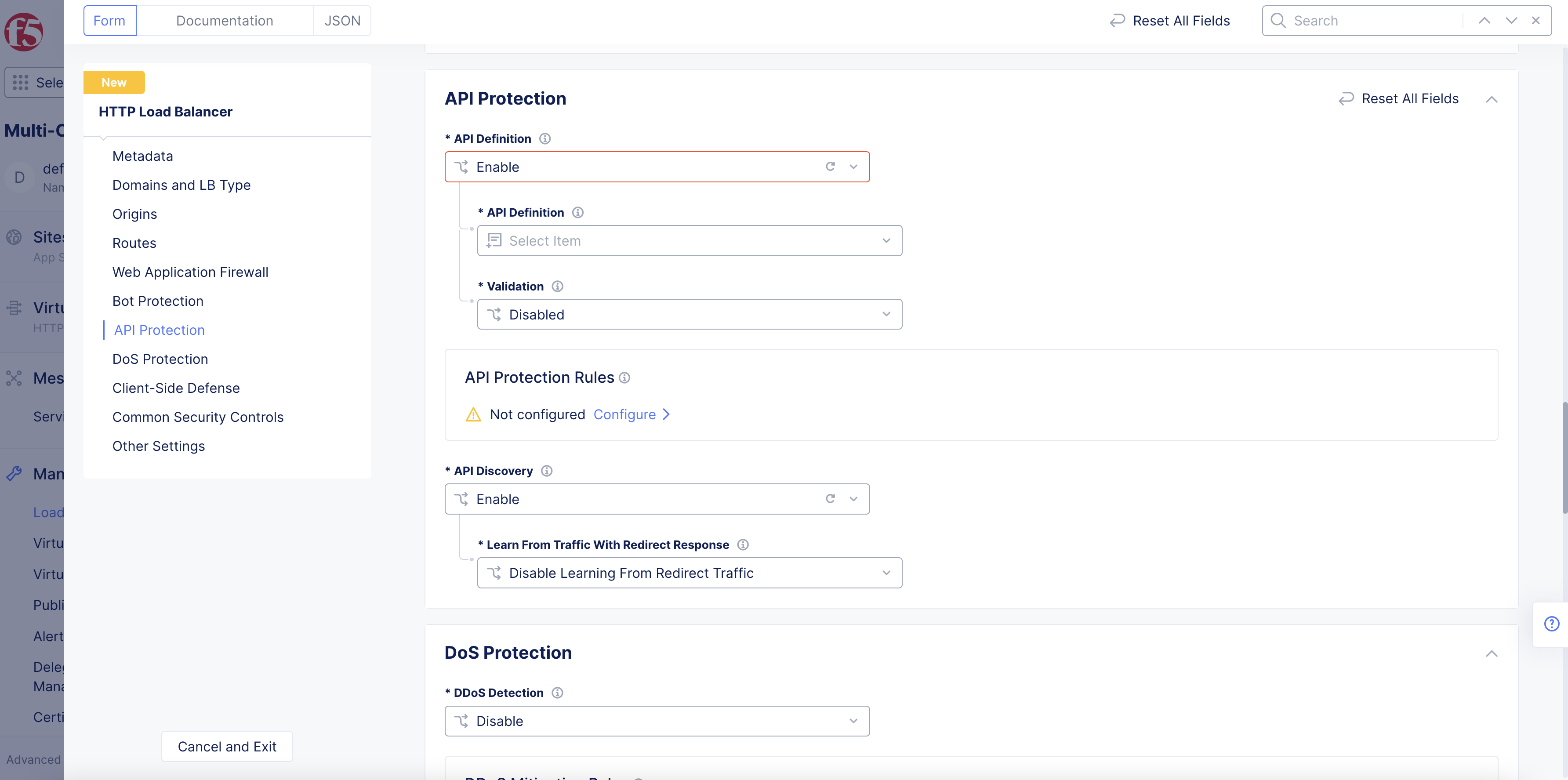
Figure: Enable API Definition
-
From the
Validationmenu, select an option to perform OpenAPI specification validation. Following are the options:-
Disabled: Default option. No validation is performed. -
All Endpoints: Validate all endpoints listed in the OpenAPI specification file. Any other endpoints not listed will act according toFall Through Mode. -
Custom List: Define API groups, base path, or API endpoints and their validation modes. Any other endpoints not listed will act according toFall Through Mode.
-
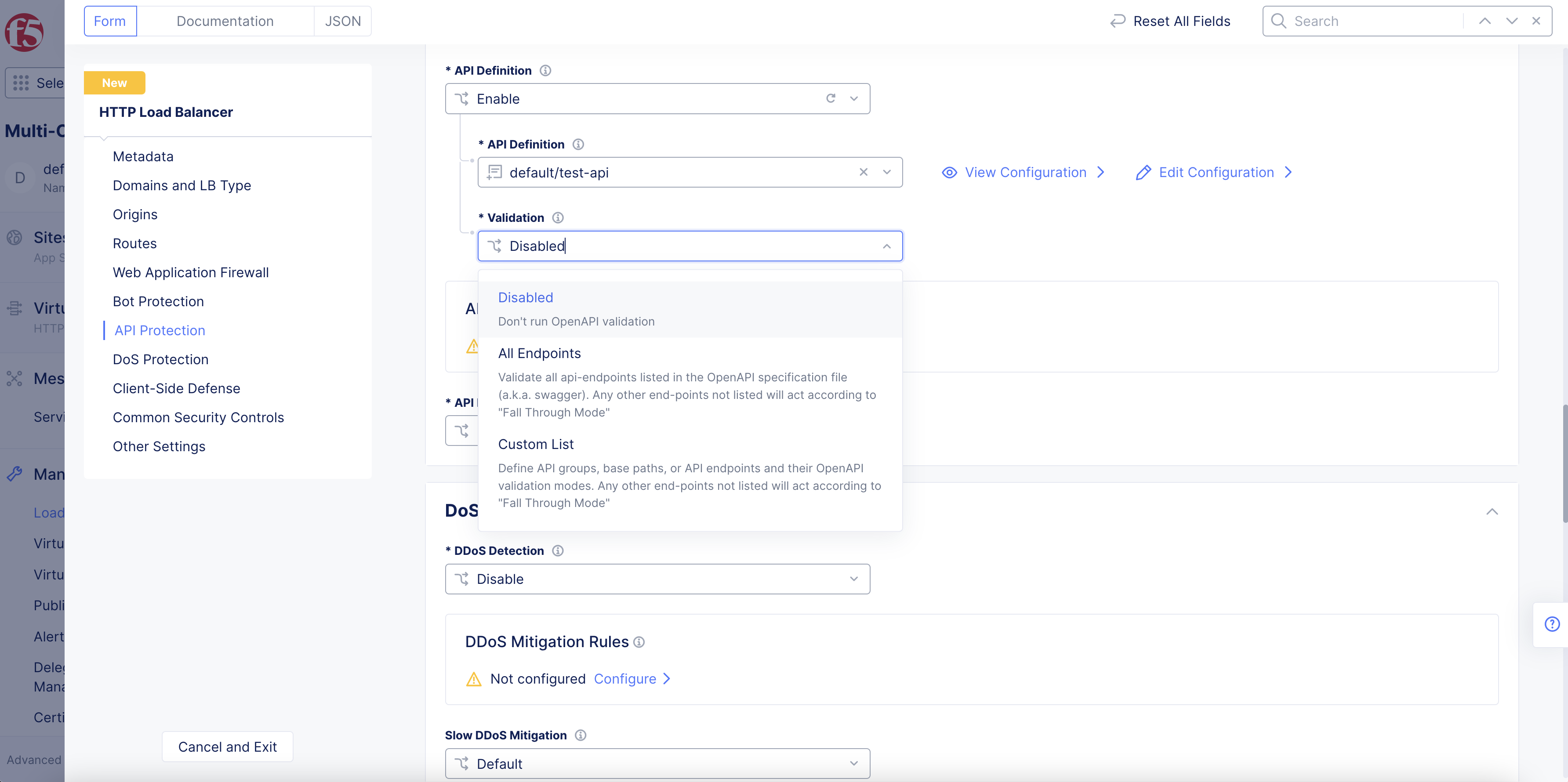
Figure: API Validation Options
Note: OpenAPI Validation is a feature that ensures API traffic complies with the specified schema and can block or report non-compliant traffic. Validation can be configured on a per-endpoint, per-group, or per-base-path basis. The
Fall Through Modeallows for identifying and handling Shadow APIs by either blocking, reporting, or allowing them. Allowed IPs list can be created to pass OpenAPI Validation by specific IP addresses.
-
From the
OpenAPI Validation Processing Modemenu, select whether toValidateorSkip. -
From the
Validation Enforcement Typemenu, select an option to specify the type of enforcement. -
From the
Request Validation Propertiesmenu, select one or multiple options from the following:-
Query Parameters: The incoming requests are validated against the query parameters specified in the API definition. -
Path Parameters: The incoming requests are validated against the path parameters specified in the API definition. -
Content-type: The incoming requests are validated against the content-types specified in the API definition. -
Cookie Parameters: The incoming requests are validated against the cookie parameters specified in the API definition. -
HTTP Headers: The incoming requests are validated against the HTTP headers specified in the API definition. -
HTTP Body: The incoming requests are validated against the HTTP body specified in the API definition.
-
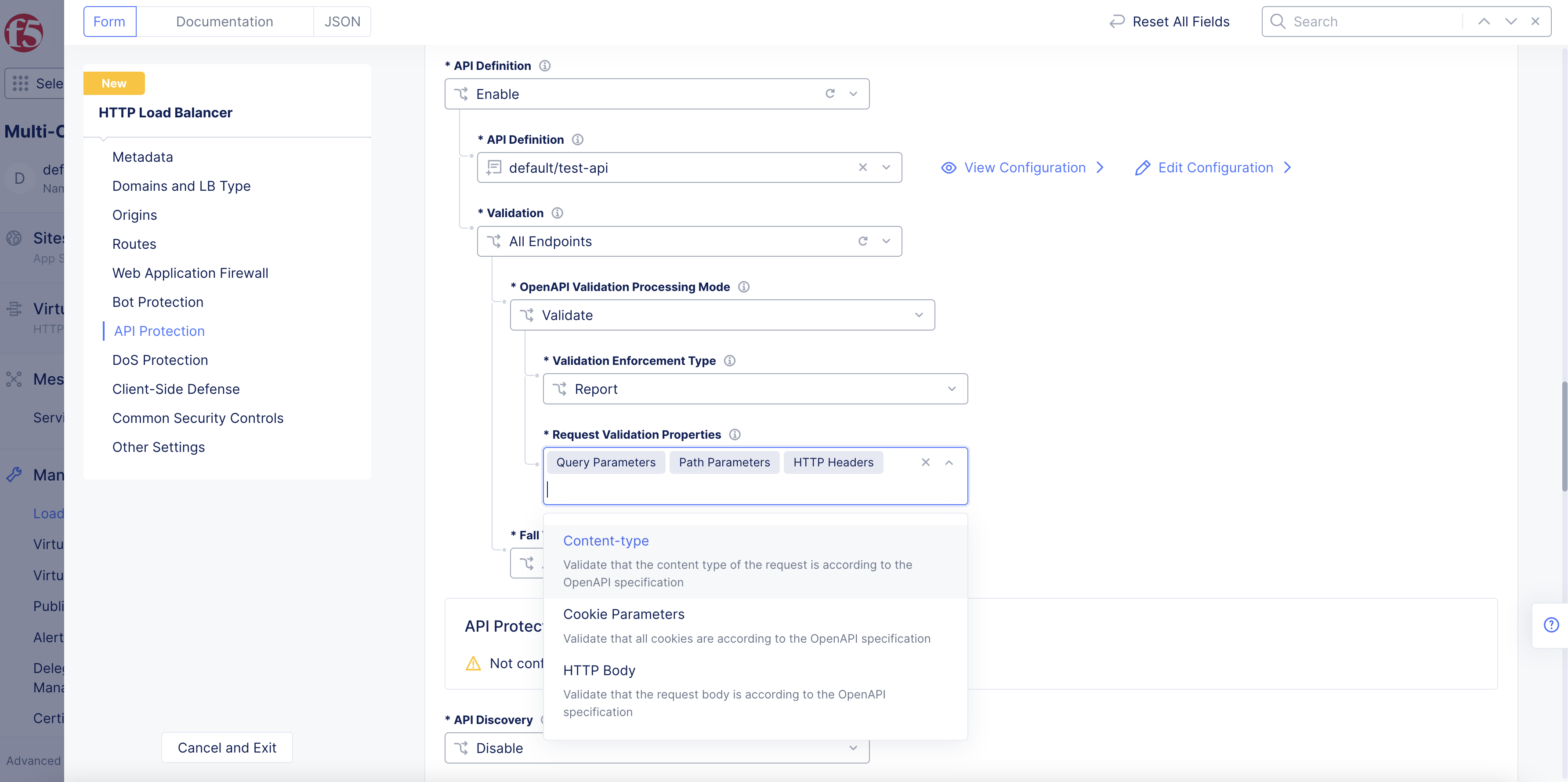
Figure: Request Validation Properties
- From the
Fall Through Modemenu, select an action for every request that targets endpoints which are not in validation list.
Step 7.2: Optionally Configure API Protection Rules.
- Click
Configurein theAPI Protection Rulesfield. - See the Configure API Protection Rules guide for more instructions.
Step 7.3: Optionally Configure JWT Validation.
This feature allows you to cryptographically verify incoming JSON web tokens (JWTs) before they are passed to origin APIs. This can prevent JWT replay attacks, JWT tampering, and it can block requests with expired tokens or tokens that are not yet valid.
-
Under
JWT Validation, clickConfigure. -
From the
Targetmenu, select whether to perform validation on all endpoints, specific API groups, or a specific path. -
Target location(Bearer)will look for the JWT token in the Authorization HTTP header with Bearer authentication scheme. -
From the
Actionmenu, select whether to block or report if the JWT is not valid. See the following options:-
Report action: In monitoring mode, the request is allowed to pass through, and the security event is logged.
-
Block action: The request will be blocked, a 401 Unauthorized error will be returned, and the security event is logged.
-
-
Under
JSON Web Key Set (JWKS), clickConfigure. -
In the text box, copy and paste the JSON Web Key Set (JWKS) used for authorization with the server. JWKS should be in JSON format.
-
Click
Apply. -
In the
Reserved Claims Validationsection, perform the following:-
From the
Issuer (iss)menu, select whether to match exactly the issuer’s reserved claim, or to disable this functionality. If you choose to match exactly, provide the exact match value in the corresponding field. -
From the
Audience (aud)menu, select whether to match exactly the JWT pre-configured value, or to disable this functionality. If you choose to match exactly, provide the exact match value in the corresponding field. You can add more than one value to match for usingAdd Item. -
From the
Validation Periodmenu, selectEnable(default value) orDisable. Enable selection will validate the JWT expiration and not before (nbf) values (if present in the request token). Disable selection will not perform validation against these fields. After you finish with configuration, clickApply.
-
-
In the
Mandatory Claimssection, perform the following:- Click
Add Item. Enter the name of the claim. It must match the claim already present in the payload, in the JWT. After you finish with configuration, clickApply. If you need to delete a claim, click...and then clickDelete.
- Click
-
From the
API Discoverymenu, selectEnableto enable API discovery. -
From the
Purge Duration for Inactive Discovered APIsmenu, enter a number to represent the number of days worth of inactive Discovered APIs to purge. -
To manage rules for sensitive data detection, click
Configureand perform the following:-
To disable specific data types from detection, click
Add Itemunder theDisabled Built-In Sensitive Data Typessection. Then select the data type from the menu list. You can select more than one option. -
To define custom rules for data types to detect, click
Add Itemunder theDefined Custom Sensitive Data Typessection: -
Enter a name for this new custom rule.
-
From the
Typemenu, enter a value for the type of sensitive data. -
From the
Rule's Targetmenu, select if this rule applies to all detected endpoints or a specific endpoint. If specific only, select theAPI EndpointandMethods. -
From the
Sectionmenu, select where to apply the rule during the search process. You can choose the default value to search all requests and responses header sections, only request, only responses, or a custom search. For custom, select your options to search from the header sections. You can choose more than one option from theCustom Sectionsmenu. -
From the
Pattern Choicemenu, select how to search for the sensitive data. You can search byKey Pattern,Value Pattern, orKey-Value Pattern. For each of these options, you can search by exact value or using regular expressions (regex) using the menu options provided. -
Click
Applyto complete rule creation. -
Click
Applyto add the new rule to the configuration.
-
Note: For more information, see Import Swagger to Define and Control API Groups.
Step 7.4: API Discovery.
API Discovery samples traffic through the load balancer to build a schema of an app's API endpoints, and it can also generate a swagger definition file.
-
From the
API Discoverymenu, selectEnableto start the discovery process. The default value isDisable, meaning an API discovery will not be done. -
From the
Learn From Traffic With Redirect Responsemenu, choose whether to enable learning from redirect traffic (requests resulting in a 3xx response code). -
In the
Purge Duration for Inactive Discovered APIs (d), enter the number of days for the API endpoint to live. If no 2xx responses occur from an endpoint (or 3xx if so configured) occur for the span of days entered, then the API endpoint will be removed. -
Click
Configurein theAPI repositoriessection to setup the API code repositories (e.g. Github, Gitlab, BitBucket, or Azure Repos) to the load balancer as the source for API endpoint discovery.
Step 7.5: Sensitive Data Discovery (or Sensitive Data Policy).
This feature allows you to configure a policy for for how sensitive data is detected. You can specify which privacy or compliance frameworks (PCI_DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, etc.) to use when detecting sensitive data, you can disable specific sensitive data types, and you can add your own sensitive data types.
-
Select
Defaultto use system defaults for sensitive data discovery. -
Select
Customfor a custom data discovery. Next select an existing policy from theSpecify Sensitive Data Discoverydrop-down list, or clickAdd Itemin the list to create a new policy. -
For a new policy,
- Enter a name for the policy and optionally labels and a description.
- Select one or more entries from the
Compliance Frameworksdrop-down list. These frameworks will define the set of sensitive data types that will be detected. - For each specific sensitive data type you would like to disable (these will not be shown as sensitive in the API discovery), click
Add ItemunderDisabled Built-In Sensitive Data Typesand then select a data type from the drop-down list. - To define your own sensitive data types, click
Configurein theDefined Custom Sensitive Data Typessection. Next, for each data type you want to add, clickAdd Itemto get a blank entry in theDefined Custom Sensitive Data Types List. Select an existing entry in the drop-down list or clickAdd Itemin the list to create a new one. - For a new sensitive data type,
- Enter a name an optionally labels and a description.
- Click
Configureto create the datatype rules. For each rule, clickAdd Item. - Select an entry in the
Pattern Choicedrop-down menu:Key Pattern,Value Pattern, orKey-Value Pattern. - Select an entry in the
Patterndrop-down menu and then enter the value or substring to match. - Click
Applyto save the detection rule and then click apply to save the rule list.
- Ensure that
Mark as Sensitive Datais checked. - Check
Mark as PIIif this data type is personally identifiable information (PII). This allows the system to classify discovered sensitive data appropriately. - Click
Continueto save the new data type. - Click
Applyto save the list of defined custom sensitive data types.
-
Click
Continueto save the new custom policy.
Once this feature is configured, you will be able to see which API endpoints contain sensitive data and which API compliance framework(s) they are governed by. These will be shown on the Overview > Security page under the API Endpoints tab. Make sure the Sensitive Data and API Compliance columns are visible to see the information. There, you can also see the information by examining the endpoint details. See Explore Security Monitoring for a Load Balancer for more information on monitoring.
Step 7.6: Optionally Configure Sensitive Data Exposure Rules.
This feature allows you to specify rules to mask sensitive data in API responses.
-
Click
Configurein theSensitive Data Exposure Rulessection. -
Click
Add Itemto create the first rule. -
In the
Targetsection, enter the path that will respond to the request. Also enter one or more methods with responses containing sensitive information. -
In the
Valuesfield in thePatternsection, enter the JSON field value you want to mask. For example, given the JSON below is the response,
{ "user":
{ "Email":"elmer1980@yahoo.com",
"ID":1,
"altEmails":["elmo@sesamest.com, Mr.E@Muppets.net"]
}
}
- To mask the
Emailvalue, enteruser.Email. - To mask all emails in the array
altEmails, enter user.altEmails[_]. Note that an underscore between the square brackets indicates the array's elements. - Masked values in the response will be masked as follows: All letters changed to
aorA(matching case) and all numbers converted to1. Thus the response example above will be masked as shown below:
{ "user":
{ "Email":"aaaa1111@aaaaa.aaa",
"ID":1,
"altEmails":["aaaa@aaaaaaaa.aaa, Aa.A@Aaaaaaa.aaa"]
}
}
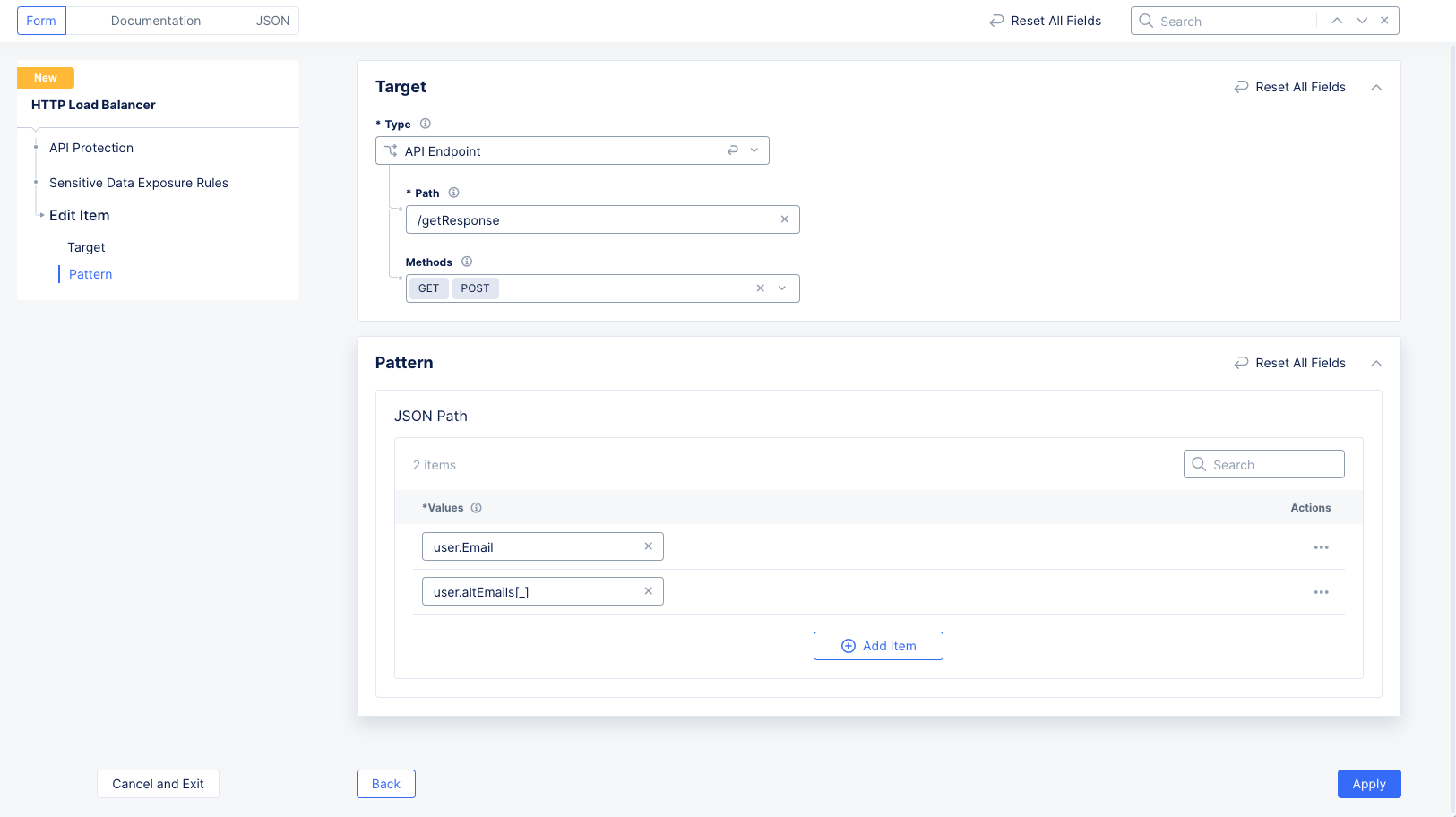
Figure: Request Validation Properties
Note: To apply masking to nested objects, the exact location of the key must be specified. For the example shown below,
{ "A": { "B": { "key1": "val1", "key2": "val2" } } }Copied!the masking configuration should be set as A.B.key1 or A.B.key2, depending on which value you want to mask.
-
Click
Applyto save the rule to the list ofSensitive Data Exposure Rules. -
Click
Add Itemto add more rules. -
Click
Applyto save the list of rules to your load balancer.
Step 8: Configure Malware Protection.
Malware protection guards against uploaded files infected with malicious content. All filetypes, except compressed files such as .zip, .tar, .gz, are scanned, including the following:
- Executable files (e.g.
.exe,.bat,.csh) - Document files (e.g.
.doc,.pdf,.xlsx) - Image files (e.g.
.jpg,.png,.bmp) - Video files (e.g.
.avi,.mp4,.mov) - Audio files (e.g.
.mp3,.aac,.wav)
Files that exceed 1 MB in size will only have their first 1 MB scanned. That partial scan will be used to determine whether the file is malicious or not.
Note: This feature is an add-on and must first be enabled in the catalog in order to enable it in a load balancer.
-
Select
Enablefrom theMalware Protectiondrop-down menu to enable file upload scanning in real time to protect against malware. -
Click
Configureto create a list of malware detection rules.
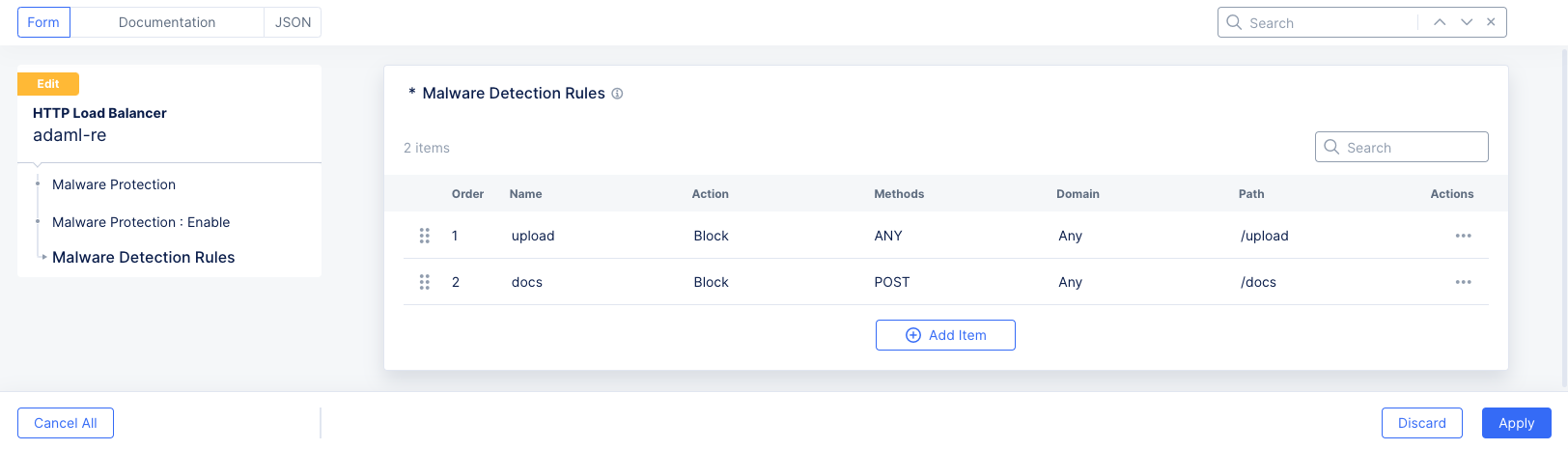
Figure: Malware Detection Rules
- Click
Add Itemto add a malware detection rule.
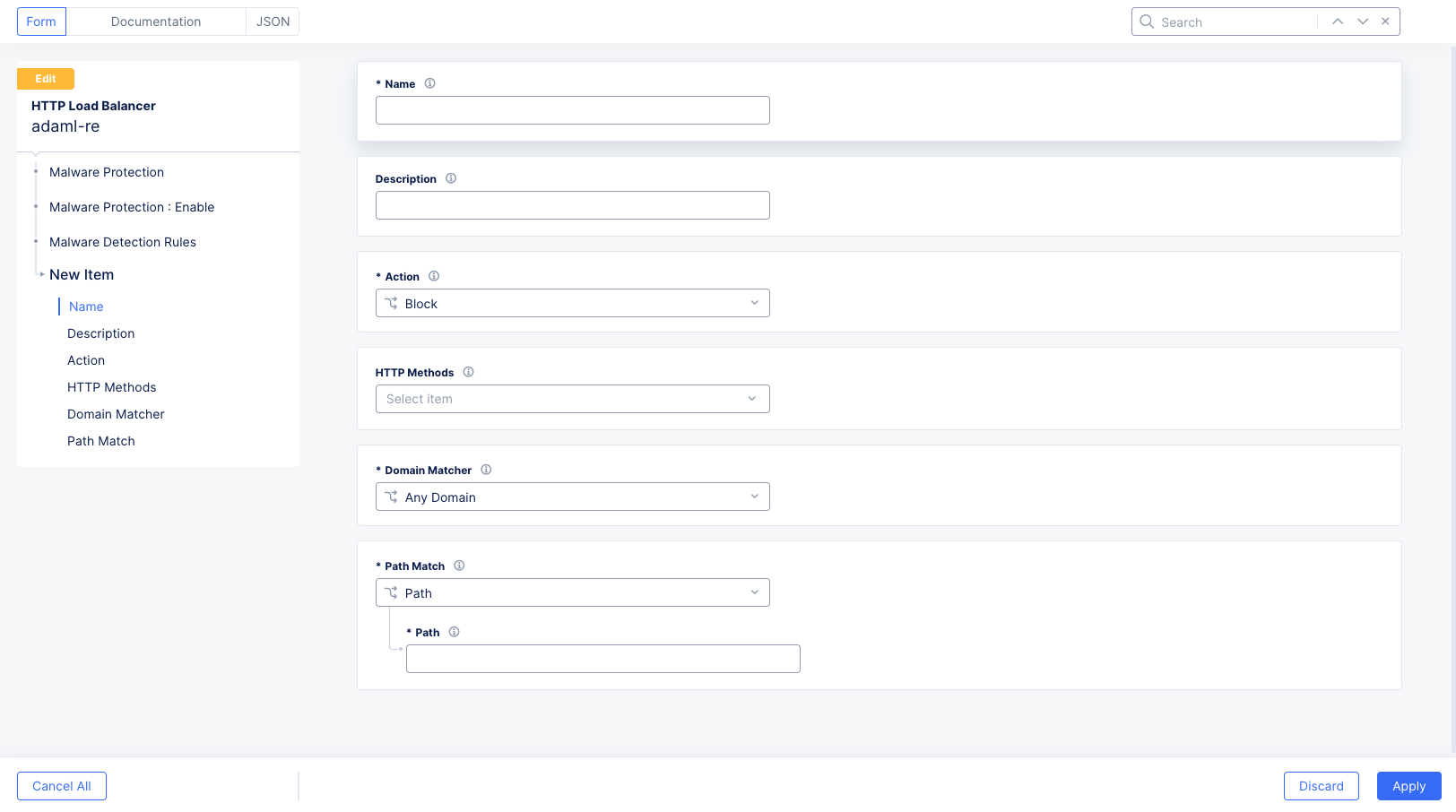
Figure: Malware Detection Rule Form
-
Enter a name for your rule and optionally a description.
-
In the
Actiondrop-down menu, choose what to do when a match occurs (defined in the following steps).Blockwill deny the upload request and report the issue.Reportwill allow the upload request and report the issue. -
In the
HTTP Methodsdrop-down menu, choose which HTTP methods you want to match in this rule. You can select multiple methods. -
From the
Domain Matcherdrop-down menu, selectAny Domain: All domains will use this rule.Domain: Only the domains you specify will use this rule. You can specify the domains byExact Value(only the domain that you specify will use this rule),Suffix Value(domains with your specified suffix will use this rule: e.g. x.abc.com and y.abc.com will use this rule if you enter abc.com), andRegex Values of Domains(any domain that matches your entered regular expression will use this rule).
-
From the
Path Match, enter the exact path to match. -
Click
Applyto save the rule to your rules list. -
Click
Applyto save your rules list.
Step 9: Configure DoS Protection.
-
From the
L7 DDoS Auto Mitigationmenu, select an option:-
Default: This option blocks traffic from suspicious sources. No JavaScript challenge is returned. -
Block: This option blocks traffic from suspicious sources. No JavaScript challenge is returned. -
JavaScript Challenge: This option serves a JavaScript challenge to all traffic from suspicious sources. ClickView Configurationto change the default settings and message for the JavaScript challenge.
-
-
Under
DDoS Mitigation Rules, selectConfigureto open the rules list page. UseAdd Itemto add a rule:-
In the
DDoS Mitigation Rulepage, set a name for the rule. -
Select a choice for the
Mitigation Choicemenu. The mitigation choice can be either a list of IP addresses or combination of ASN, Region, and TLS Fingerprinting. -
Click
Applyto add the rule to the list of rules. -
Click
Applyto add the rules list to the DDoS protection configuration.
-
-
From the
Slow DDoS Mitigationmenu, select an option:- For the
Customoption, enterRequest Headers TimeoutandTotal Request Timeoutvalues.
- For the
Note: See the
Explore Security Monitoringsection in the Monitor HTTP Load balancer guide to learn more about observing and reacting to an active DDoS attack.
Step 10: Configure Client-Side Defense.
Ensure that this service is enabled for your tenant. See Client-Side Defense for more information and configuration instructions.
Step 11: Configure Common Security Controls.
Go to the Common Security Controls section and perform the following:
Step 11.1: Configure Service Policies.
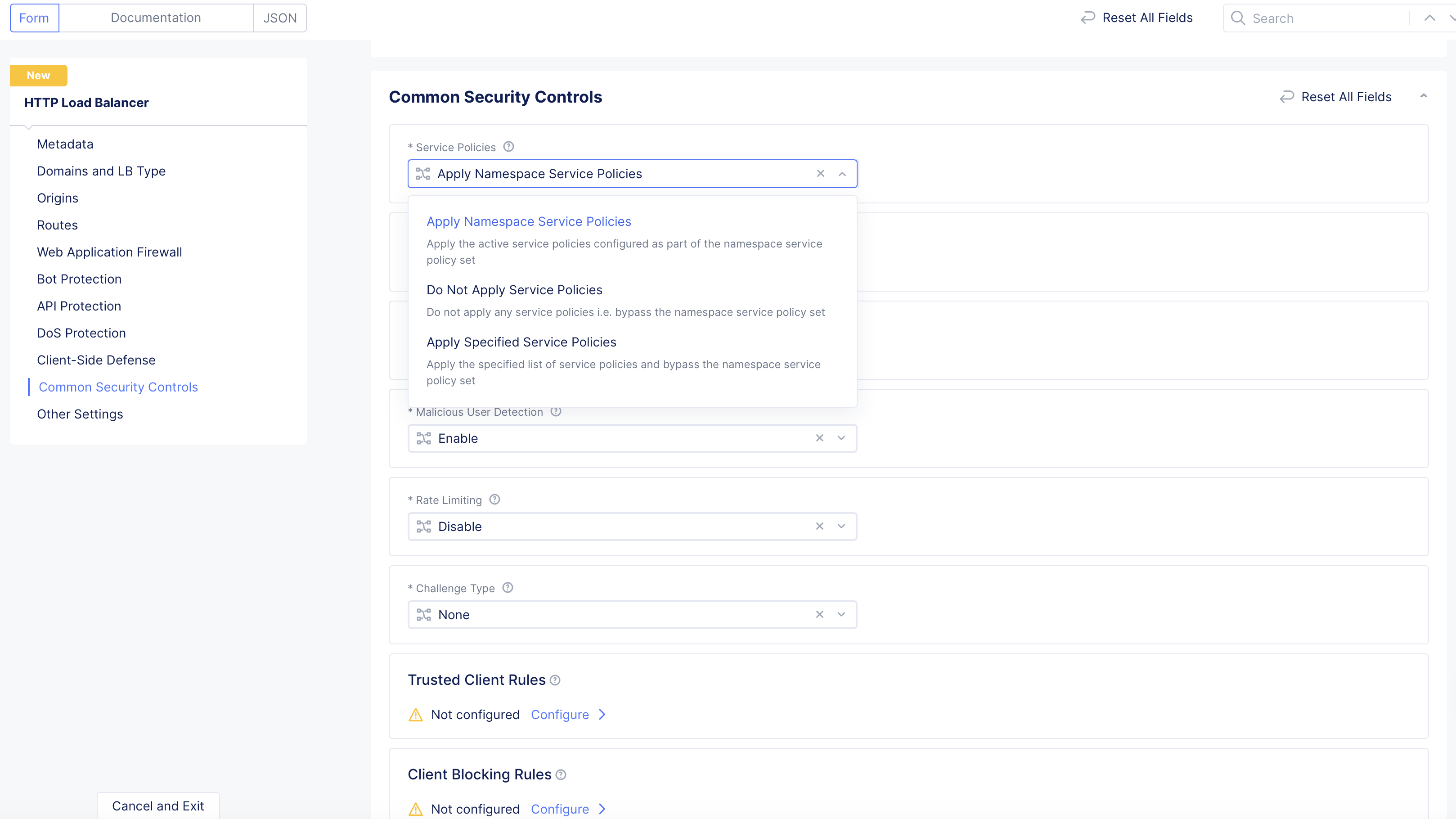
-
From the
Service Policiesmenu, select an option for how to apply one or more service policies to this load balancer. The following options are available: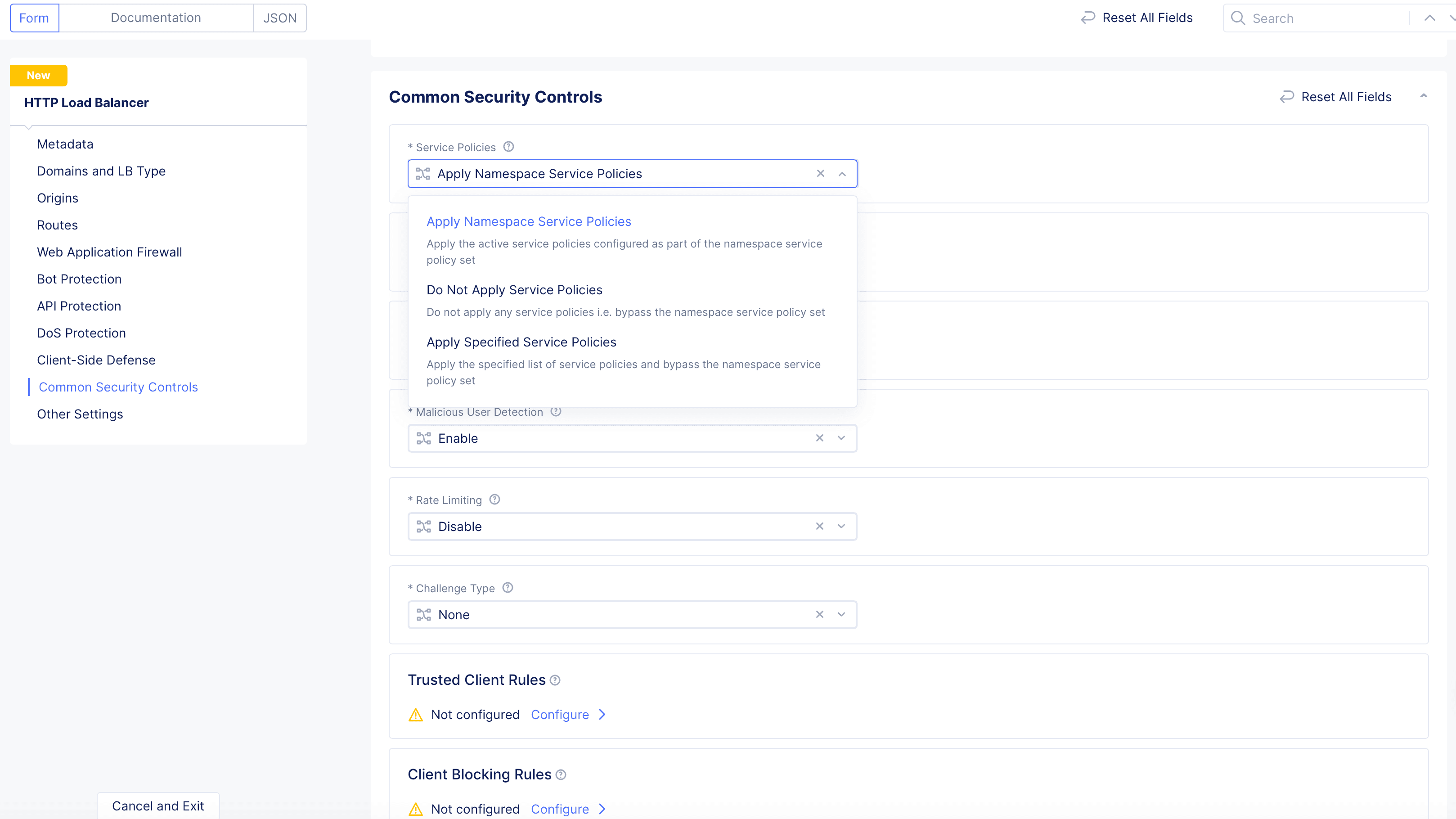
Figure: Service Policy Configuration
-
Apply Namespace Service Policies: This option applies the service policies from the namespace to this load balancer. -
Do Not Apply Service Policies: This option does not apply any service policies to this load balancer. -
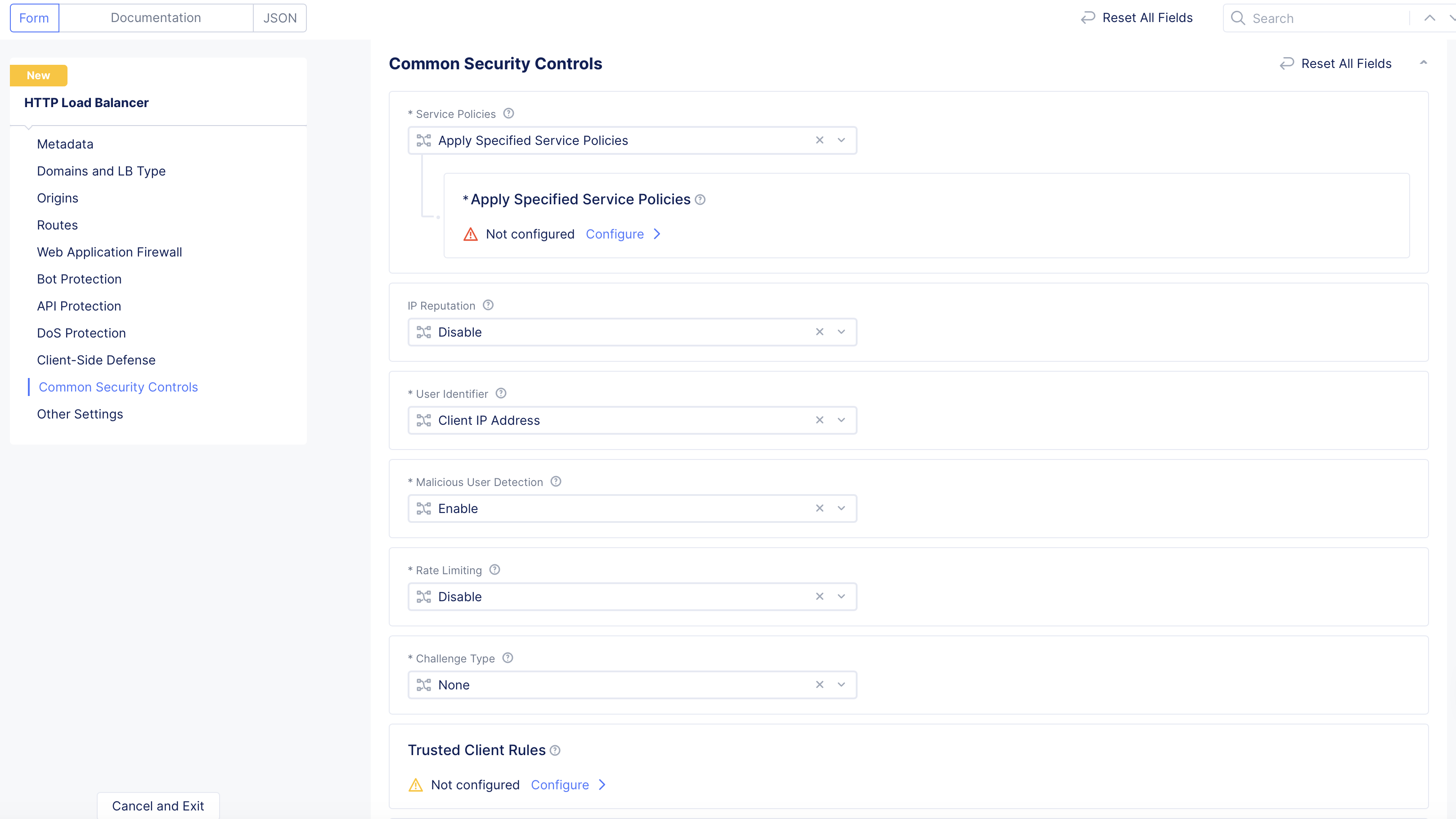
Apply Specified Service Policies: This option allows you to apply one or more specific service policies to this load balancer.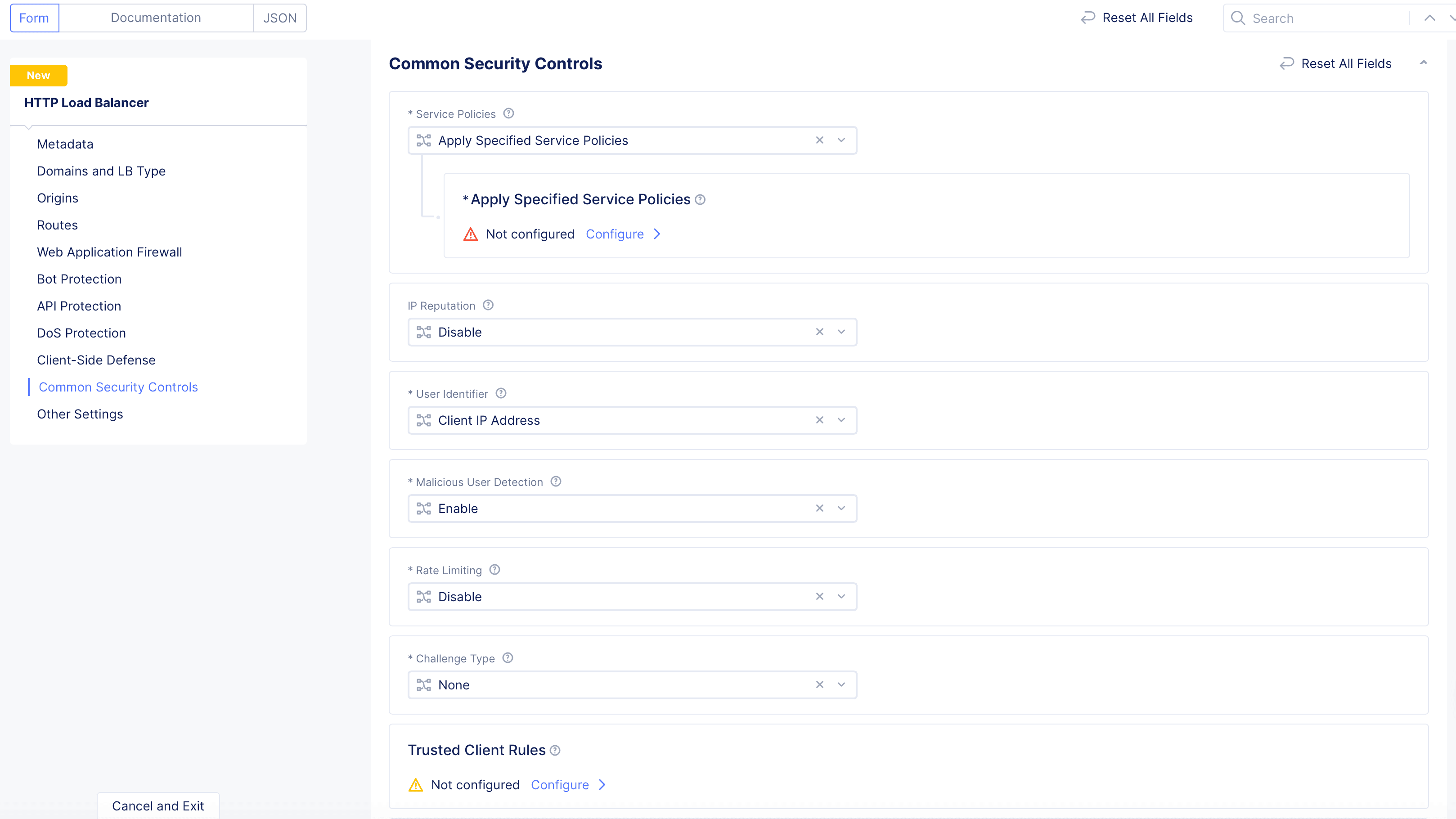
Figure: Apply Specific Service Policy
- Click
Configureto add service policies.
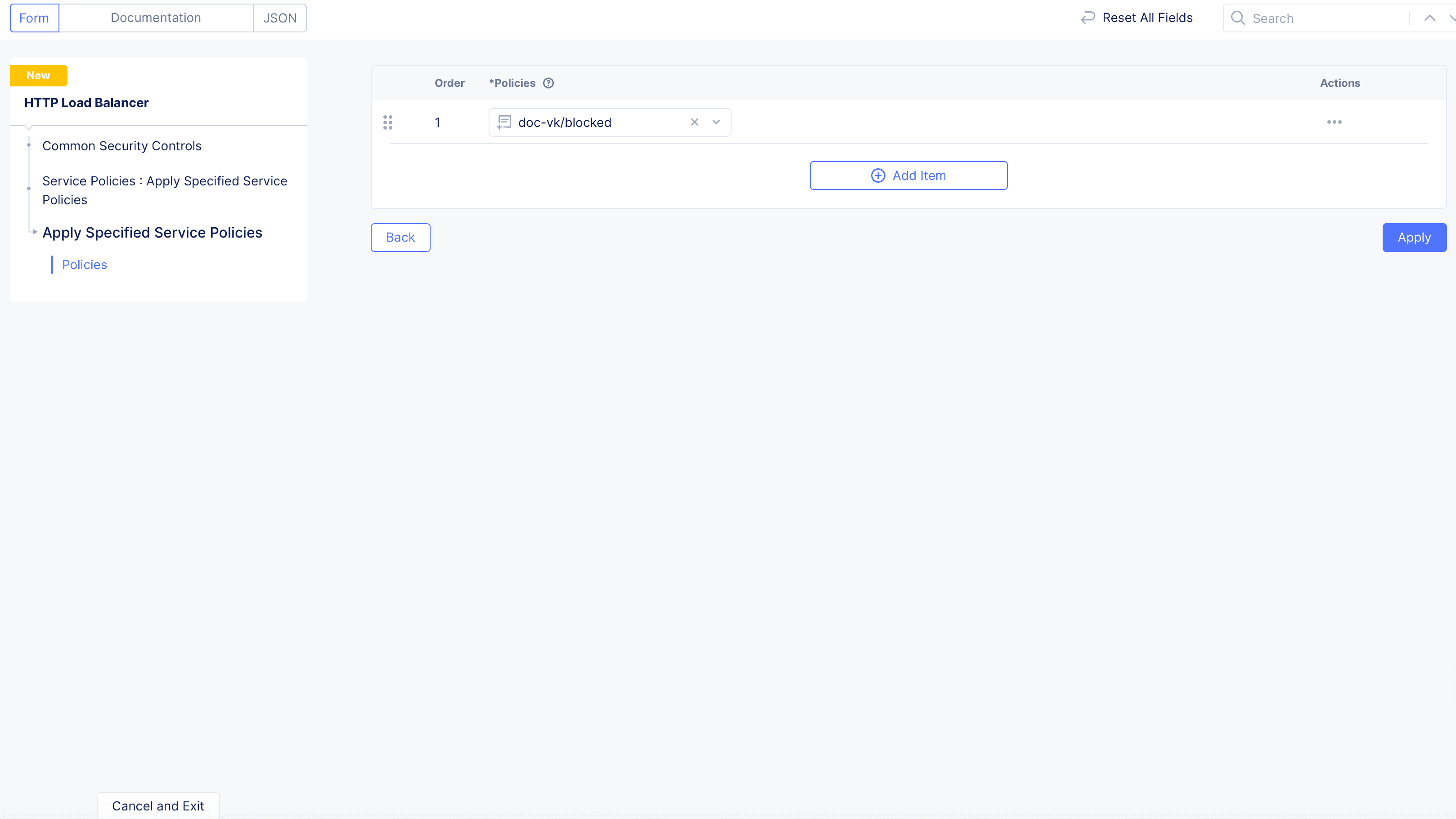
Figure: Select Specific Service Policy
- In the
Policieslist, select a service policy, from the drop-down menu. - Use the
Add Itembutton to add more policies to the list. - Click
Applywhen you're finished building the list.
- Click
-
Step 11.2: Configure IP Reputation service.
The IP reputation service analyzes IP threats and publishes a dynamic data set of millions of high-risk IP addresses, to protect users from inbound traffic from malicious IPs. IP threat categories include Spam Sources, Windows Exploits, Web Attacks, BotNets, Scanners, Denial of Service, Reputation, Phishing, Proxy, Mobile Threats, and TOR Proxy.
For more information, see Deny Malicious IPs Using IP Threat Categories.
Step 11.3: Configure Threat Mesh.
Threat Mesh provides F5 Distributed Cloud customers with an additional layer of protection against web application attacks. Threat Mesh leverages cross-customer correlation (i.e. correlation of client attacks across different customers) to identify malicious intent of a client. Whenever a client is flagged due to a malicious intent by our WAAP decisions engines, that client will be added to the ThreatDB.
Enabling Threat Mesh means that requests coming into an application from an IP that is in the ThreatDB will be automatically blocked by the load balancer.
Requests that are blocked due to Threat Mesh can be seen and evaluated in the Web App & API Protection workspace on the Overview > Security > Security Analytics tab for a specific load balancer and the Multi-Cloud App Connect workspace on the Overview > Applications > Security Analytics tab for a specific load balancer. Blocked requests will show as a Service Policy violation in the Event Type column with Threat Mesh in the Threat Name column. For more information, see Load Balancer Security Monitoring in the Security Analytics section.
From the Threat Mesh drop-down menu, select the Enable or Disable for the feature.
Step 11.4: Configure User Identification.
Select a user identifier for rate limiting and malicious user mitigation.
-
From the
User Identifierdrop-down menu, select the method for user identification:-
Select
Client IP Addressto use the user's IP address. -
Select
User Identification Policyto use the object to evaluate the identity. To create a new user ID, clickAdd itemfrom theUser Identification Policymenu.
-
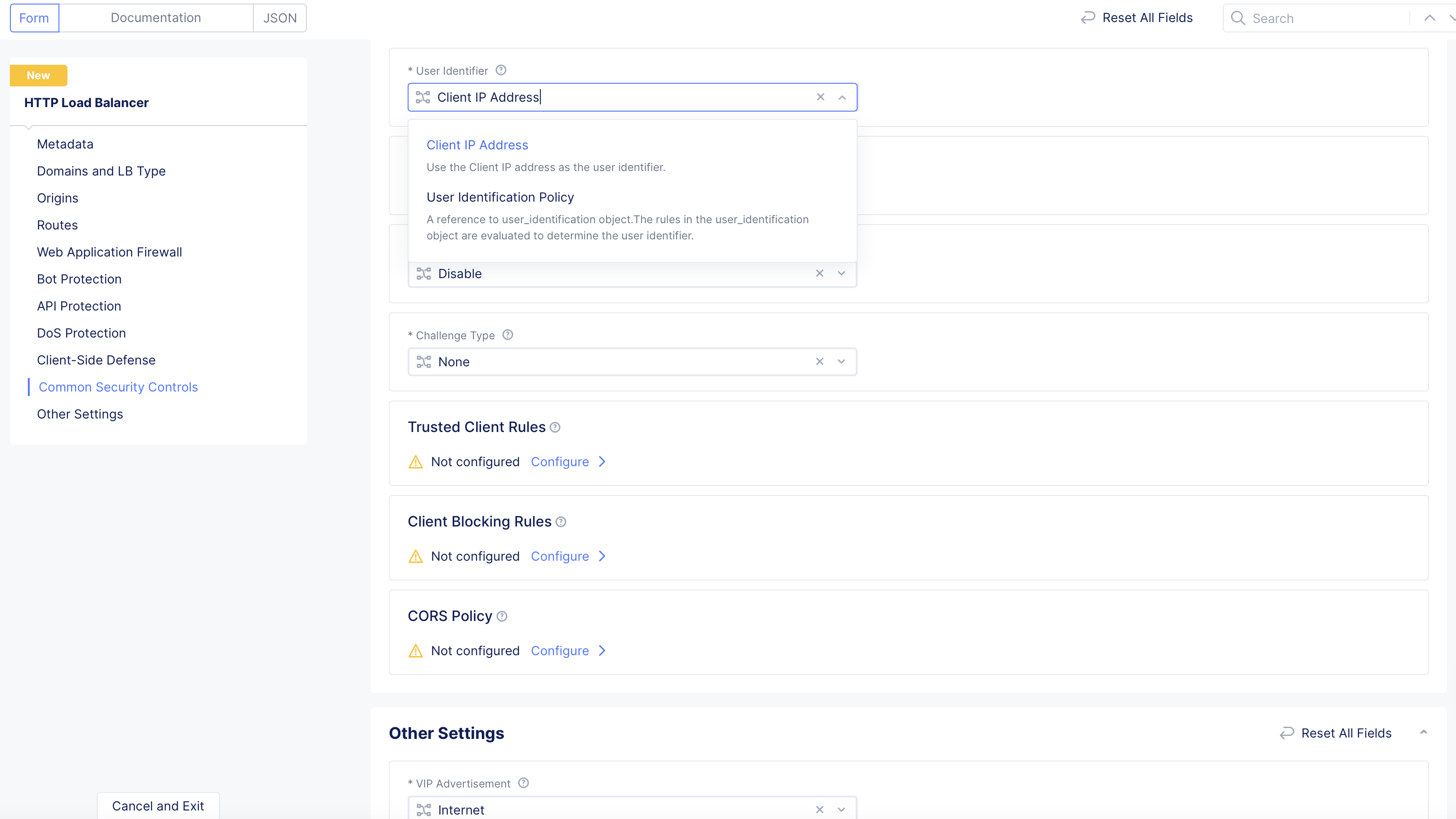
Figure: User ID Policy
Note: For more information, see Configure Rate Limiting per User.
Step 11.5: Configure Malicious User Detection.
Malicious User Detection performs user behavior analysis and assigns a risk score and threat level of low, medium or high based on the suspicious activity of the user. The risk score of the user is decayed over time, if no further suspicious activity is noticed. The feature can be configured also via external app_type and labeling this HTTP Load Balancer. In this case, the external app_type configuration overrides the internally disabled feature. Enabling the feature internally is allowed only when there is no labeling to an external app_type.
From the Malicious User Detection drop-down menu, select Enable.
Step 11.6: Configure Malicious User Mitigation And Challenges.
-
In the
Common Security Controlssection, enable theShow Advanced Fieldsoption. -
From the
Malicious User Mitigation And Challengesdrop-down menu, selectEnable. This option enables you to configure a challenge for users detected as malicious.
Note: For the
JavaScript Challenge,Captcha Challenge, andPolicy Based Challengeoptions, you can enable a challenge for all users and/or requests matching specific conditions. For any of these options, clickView Configurationto create that challenge for users/requests that meet specific criteria.
-
From the
Malicious User Mitigation Settingsmenu, select an option for malicious users at different threat levels:-
Default: Applies low, medium, and high levels. -
Custom: Defines different levels and actions to take. Select an option from theCustommenu. Or clickAdd Itemto create a custom option.
-
-
From the
JavaScript Challenge Parametersmenu, select the type of JavaScript challenge to enable:-
JavaScript Challenge Parameters: This option enables you to configure a custom JavaScript challenge for this load balancer. ClickConfigure. Set the delay value, cookie expiration value, and custom message to use. After you finish, clickApply. For more information, see Configure JavaScript Challenge. -
Use Default Parameters: This option sets the default challenge with no customization.
-
-
From the
Captcha Challenge Parametersmenu, select the type of captcha challenge to enable:-
Use Default Parameters: This option takes the default settings and applies them. -
Captcha Challenge Parameters: This option enables you to define the challenge parameters. ClickConfigure. Set the cookie expiration value and the custom message to use. After you finish, clickApply.
-
Policy Based Challenge
-
If you selected
Policy Based Challenge, perform the following:-
Click
View Configuration. -
Configure the JavaScript, captcha, and malicious user settings.
-
Select a challenge type.
-
-
In the
Rulessection:-
Click
Configure. -
Click
Add Item. -
Enter a
Namevalue and an optional description. -
In the
Challenge Rule Specificationfield, selectView Configuration. -
From the
Select Challenge Action Typedrop-down menu, select the challenge action to take.Disable challengeis the default setting. The two options includeEnable javascript challengeandEnable captcha challenge. -
From the
Source IP Matchdrop-down menu, select the source IP to match the requests. The options include:-
Any Source IP: This option enables any source IP to match requests. -
IP Prefix List: This option provides a list of prefix values. You must provide a list of IP prefixes. -
IP Prefix Sets: This option provides a list of references to IP prefix set objects. You must create the prefix set.
-
-
From the
Source ASN Matchdrop-down menu, select an option for the origin Autonomous System Number (ASN) to match requests:-
Any Source ASN: This option matches any source ASN. -
ASN List: This option provides a list of ASN values to match requests. You must enter the ASN values. -
BGP ASN Sets: This option provides a list of references for Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) ASN objects to match requests. You must create the ASN set.
-
-
From the
Client Selectiondrop-down menu, select how the clients will match the challenge rules. The options include:-
Any Client: This option is for all clients to match the challenge rules. -
Group of Clients by Label Selector: This option provides a label selector for the set of clients. You must select the expression from the list.
-
-
To configure the TLS fingerprint matcher, select
Configure:-
From the
TLS fingerprint classesdrop-down menu, select a class. -
Optionally, you can add an exact value or exclude a value with
Add item. -
Click
Apply. -
Optionally, you can set the parameters for the request matching from the
Request Matchsection, and you can set an optionalExpiration Timestampfrom theAdvanced Matchsection. -
Click
Apply.
-
-
Click
Apply.
-
-
Click
Apply. -
Click
Apply.
Step 11.7: Configure Rate Limiting.
Rate Limiting allows you to control the rate of requests sent to your origin servers and protect against API traffic surge and denial of services attacks.
-
To configure rate limiting, select an option from the list:
-
Disable: Default option. No rate limiting enabled for this load balancer. -
API Rate Limit: Set rate limiting for specific API endpoints. -
Custom Rate Limiting Parameters: Allows you to set custom parameters to rate limit.
-
Note: For detailed instruction to set up rate limiting, see Configure API Rate Limiting.
Step 11.8: Configure Trusted Client Rules.
These rules define specific clients for which WAF processing and Bot Defense will be skipped. Add rules to allow trusted clients based on the match conditions configured. You can skip WAF, skip bot processing, or both. The match conditions include IP prefix, AS number, and HTTP headers to identify specific clients.
-
To configure the
Trusted Client Rulesoption:-
Click
Configure, and then clickAdd Item. -
Complete the configuration process to add rules to allow trusted clients and to prevent the WAF from applying the block rules you previously configured.
-
Click
Apply. -
Select the newly created rules option and then click
Apply.
-
Step 11.9: Configure Client Blocking Rules.
You can choose match condition rules, such as IP prefix, AS number, and HTTP headers to identify specific clients to block from accessing your applications.
-
To configure the
Client Blocking Rulesoption:-
Click
Configure, and then clickAdd Item. -
Complete the configuration process to add rules to block specific clients from making requests.
-
Click
Apply. -
Select the newly created rules option, and then click
Apply.
-
Step 11.10: Configure CORS Policy.
The Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) policy is an HTTP-header based mechanism that allows a server to indicate any origins (domain, scheme, or port) other than its own from which a browser should permit loading resources.
-
In the
CORS Policyfield, clickConfigure. -
To enable a specific origin server, click
Add itemunder theAllow Originfield. -
To enable origin servers by regex, click
Add itemunder theAllow Origin Regexfield. -
In the
Allow Methodsfield, enter information to be used for theaccess-control-allow-methodsheader. -
In the
Allow Headersfield, enter information to be used for theaccess-control-allow-headersheader.Important: When you enable Bot Defense on your HTTP load balancer, Bot Defense adds the following headers to the
Allow Headersfield in your CORS policy:Xa4vrhYP3Q-a,Xa4vrhYP3Q-a0,Xa4vrhYP3Q-b,Xa4vrhYP3Q-c,Xa4vrhYP3Q-d,Xa4vrhYP3Q-e,Xa4vrhYP3Q-fandXa4vrhYP3Q-z. These headers are required for Bot Defense to support requests that use CORS. -
In the
Expose Headersfield, enter information to be used for theaccess-control-expose-headersheader.
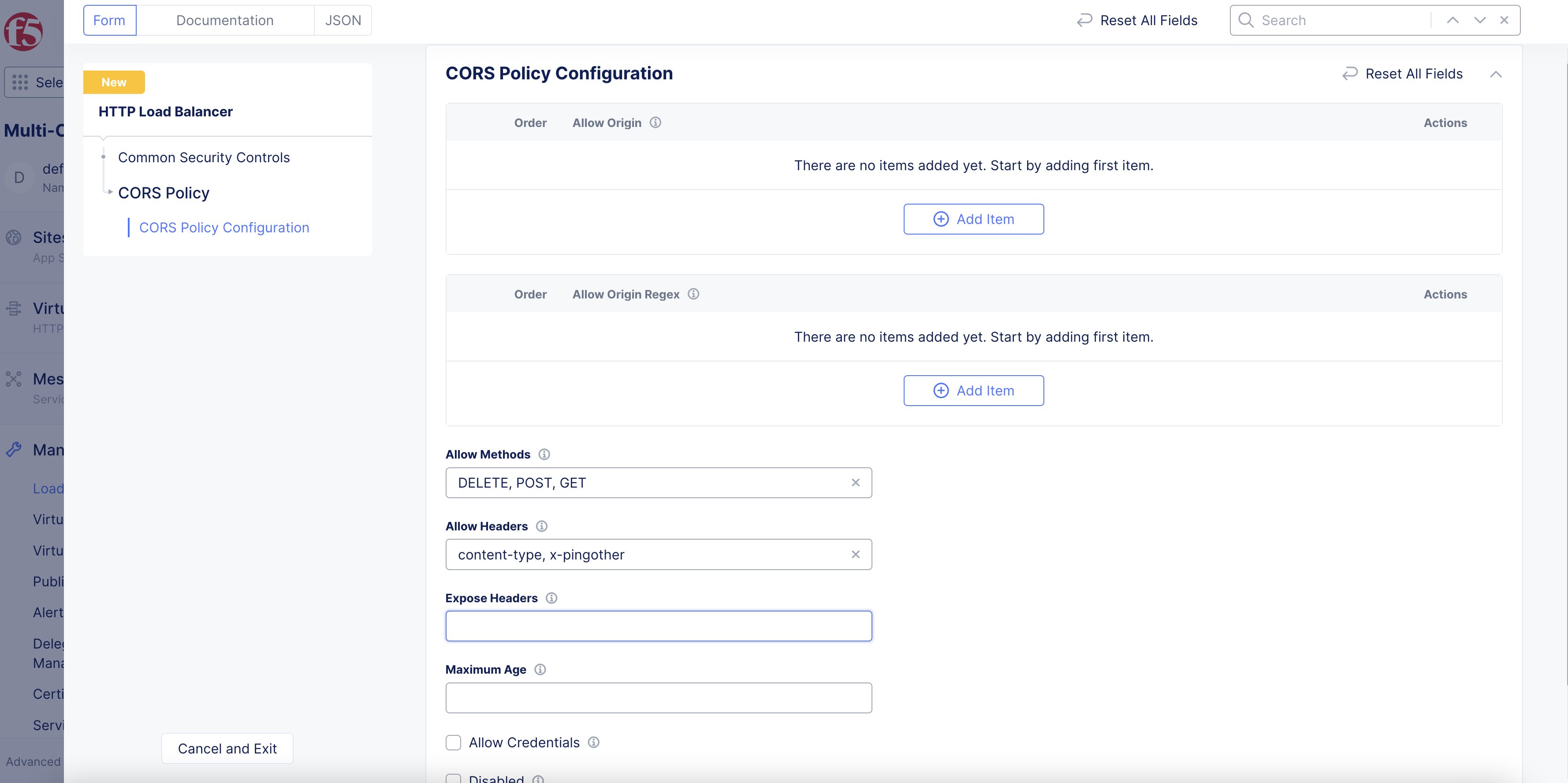
Figure: CORS Policy
-
In the
Maximum Agefield, enter information in seconds to cache the headers. -
After you finish, click
Apply.
Step 12: Configure Other Settings.
In the Other Settings section, perform additional configuration.
Step 12.1: Configure VIP advertisement.
From the VIP Advertisement drop-down menu, select from one of the options available:
-
Select
Internetto advertise the default VIP on the public network. -
Select
Internet (Specified VIP)and enter an IP address in thePublic IPfield to advertise that IP as VIP on a public network. -
Select
Custom. ClickConfigurein theAdvertise Customfield, and then clickAdd Itemfor each site you want to advertise. Perform the configuration per the following guidelines for each site:-
From the
Select Where to Advertisemenu, select an option for where a load balancer should be advertised.-
Choose
Site:- From the
Networkdrop-down menu, choose a network type to be used on the site. - Select a
Site Referenceobject from the drop-down menu. - Optionally enable the
Show Advanced Fieldsoption and enter an IPv4 and/or an IPv6 to be used as the VIP on the site.
- From the
-
Choose
Virtual Site:- From the
Networkdrop-down menu, choose a network type to be used on the site. - Select a
Site Referenceobject from the drop-down menu.
- From the
-
Choose
vK8s Service Network on RE:- Select
REorVirtual Site Referencefrom the drop-down menu. - Select a reference (RE or virtual site) from the associated
Referencedrop-down menu.
- Select
-
Choose
Virtual Network:- Select a network reference from the
Networkdrop-down menu. - Select
Default V4 VIPorSpecific V4 VIPfrom theSelect V4 VIPdrop-down menu. If you select a specific one, then enter the specific V4 VIP. - Select
Default V6 VIPorSpecific V4 VIPfrom theSelect V6 VIPdrop-down menu. If you select a specific one, then enter the specific V6 VIP.
- Select a network reference from the
-
Choose
Segment on Site:- Select a segment from the
Segmentdrop-down menu. - Select a site from the
Sitedrop-down menu. - Enter the IPv4 address of the VIP on the site.
- Enter the IPv6 address of the VIP on the site.
- Select a segment from the
-
Choose
Segment on Virtual Site:- Select a segment from the
Segmentdrop-down menu. - Select a virtual site from the
Virtual Site Referencedrop-down menu. - Enter the IPv4 address of the VIP on the virtual site.
- Enter the IPv6 address of the VIP on the virtual site.
- Select a segment from the
-
Choose
Segment on Cloud Edge:- Select a segment from the
Segmentdrop-down menu. - Select a cloud edge from the
Cloud Edgedrop-down menu. - Enter the IPv4 address of the VIP on the cloud edge.
- Enter the IPv6 address of the VIP on the cloud edge.
- Select a segment from the
-
-
Configure a TCP listener port or select a default option for the
TCP Listen Port Choicefield. The default option sets port 80 for the HTTP load balancer and 443 for the HTTPS load balancer. -
Click
Applyto save the site to advertise to the list. Then clickApplyto save the list of sites to advertise.
-
-
Select
Do Not Advertiseto disable VIP advertisement.
Note: If you have enabled Internet VIP on the AWS cloud site to allow clients to access Load Balancer VIP directly from the internet, set the
VIP Advertisementselection toCustom, and then configure the custom VIP advertisement to advertise on aSiteorVirtual SitewithSite Networkset to eitherOutside Network with internet VIPorInside and Outside Network with internet VIP. For more information, see Create AWS Site.
Note: The following ports are not supported for advertising on a Distributed Cloud Services site:
- K8s node port range 28000-32767
- Distributed Cloud Services port range 65000-65535
- 10249
- 10250
- 10251
- 10252
- 10256
- 10257
- 10259
- 1067
- 18091
- 18092
- 18093
- 18095
- 22
- 22222
- 2379
- 23790
- 23791
- 2380
- 23801
- 23802
- 323
- 4500
- 500
- 53
- 5355
- 6443
- 68
- 8005
- 8007
- 8087
- 8443
- 8444
- 8505
- 8507
- 9007
- 9090
- 9153
- 9999
Step 12.2: Configure Load Balancing Algorithm.
-
From the
Load Balancing Algorithmmenu, set how the HTTP/HTTPS requests are load balanced. The options include:-
Round Robin: This option sends requests to all eligible servers in a round robin fashion. -
Least Active Request: This option sends requests to an origin server that has least active requests set. -
Random: This option sends requests to all origin servers randomly. -
Source IP Stickiness: This option sends requests to all origin servers using the hash value of the source IP. -
Cookie Based Stickiness: This option sends requests to all origin servers using the hash value of the cookie. The cookie can be passive or generated. The consistent hashing algorithm, ring hash, is used to select the origin server. Requires you to further configure the parameters. -
Ring Hash Policy: This option sends requests to all origin servers using the hash value of the request. Requires you to further configure the parameters.
-
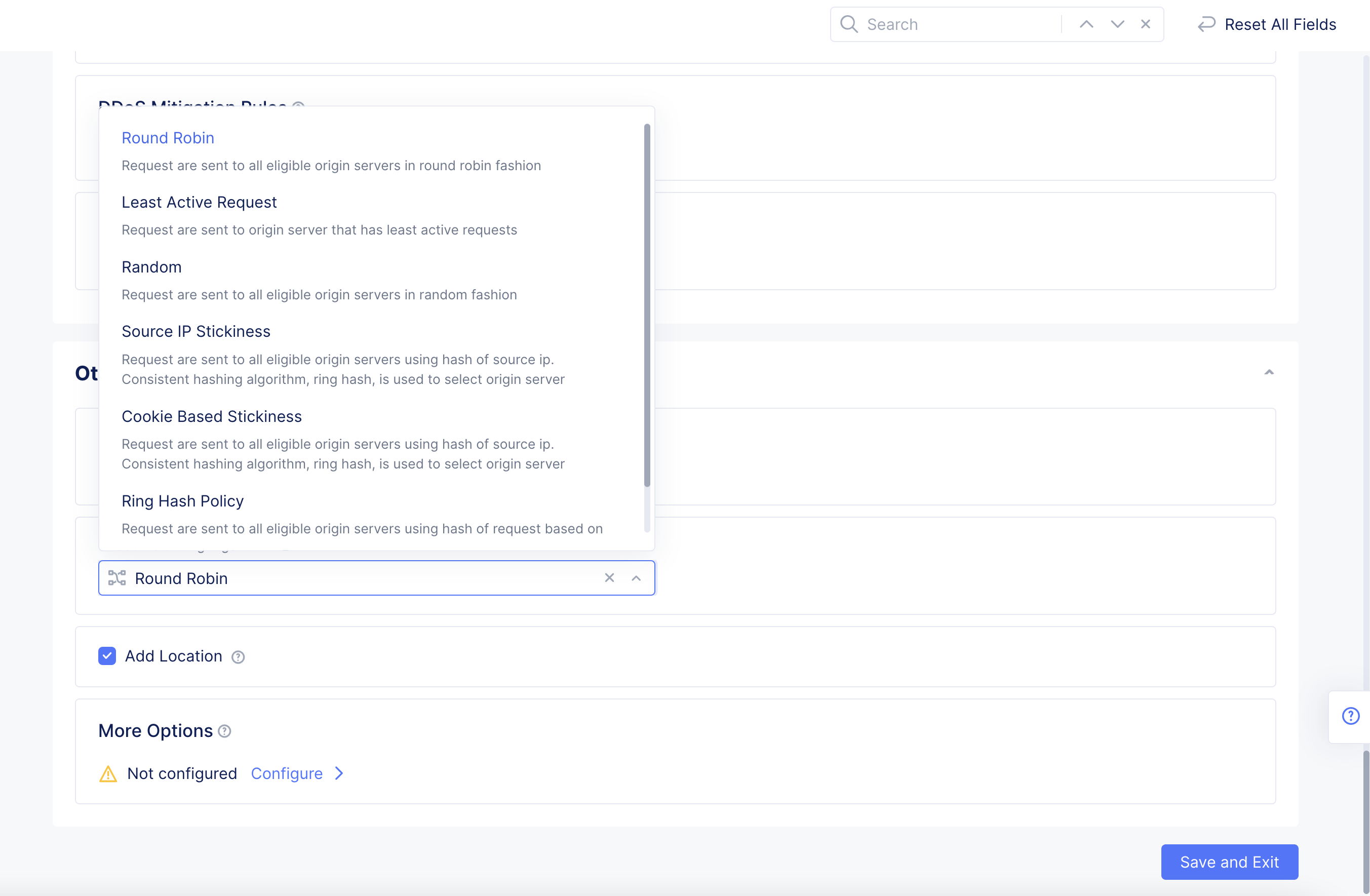
Figure: Load Balancer Control
-
If you select
Cookie Based Stickiness:-
In the
Namefield, enter a name for the cookie. -
Optionally, set a TTL value in milliseconds and set a path name value.
-
-
If you select
Ring Hash Policy:-
Click
Configureto specify a list of hash policies to use. -
Click
Add Item. -
From the
Hash Policy Specifierdrop-down menu, select what to apply the hash policy to. The options include:-
Cookie: Hash policies are applied to a cookie. -
Header Name: Hash policies are applied to the name of key of the request header used to obtain the hash key. -
Source IP: Hash policies are applied to the source IP address.
-
-
In the
Namefield, enter a name for the cookie that is used to obtain the hash key. -
To apply the hash policy as a terminal policy, select the
Terminaloption. -
Click
Apply. -
Select the newly created hash policy, and then click
Apply.
-
Step 12.3: Configure Trusted Client IP Headers.
- Select the
Enablefrom theTrusted Client IP Headersdrop-down menu. - Use
Add Itembutton to add one or more headers. The headers are processed in the numerical order they are added, as shown on the page.
When trusted client headers are enabled, system uses real client IP address as the source IP, instead of the proxy's IP address. The following apply when configuring trusted client IP headers:
- When multiple headers are configured, F5 Distributed Cloud platform follows top to bottom precedence. This means initially first header is considered and system checks for its availability in the request. If not present in the request, system proceeds to check for the second header, and so on, until one of the listed headers is found.
- When none of the configured headers exists, or the value of the configured header is not an IP address, then the source IP of the packet is used.
- When multiple IP addresses are available in header value, system reads the rightmost IP address, and considers it as real Client IP address. However, when using the
X-Forwarded-Forheader, and if multiple IPs are available in value, the system reads the rightmost-1 IP address, and considers it as real client IP address.
Note: See Overview of Trusted Client IP Headers in F5 Distributed Cloud Platform for more information.
Step 12.4: Configure Add Location and More Options.
- Select the
Add Locationcheckbox to specify the regional edge (RE) site name in the header responses.
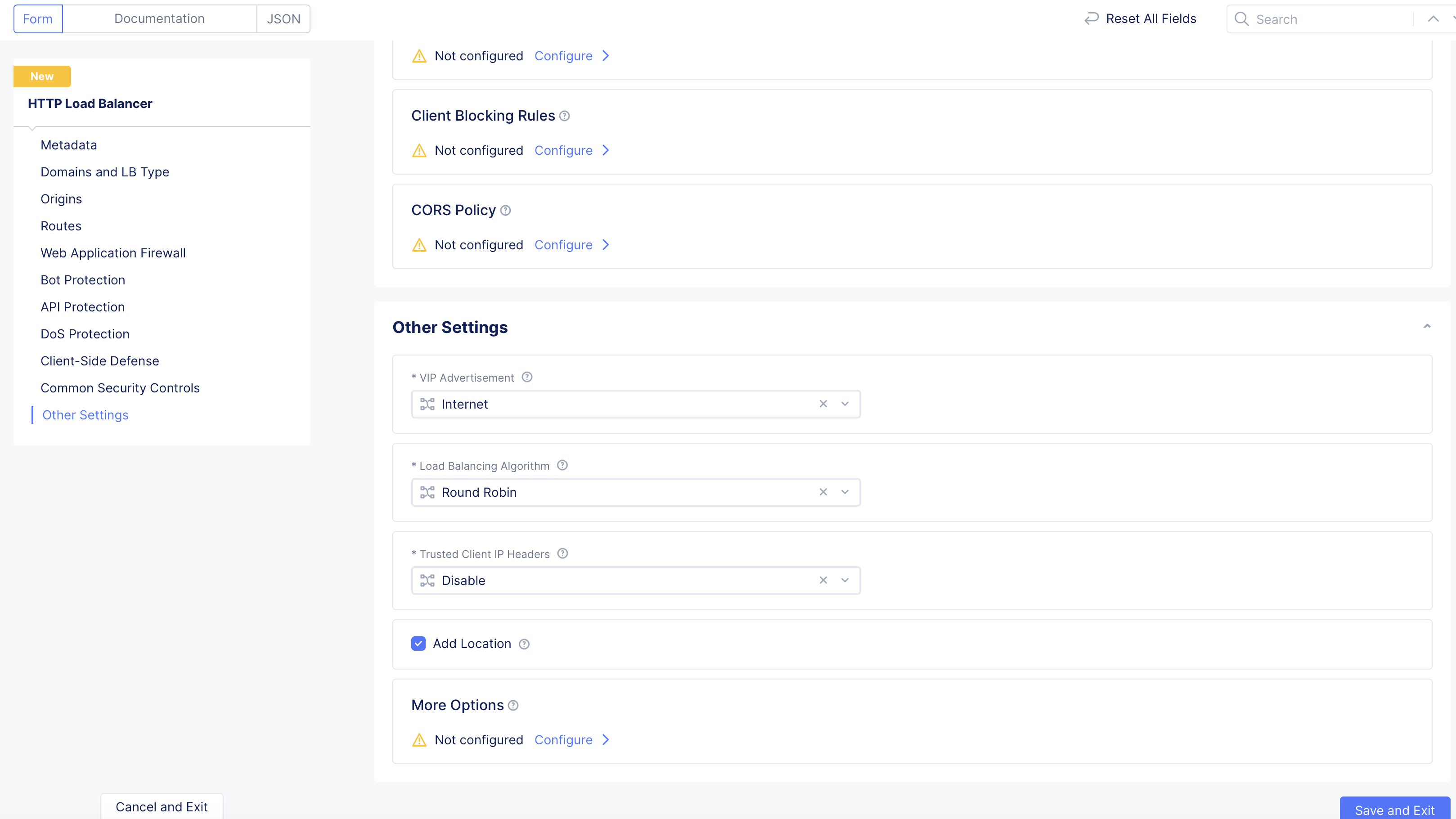
Figure: Enable RE Site Header Responses
-
Click
Configurein theMore Optionsfield and perform the configuration per the following guidelines:-
In the
Header Optionssection, clickAdd Itemand add details in each of the request headers and response headers fields to specify add and remove headers accordingly. -
In the
Configure Error Response Optionssection, clickConfigureto customize error responses. -
In the
Miscellaneous Optionssection, clickConfigure. Complete the configuration options.
-
-
Click
Apply.
Step 13: Complete creating the load balancer.
Click Save and Exit.
Step 14: Verify the load balancer status.
Note: If the load balancer is of type
HTTP, then it is reachable by configured domains as well as automatically generated CNAME.
Distributed Cloud DNS Managed Domain:
- Wait for the
DNS InfoandCertificate statusto display theVIRTUAL_HOST_READYandCertificate statusValidvalues.
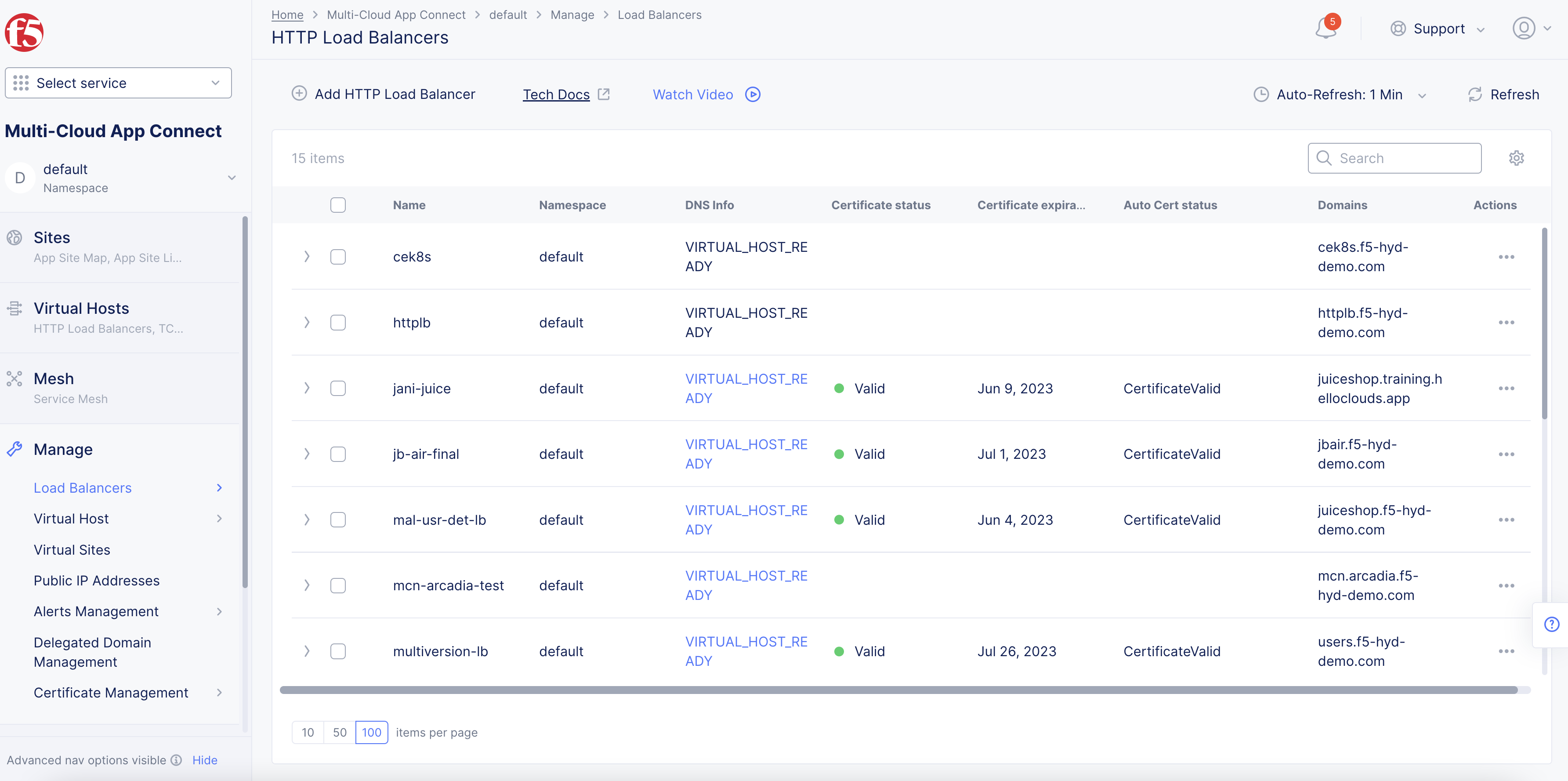
Figure: Load Balancer Created
- Verify that the requests to your virtual host domain are processed and load balanced between the configured origin servers.
Note: The
Certificate expiration datecolumn displays the expiration date for the certificates. Certificates managed by F5 Distributed Cloud Services are issued for 90 days and auto-renewed after 75 days from the date of issuance.
Domain with other DNS management:
-
Verify that the
Certificate statusfield showsDomain Challenge Pending. -
Click
>to view the load balancer information in JSON format. -
Verify that ACME challenge record exists under
get_spec>auto_cert_info>dns_recordsfield in the JSON. The record name starts with_acme-challengeand the value is the name of the TXT record created by Distributed Cloud Services. -
Create a CNAME record with the obtained ACME challenge name and value in your DNS server.
-
Verify that the
Certificate statusfield value changes toCertificate Valid. -
Verify that the
Certificate expiration datefield value displays the expiration date for the certificates.
Note: Some client browsers can employ a performance optimization known as "connection coalescing." In this optimization, if two host names resolve to the same IP address and are present in the same TLS certificate, the HTTP/2 connection will be reused between them. This can land the HTTP request in the wrong load balancer and results in a
404error. See HTTP2 RFC for more information.