Configure Client-Side Defense
This guide provides instructions about how to enable Client-Side Defense (CSD) and how to apply it to your web applications using F5 Distributed Cloud Console. For more information about CSD, see About Client-Side Defense.
Prerequisites
- A valid F5 Distributed Cloud Console Account. If you do not have an account, see Getting Started with Distributed Cloud Console.
Enable CSD
To enable CSD on Distributed Cloud Console, do the following:
-
In Common services, select the Client-Side Defense tile.
-
In the Client-Side Defense screen that appears, select Enable Client-Side Defense.
CSD is now enabled and ready for use.
Add a domain for CSD protection
After you enable CSD on Distributed Cloud Console, add the root domain for all domains where you want to apply CSD protection:
-
In the CSD dashboard, go to Configuration.
-
Select Add domain to protect. The Domain to protect screen appears.
-
In the Domain to protect screen, enter the root domain you want to protect and select Add Domain to Protect.
The domain you added now appears in the list of domains to protect.
Injecting the CSD JS on your web pages
After you add the domains on which to apply CSD protection, you must inject the CSD JavaScript on the web pages in the domain. F5 recommends injecting the CSD JavaScript on all web pages in the domain to maximize CSD protection.
Note: You can also use BIG-IP to inject the CSD JavaScript in your website pages. For information, see https://techdocs.f5.com/en-us/bigip-17-1-0/big-ip-dcs-client-side-defense-implementation.html.
To inject the CSD JavaScript on web pages:
-
In the CSD dashboard, go to Configuration.
-
Select How to Inject JS. The How to Inject JS screen appears.
-
Follow the instructions for injecting the CSD JavaScript in the How to Inject JS screen.
Verifying your email on the Alert Receiver
When you enable CSD, CSD automatically creates an Alert Receiver using the email address you entered for your account on Distributed Cloud Console. CSD also automatically creates an Alert Policy and adds a CSD alerts group to this policy. To ensure that you receive alerts when CSD detects suspicious activity, you need to verify your email on the Alert Receiver.
To verify your email on the Alert Receiver:
-
In the System namespace, in the left navigation pane, go to Manage > Alerts Management > Alert Receivers.
-
In the Alert Receivers screen, find the
client-side-defense-receiverrow and in its Actions column select the icon with three dots. A pop-up menu appears. -
Select Verify Email, and then select Send email to send the verification email.
-
After you receive the email, return to the Alert Receivers screen.
-
Find the
client-side-defense-receiverrow and in its Actions column select the icon with three dots. A pop-up window appears. -
Select Enter verification code, enter the verification from the email, and then select Verify receiver.
There is no CSD-specific alert receiver configuration. For information about how to create and configure Alert Receivers and Alert Policies, see Alerts - Email & SMS.
Testing the JS injection on your web pages
After you add domains for CSD protection and inject the CSD JavaScript on your web pages, you can test if the JavaScript injection was successful on a web page. Testing for the CSD JavaScript injection is not required, but F5 recommends performing this test to verify that your web pages are receiving CSD protection.
To perform testing for the CSD JavaScript injection:
-
In the CSD dashboard, go to Configuration.
-
Find the domain in the list that contains the web page that you want to test, and select the Test JS Injection button at the end of the row on the right. The Test JS Injection screen appears.
-
In the Test JS Injection screen, paste the URL of the web page that you want to test and select Test JS Injection.
When the test is finished, the CSD dashboard displays a confirmation message indicating whether or not the CSD JavaScript was detected on the web page.
Using the CSD dashboard
Monitoring > Dashboard
The CSD Monitoring Dashboard page displays the suspicious network interactions with additional information for deciding whether to mitigate or allow a suspicious domain. When a web page with CSD protection is loaded on the end-user’s browser, scripts running on that webpage interact with other domains. The Suspicious Domains list displays a list of the domains that those scripts interact with and which CSD detected to be potentially malicious.
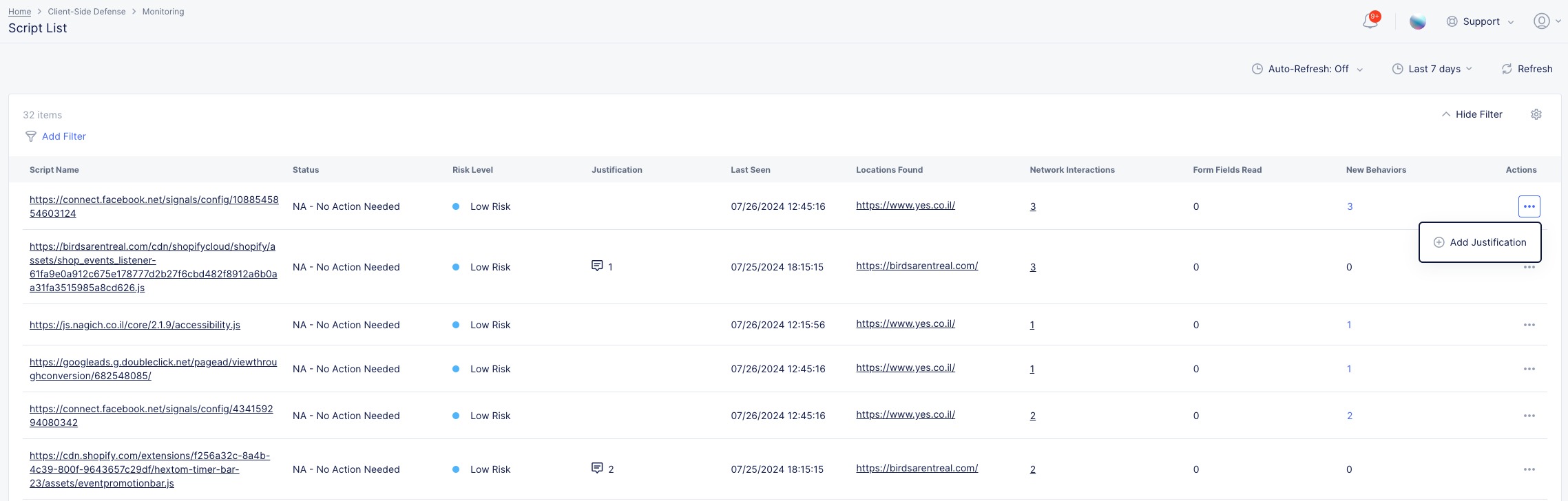
Monitoring > Script List
For your reference, XC Client-Side Defense lists all discovered JavaScript scripts for a page. The list provides an overview of which scripts interact with the different webpage elements.
To view the list, in the left navigation menu go to Monitoring > Script List.
Select a script to see the following information:
- Script behaviors (new or otherwise) over time.
- All network interactions for the script.
- All form fields read by this script.
For information about script objects, see The Script Object - Detailed Information on Script Behavior.
Note that script behavior is not currently represented in the dashboard. Use the "Status" column on this page to track scripts that display suspicious behaviors. Scripts have one of the following statuses:
- NA - No Action Needed: CSD did not find anything suspicious with this script.
- Resolved - No Action Needed: CSD found some suspicious behaviors with this script that a user has already taken action on.
- AN - Action Needed: CSD found some suspicious behaviors with the script that needs your attention.
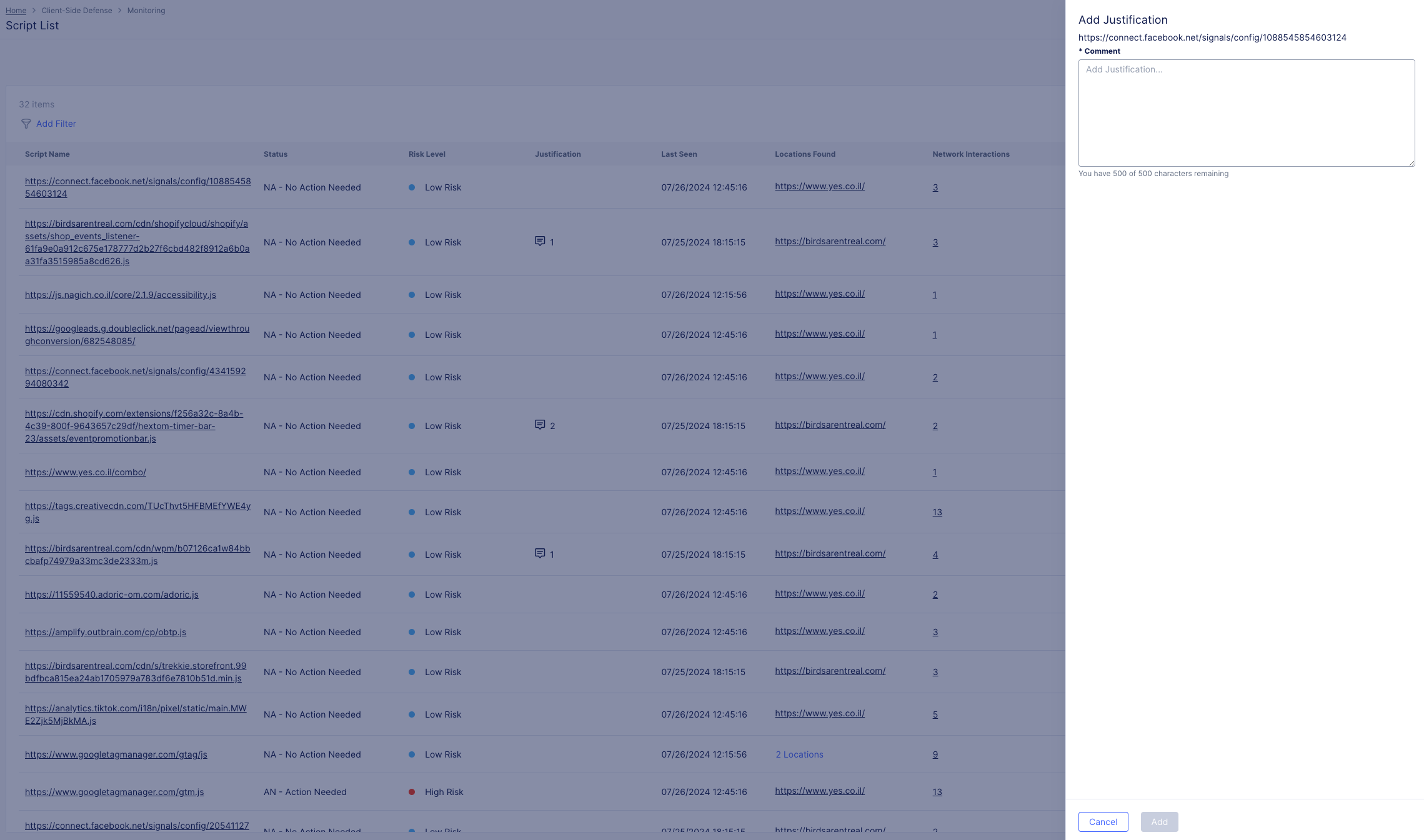
To assist in demonstrating compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) v4.0 Requirement 6.4.3, users can add comments containing written justifications for the specific utility of each script in the script list.
To add a script justification:
-
Go to the row of the script you would like to add a justification for and in its Actions column select the icon with three dots. A pop-up menu appears.
-
Select Add Justification

Figure: Add Justification Button
-
Add a justification in the text box and select Add

Figure: Justification Form Field
Monitoring > Network
The CSD Monitoring Network page displays several tabs for displaying holistic network data, which can assist you when deciding whether to mitigate or allow a suspicious domain:
-
All Domains: When a web page with CSD protection is loaded, scripts running on that web page interact with other domains. The All Domains list displays a list of the domains that those scripts interact with.
-
Mitigate List: Displays a list of domains that the user has assigned for mitigation. When a domain is assigned for mitigation, CSD blocks that domain and it cannot be accessed by any script running on the end-user's browser when accessing a CSD protected web page.
-
Allow List: Displays a list of domains that the user has decided don't need mitigation and are allowed free access.
Manage > Configuration
The CSD Manage Configuration page is for configuring your web application for CSD protection. The page displays a list of your root domains that are configured for CSD protection, and also the following:
-
Add domains for CSD protection.
-
Display instructions for injecting the CSD JS on web pages in a domain.
-
Schedule a CSD training session.
Viewing suspicious domains
When CSD detects suspicious activity on a domain that has been configured for CSD protection, the user is alerted and that domain is added to the dashboard.
Filtering suspicious domains by location
You can filter the Suspicious Domains list according to a specific location or locations where CSD detected suspicious activity.
To filter the Suspicious Domains list by location:
-
In the upper-right of the page, select Select Page. A pop-up list appears.
-
Select one or more locations, and then select Apply.
The list now displays only those domains containing the locations you selected.
Adding a domain to the Mitigate List or Allow List
To add a domain to the Mitigate List or Allow List:
-
From the Client-Side Defense navigation panel, select Monitoring > Network.
-
Go to the Suspicious Domains list or All Domains list.
-
Go to the row of the relevant domain, and in its Actions column select the icon with three dots. A pop-up menu appears.
-
Select Add to Allow List/Add to Mitigate List.
Alternatively, you can add a domain directly from the Mitigation List or Allow List as follows:
-
In the Mitigation List or Allow List, select Add domain. A new screen appears.
-
Enter the domain name and then select Add Mitigated Domain or Add Allowed Domain.
After adding a domain to the Mitigate List or Allow List, you can delete it from the list by selecting the icon with three dots in the Actions column, and then selecting Delete.
Viewing domain details
From the Suspicious Domains list or All Domains list, you can view the following domain information by selecting the domain from the list:
- Reasons why this domain may be at risk
- Risk score
- Web pages on this domain with CSD protection
- Scripts that are potentially networking with the domain
The Script Object - Detailed Information on Script Behavior
The three main components of a script object are displayed on the following tabs:
-
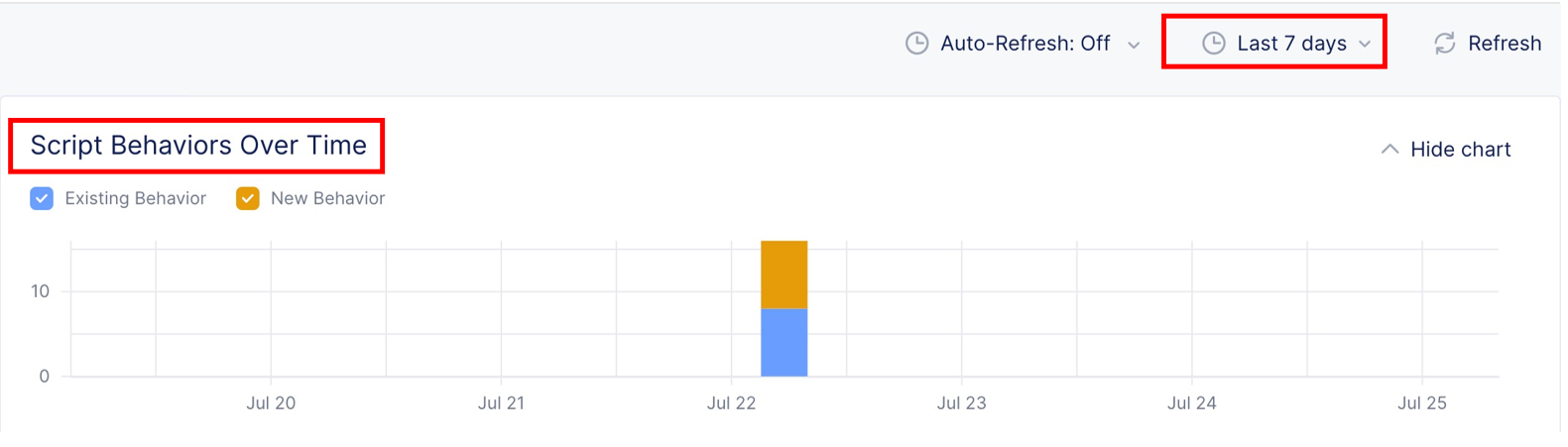
Overview: Captures behavior of the script over time.
It includes the following information:
-
Script Behaviors Over Time: A graphical representation of changes to the behavior of a script over time. You can configure the time frame and behaviors displayed in the chart.

Figure: Script Behaviors Over Time
-
New Behaviors Pane: Lists all new behaviors of this script during the selected time interval.
-
All Behaviors Pane: Lists all behaviors of this script during the selected time interval.
-
-
Network: Captures all network interactions of a specific script.
-
Form Fields: Lists all form fields read by a specific script.
Note: To take action on the behaviors of the script, navigate to either the Network or Form Fields tab.Select either the Mitigation or Allow action. Based on the action you select, the status of the script changes to reflect whether the suspicious behavior is resolved.
Modifying the CSD JS for asynchronous loading
By default, the CSD JavaScript is configured to load synchronously and F5 highly recommends against changing this configuration. However, if there is a strong need, you can modify the CSD JavaScript to load asynchronously. To modify the CSD JavaScript for asynchronous loading, add async defer to the beginning of the script, as follows:
Change: <script src="https://us.gimp.zeronaught.com/js/example.js"></script>
To: <script async defer src="https://us.gimp.zeronaught.com/js/example.js"></script>
The CSD JavaScript should always be the first JavaScript or script to load on the web page to ensure that the CSD JavaScript can detect any malicious scripts running on the web page.
Script versioning by name change
When you release a new version of a script with an updated name and path, you receive redundant alerts for the updated script. To stop the redundant alerts, contact F5 Support for information about how to define regex expressions that represent your script.
Configure Client-Side Defense in Web App & API Protection
You can optionally enable and configure Client-Side Defense on one or more HTTP load balancers that you have configured in the F5 Distributed Cloud Console in either Web App & API Protection or Multi-Cloud App Connect.
Complete the following tasks to configure Client-Side Defense on an HTTP load balancer:
-
In Client-Side Defense, add the root domain for all the domains that you want to protect.
-
Enable Client-Side Defense on each HTTP load balancer on which you want to configure Client-Side Defense.
-
Configure the Client-Side Defense Policy on each HTTP load balancer on which you want to configure Client-Side Defense, which controls how you want Client-Side Defense to inject JavaScript tags in the HTTP pages in your application.
Client-Side Defense inserts JavaScript in your application to detect network requests and form field reads by malicious scripts that may attempt to exfiltrate PII data.
Before you Begin:
- You must purchase Client-Side Defense. Contact your F5 Account Representative for assistance.
- You must have an active F5 Distributed Cloud account. If you do not have an account, see Getting Started with Distributed Cloud Console.
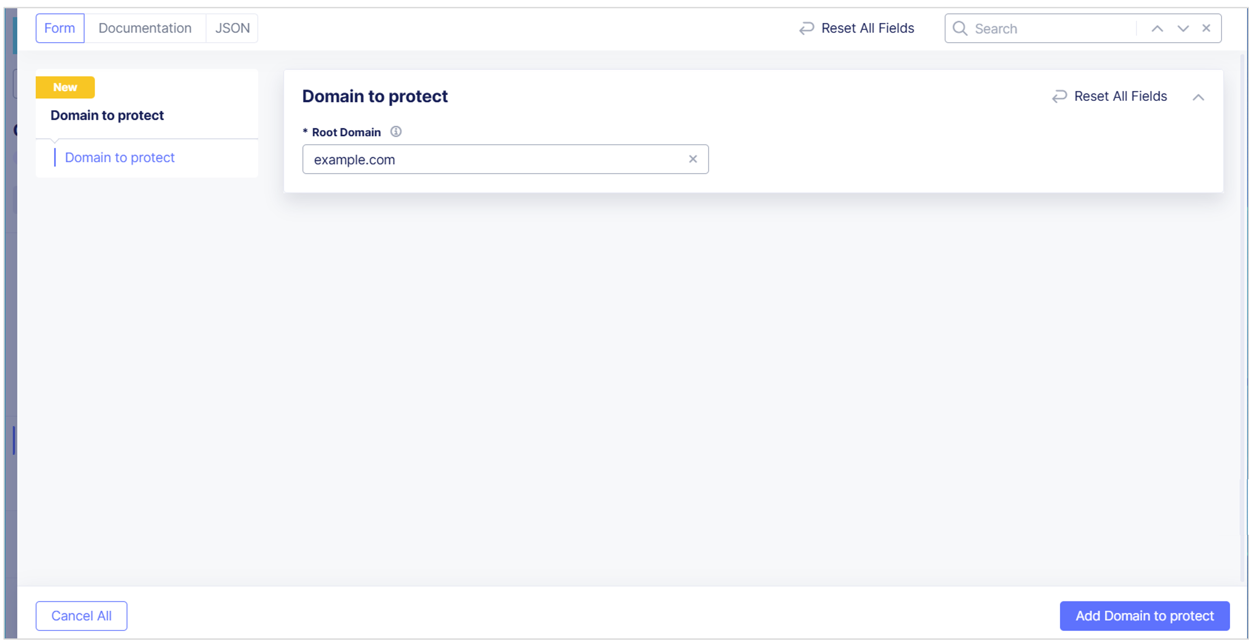
Add a Root Domain to Protect with Client-Side Defense
Add the root domain for all domains you want to protect with Client-Side Defense.
-
From the Distributed Cloud Console Homepage, select Client-Side Defense.
-
From the navigation menu, select Manage > Configuration and then select Add Domain to Protect.
-
In the Root Domain field, enter the domain you want to protect. This should be the root of the pages where you inject JavaScript. Then select Add Domain to Protect to save the domain.

Figure: Protect a Root Domain
Enable Client-Side Defense on an HTTP Load Balancer
Enable and configure Client-Side Defense on one or more HTTP load balancers in Web App & API Protection.
Important: You must add the root domain you want to protect in Client-Side Defense before you can configure Client-Side Defense on your HTTP load balancer.
- From the Distributed Cloud Console Homepage, select Web App & API Protection.
- From the navigation menu, confirm that you selected the correct namespace.
- Select Manage > Load Balancers > HTTP Load Balancers.
- From the Actions column, select the Action (…) menu next to the load balancer where you want to configure Client-Side Defense and then select Manage Configuration.
- Select Edit Configuration and then select Client-Side Defense.
- From the Client-Side Defense drop-down menu, select Enable.
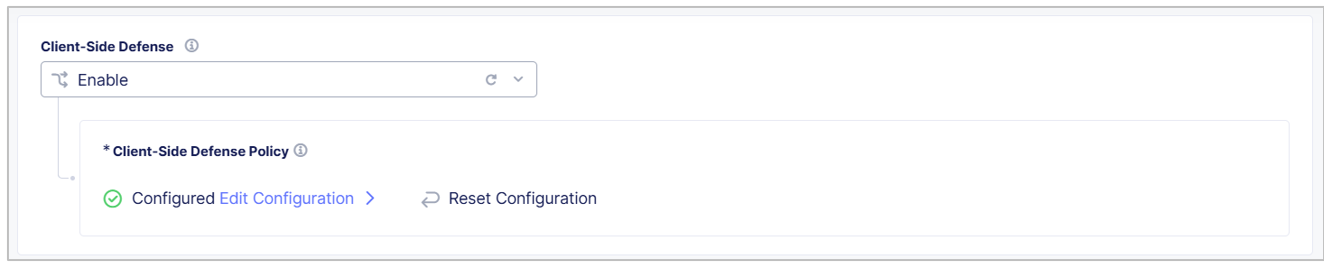
Configure Client-Side Defense Policy
Configure the Client-Side Defense policy to control in which of your application pages Client-Side Defense inserts JavaScript tags.
-
From the Client-Side Defense Policy box, select Edit Configuration.

Figure: Enable Client-Side Defense on an HTTP Load Balancer
-
From the JavaScript Insertion Settings drop-down menu, select the pages in which you want Client-Side Defense to insert JavaScript. Select one of the following options:
-
Insert JavaScript in All Pages: Client-Side Defense inserts JavaScript tags in all your application pages.
-
Insert JavaScript in All Pages with the Exceptions: Configure the pages in which you do not want Client-Side Defense to insert JavaScript tags:
-
In the JavaScript Insertions section, select Configure and then select Add Item.
-
Enter a Name and Description to identify the new exclusion rule.
-
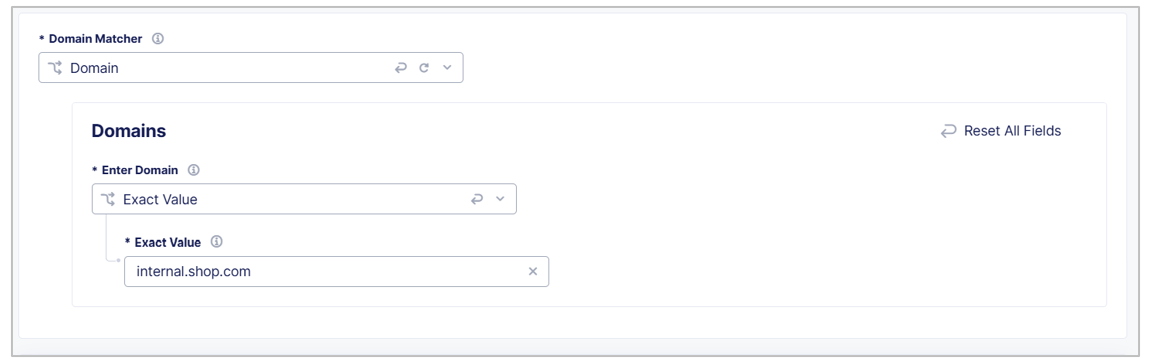
Use the Domain Matcher fields to specify domains you want to exclude from JavaScript insertion. Enter an Exact Value, a Suffix Value, or a Regex Value. If you select** Any Domain**, then Client-Side Defense injects JavaScript tags in HTML pages from all domains.

Figure: Configure a Domain Matcher
-
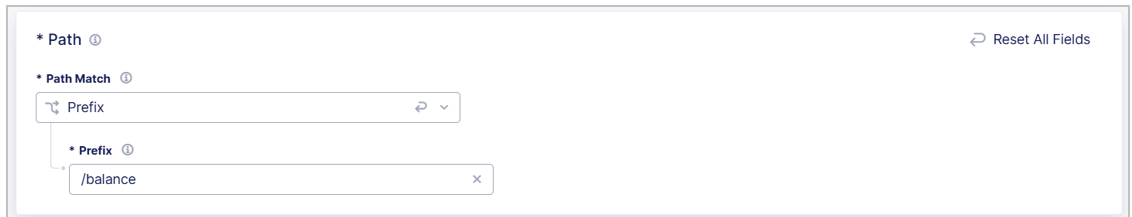
Use the Path fields to specify paths of pages in which you do not want to insert JavaScript tags, such as
/helpor/about. Enter a Prefix, Exact path, or Regex value.
Figure: Configure a Path Matcher
-
Select Apply.
-
Select Apply.
-
-
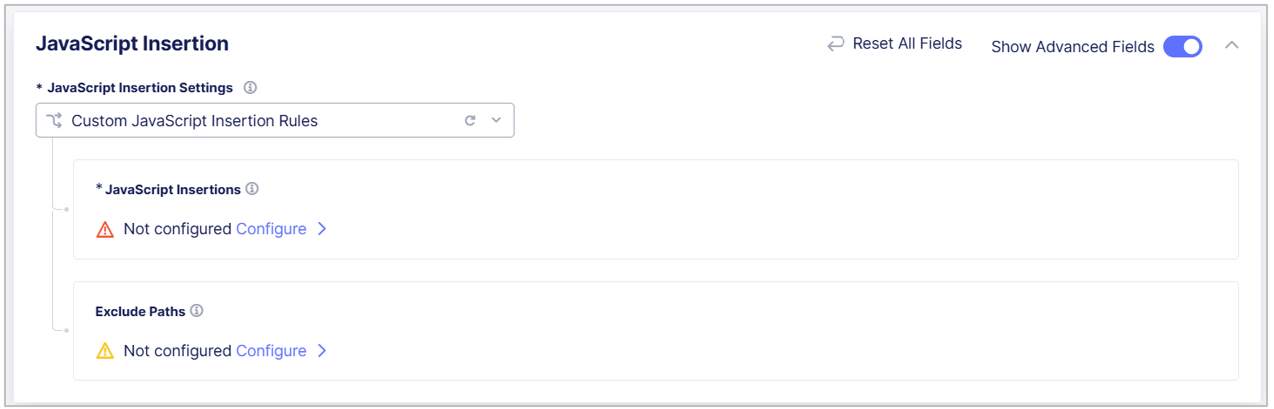
Custom JavaScript Insertion Rules: Select Show Advanced Fields and then use the instructions above to add the pages you want to include and exclude from JavaScript insertion.

Figure: Configure JavaScript Insertion
-
-
Select Apply.
-
Select Save HTTP Load Balancer.
Disable Client-Side Defense JavaScript Insertion
The following steps explain how to optionally disable JavaScript tag insertion in environments where you have enabled Client-Side Defense on an HTTP load balancer.
Important: For maximum effectiveness, Client-Side Defense requires you to enable JavaScript insertion. F5 recommends that you do not disable JavaScript insertion.
To disable JavaScript insertion in Client-Side Defense on an HTTP load balancer:
- From the Distributed Cloud Console Homepage, select Web App & API Protection.
- From the navigation menu, confirm that you selected the correct namespace.
- Select Manage > Load Balancers > HTTP Load Balancers.
- From the Actions column, select the Action (…) menu next to the load balancer on which you want to disable JavaScript tag insertion and then select Manage Configuration.
- Select Edit Configuration and then select Client-Side Defense.
- In the Client-Side Defense Policy section, select Edit Configuration.
- Enable Show Advanced Fields.
- From the JavaScript Insertion Settings drop-down menu, select Disable JavaScript Insertion and then select Apply.
- To save your changes, select Save HTTP Load Balancer.
On this page:
- Prerequisites
- Enable CSD
- Add a domain for CSD protection
- Injecting the CSD JS on your web pages
- Verifying your email on the Alert Receiver
- Testing the JS injection on your web pages
- Using the CSD dashboard
- Monitoring > Dashboard
- Monitoring > Script List
- Monitoring > Network
- Manage > Configuration
- Viewing suspicious domains
- Filtering suspicious domains by location
- Adding a domain to the Mitigate List or Allow List
- Viewing domain details
- The Script Object - Detailed Information on Script Behavior
- Modifying the CSD JS for asynchronous loading
- Script versioning by name change
- Configure Client-Side Defense in Web App & API Protection
- Add a Root Domain to Protect with Client-Side Defense
- Enable Client-Side Defense on an HTTP Load Balancer
- Configure Client-Side Defense Policy
- Disable Client-Side Defense JavaScript Insertion