Blindfold TLS Certificates
Objective
This document provides instructions on how to encrypt your TLS certificates using F5® Distributed Cloud Blindfold. This ensures additional security measures for the certificates stored in F5 Distributed Cloud Platform. To know more about Blindfold and secrets management, see Blindfold.
Note: Distributed Cloud Platform supports blindfolding the secrets directly in Console. Use the instructions provided in this document only in the case you want to apply Blindfold to your certificates Offline.
The following image illustrates the sequence of actions performed in securing the certificates.
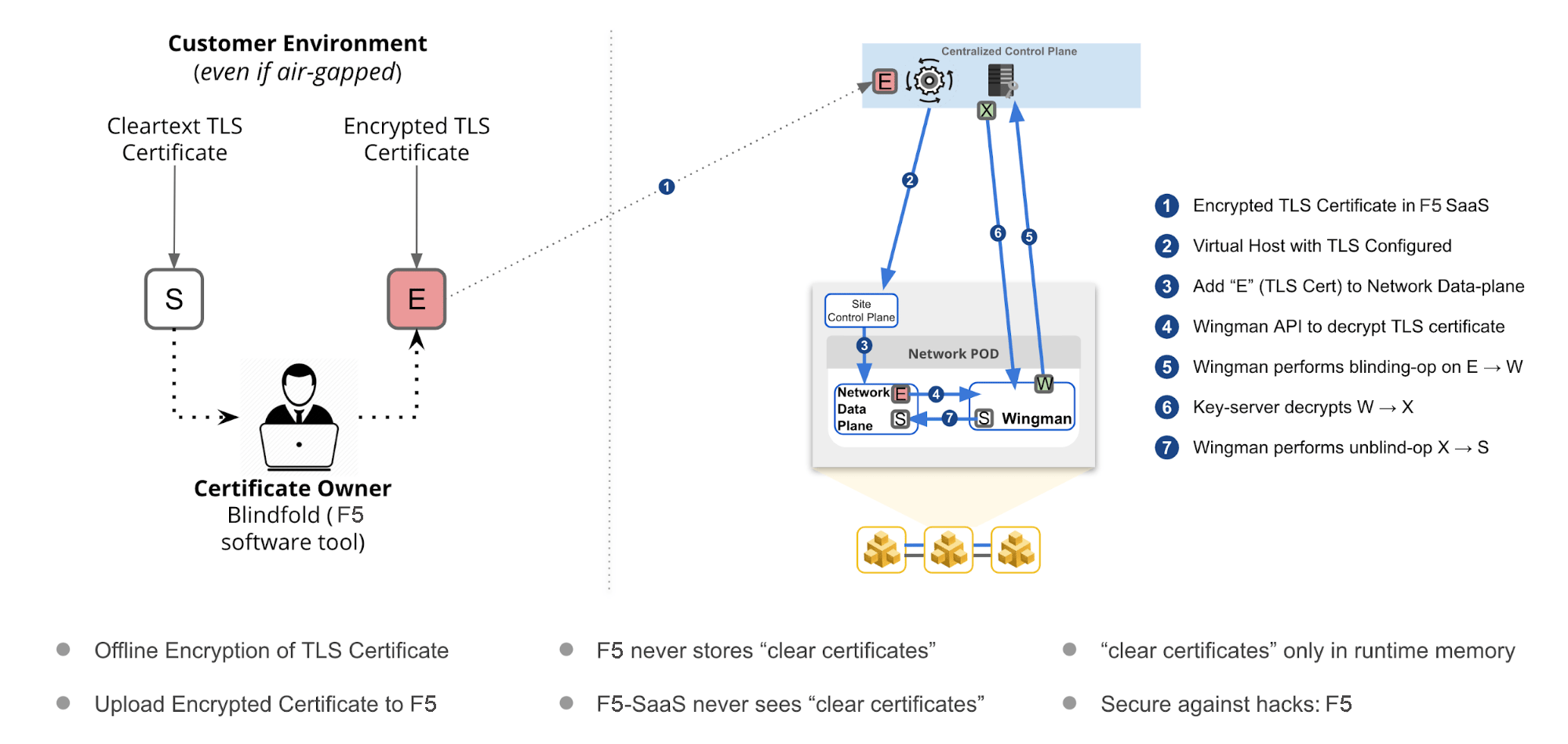
Figure: F5 Distributed Cloud Blindfold
Using the instructions provided in this guide, you can encrypt TLS certificate with Blindfold and apply it to a virtual host.
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites apply:
-
An F5 Distributed Cloud Account. If you do not have an account, see Getting Started with Console.
-
A virtual host with a signed TLS certificate. If you do not have a virtual host, see Create and Advertise Virtual Host.
-
The vesctl tool. Download vesctl on your local machine as it is used to apply Blindfold to the TLS certificate.
-
Optionally, one or more cloud or edge locations with a Distributed Cloud site. Install the Distributed Cloud node or cluster image in your cloud or edge location. See Site Management guides for more information.
-
A minimum of monitor role in the Shared namespace is required.
Configuration
The following image shows the configuration sequence of applying Blindfold encryption to your TLS certificate.
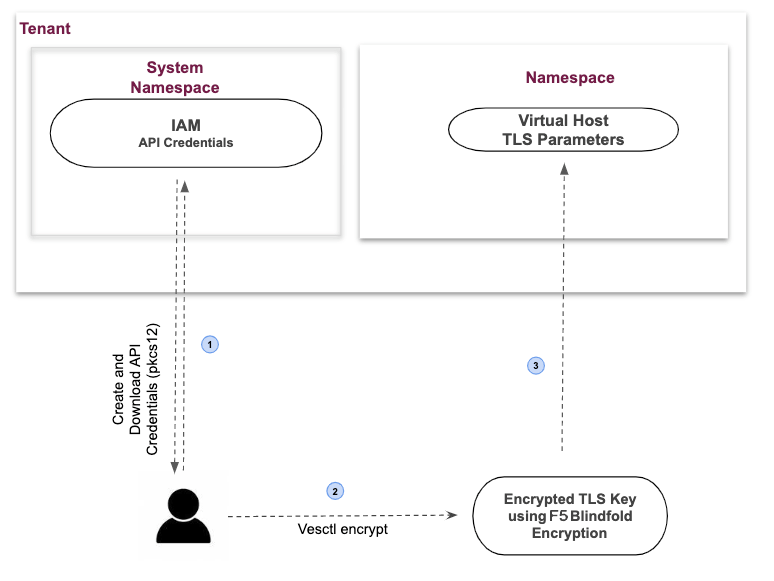
Figure: Encrypting TLS-Key using Blindfold
Configuration Sequence
Applying Blindfold to the certificates of your WebApp includes performing the following sequence of actions:
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Create a Secret Policy | Create a policy to permit F5 Distributed Cloud Wingman and data plane to access the TLS certificate. |
| Prepare Credentials and Policy | Retrieve API credentials from Console, derive certificates, derive keys, and obtain policy. |
| Encrypt TLS Certificate | Perform the encryption on a local computer. F5 recommends you use an air-gapped computer. |
| Enable TLS on the Virtual Host | Update the Virtual Host configuration with the TLS certificate and key encrypted with Blindfold. |
Note: The API credentials are required to be downloaded in PKCS #12 file format.
Create a Secret Policy
The secret policy allows Wingman and Distributed Cloud data plane access to the TLS certificate.
Note: You can also use the in-built
ves-io-allow-volterrapolicy.
Step 1: Log into Console and start creating new secret policy.
-
From the homepage, click
Multi-Cloud Network Connect. -
In the
Managesection of the configuration menu, selectSecretsfrom the options pane, and then selectSecret Policiesto see a list of existing policies. -
Click
Add secret policyto see the new secret policy form. -
In the
Metadatasection, -
Enter a unique name for the secret policy.
-
Optionally, set labels and description, as necessary.
-
Check
Allow F5XCto allow the data plane to decrypt an encrypted TLS private key. -
Enter
Decrypt Cache Timeoutto limit the time a decrypted secret is cached in Wingman.
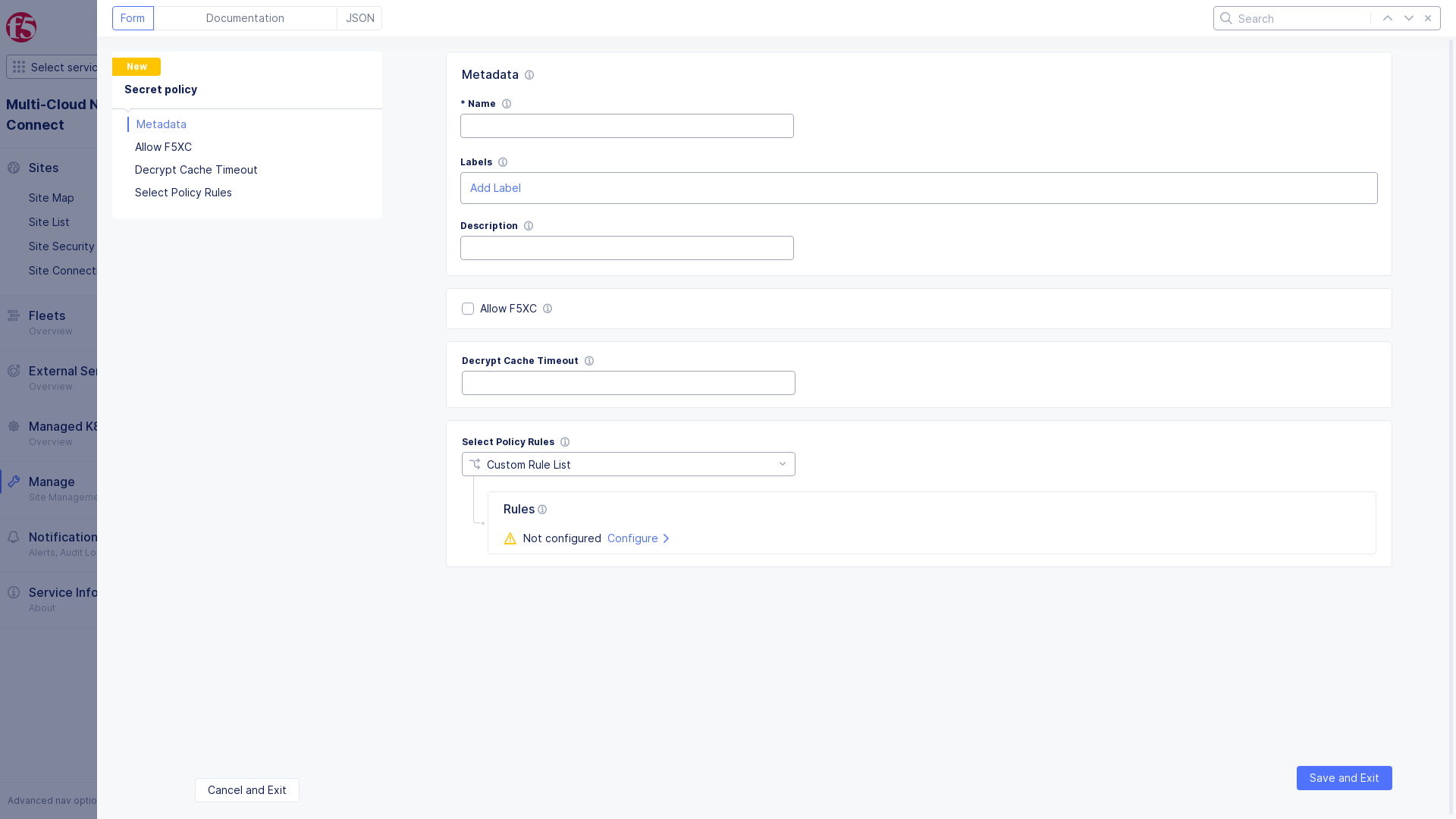
Figure: Secret Policy Metadata
Step 2: Configure the Secret Policy Rules.
The Secret Policy Rules section lists all the rules for this policy.
- To add a new rule,
Select Policy Rules> chooseConfigurelink > clickAdd itemand fill out the secret policy rule form as outlined below.
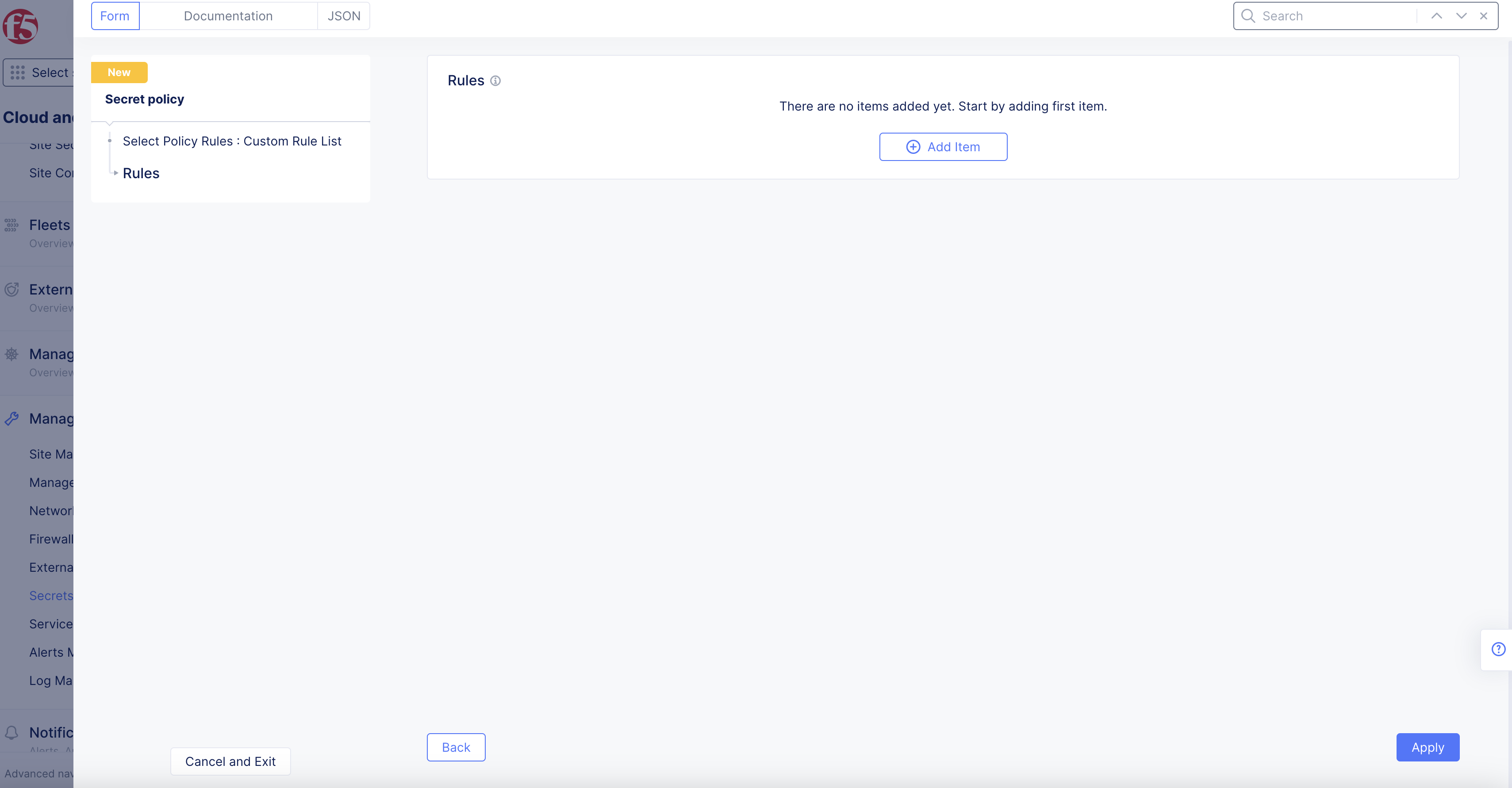
Figure: Secret Policy Metadata
-
In the
Metadatasection:-
Enter a unique name for the new rule.
-
Optionally, set labels and description, as necessary.
-
In the
Actionsection, selectingAlloworDenydetermines how to react to a request if all the predicates evaluate to true. -
In the
Client Selectionsection, specify the client(s) that will be affected by this rule:-
Group of Clients by Name: List of client names for which the rule will apply. You can specify them usingExact Valuesand/orRegex Values. ClickAdd itemand enter exact values or regular expressions for server names. Continue to clickAdd itemto build both lists. -
Group of Clients by Label Selector: Specifies the labels associated with the clients to which the rule will apply. To add labels, click in theSelector Expressionfield, and then for each label you want to add: -
Select a key from the displayed options or type a key and click
Assign Custom Key, -
Select a displayed operator,
-
Select a displayed value or enter a custom value,
-
Click
Apply. If this is the last label, click outside theSelector Expressionarea or press thetabkey.
-
-
Client Name: Enter a single client name.
-
-
When finished entering clients for this rule, click
Apply.
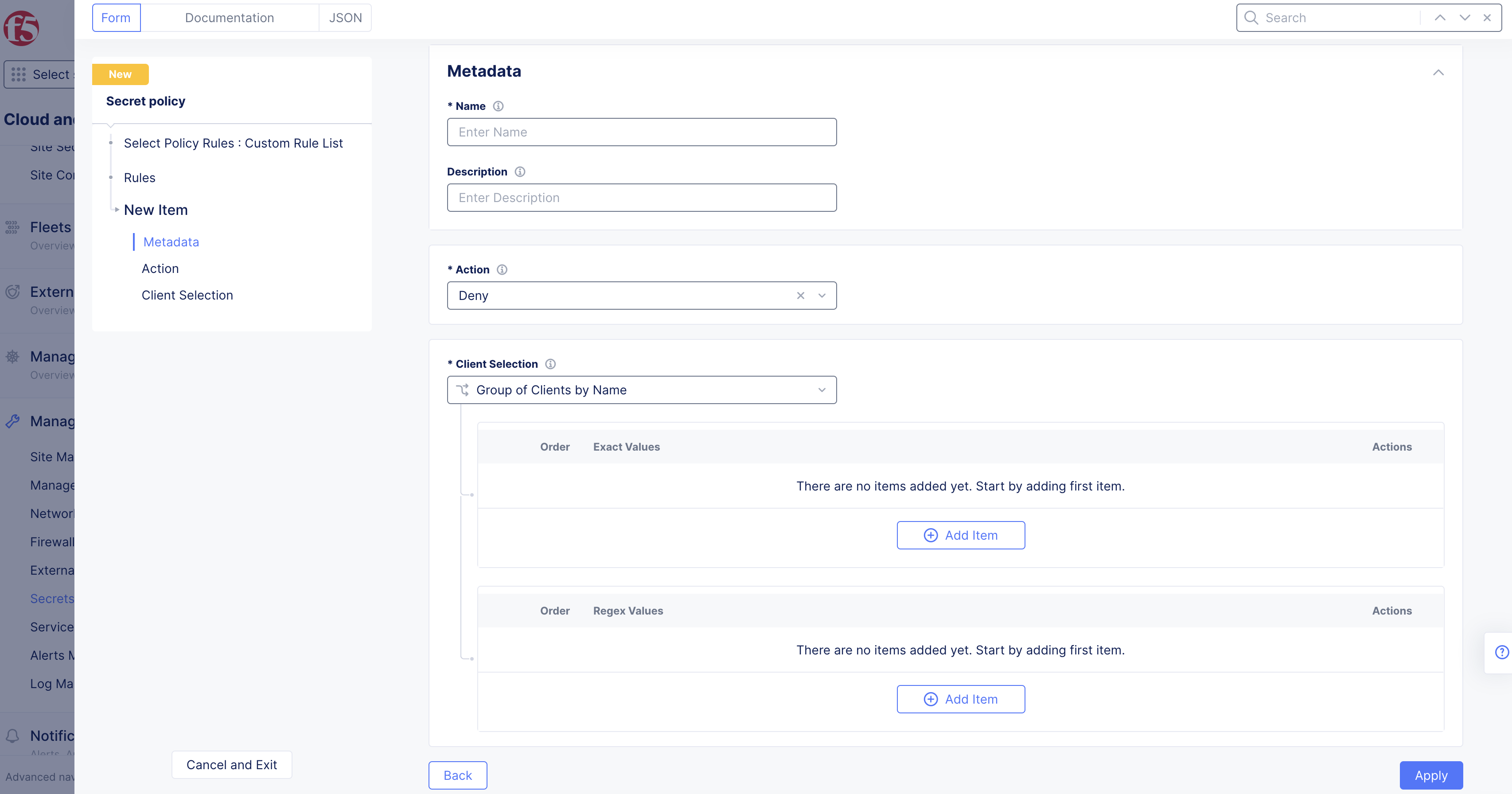
Figure: Secret Policy Action
- Click
Applyto save the custom rule list.
Step 3: Complete the policy.
- Click
Save and Exitto complete the secret policy.

Figure: Secret Policy Metadata
Prepare Credentials and Policy
Step 1: Create an API Certificate.
-
Log into F5 Distributed Cloud.
-
Create an API certificate using the instructions in the Credentials guide.
-
Download the certificate in the PKCS #12 (P12) format.
Step 2: Create a config file and add P12 bundle and server URLs to that file
Create a file named .vesconfig and add the P12 certificate bundle and the tenant server URLs to that file.
Step 3: Set the environment for P12 password.
Enter the following command:
export VES_P12_PASSWORD=<p12 password>
Note: The password for the P12 file is set during the generation of API certificate.
Step 4: Obtain a public-key using vesctl and store the output to a file.
This example stores the output to a file named demo-api-pubkey.
vesctl request secrets get-public-key > demo-api-pubkey
Step 5: Obtain a policy-document using vesctl and store the output to a file.
This example stores the output to a file named demo-api-policy. You can use the in-built policy or the policy created in the previous section. This example uses the in-built ves-io-allow-volterra policy.
vesctl request secrets get-policy-document --namespace shared --name ves-io-allow-volterra > demo-api-policy
Encrypt TLS Key Using Blindfold
Step 1: Encrypt TLS Key using vesctl and Blindfold.
This example stores the output to a file named bl-enckey.
vesctl request secrets encrypt --policy-document demo-api-policy --public-key demo-api-pubkey key.pem > bl-enckey
Note: Provide the public key and policy document obtained in the Prepare Credentials and Policy section. The
key.pemis the TLS key to be encrypted.
Step 2: Save the encrypted TLS Key for future use.
You will need the encrypted key in the Enable TLS on the Virtual Host section when adding your TLS key.
Enable TLS on the Virtual Host
This capability has been deprecated.
Enable TLS on a Load Balancer
Follow these steps to cut and paste a blindfolded (or non-blindfolded) TLS certificate into your load balancer.
Step 1: Log into Console and edit your load balancer configuration.
-
Log into Console.
-
Click
Web App & API Protection.
Figure: Console Homepage
-
Select your namespace from the
Namespacedrop-down menu. -
Select
Manage>Load Balancers>HTTP Load Balancers. -
Select
...>Manage Configurationfor your load balancer, and then selectEdit Configurationin the top right to edit the load balancer's configuration.
Step 2: Configure your load balancer for a custom certificate.
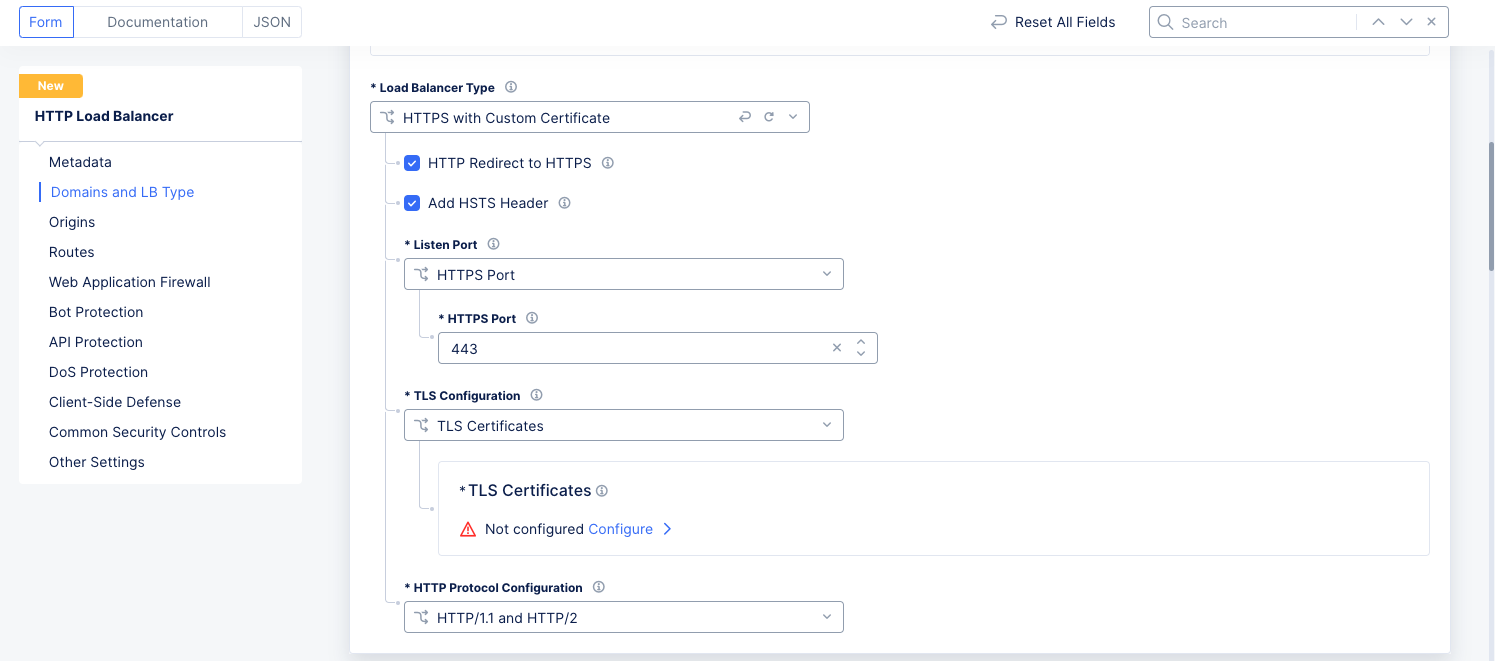
Figure: Custom TLS
-
Select
HTTPS with Custom Certificatefrom theLoad Balancer Typedrop-down menu in theDomains and LB Typesection. -
Optionally select
HTTP Redirect to HTTPSandAdd HSTS Headercheckboxes. -
Use the
HTTP Listen Port Choiceto select between using a single port or a range of ports, and then enter the port number(s). For a range of ports, enter a list of non-overlapping port ranges with a maximum of 64 ports in the list, e.g.443,100-120,8080,9080-9089. -
Select
TLS Certificatesfrom theTLS Configurationdrop-down menu, and then clickConfigure.
Step 3: Insert one or more certificates.
-
From the
TLS Security Leveldrop-down menu, select the desired level. -
From the
Certificatesdrop-down menu, selectAdd Item. This brings up theTLS Certificateform allowing you to add import a certificate. Typically, you would useImport from File, but this example will show how to paste a certificate instead.
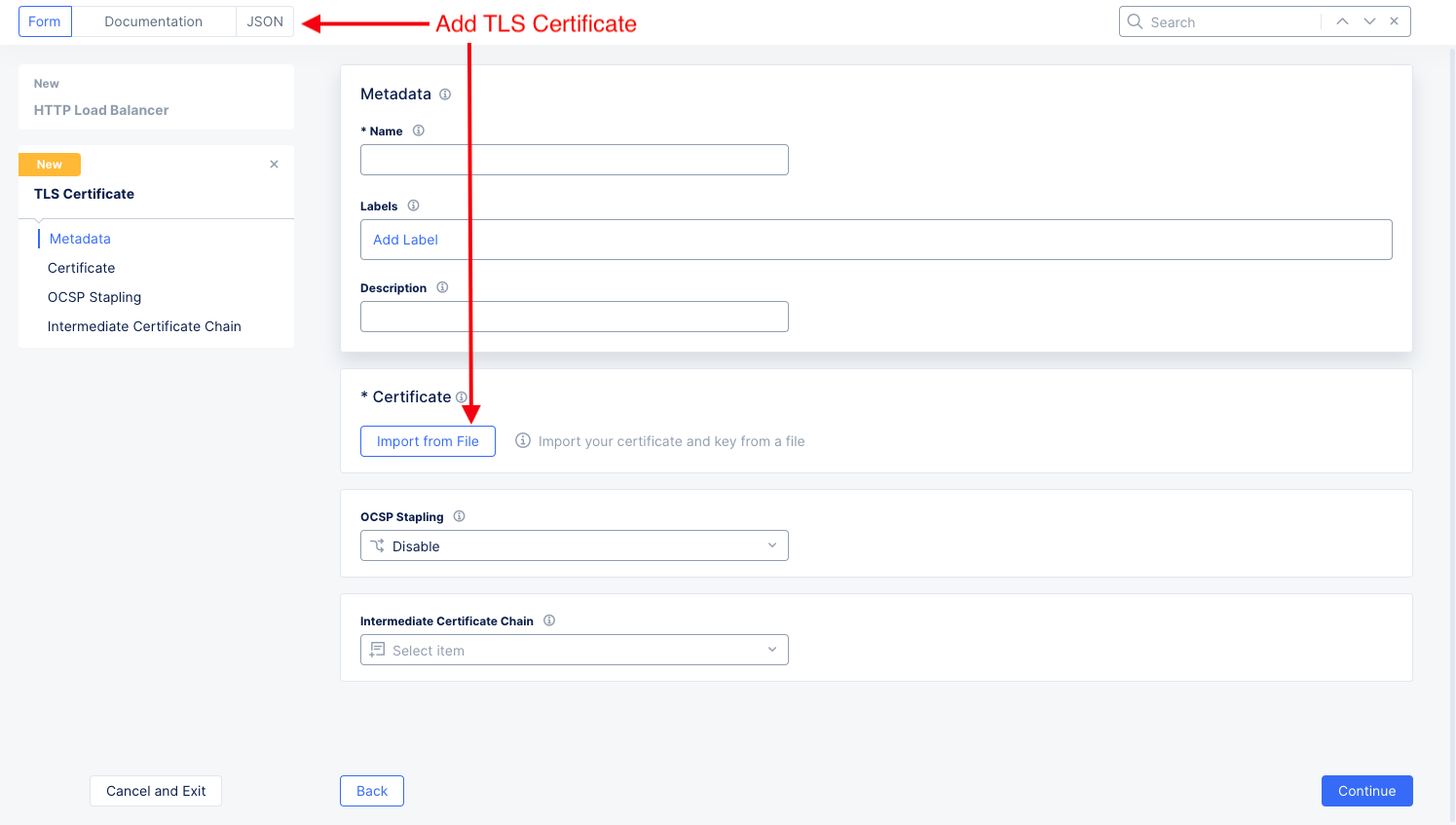
Figure: import TLS Certificate
- Click the
JSONtab above the form. This will show your TLS certificate and associated information in a JSON editor. It will be empty, except for any metadata you may have entered in the form.
Figure: Empty TLS Certificate JSON
- Add your certificate and private key to the JSON using one of the following instruction sets based on the type of certificate/key you want to enter.
Non-Blindfolded certificate and private key Instructions
- If you have a non-blindfolded certificate and private key, paste the following JSON template into the JSON editor.
Note: Using this method, you will paste your private key in the clear, and it will not be blindfolded (encrypted). Base64 encoding is not encryption.
{
"metadata": {
"name": "certificate-name",
"namespace": "my-namespace"
},
"spec": {
"disable_ocsp_stapling": {},
"certificate_url": "string:///<base64 encoded certificate>",
"private_key": {
"clear_secret_info": {
"url": "string:///<base64 encoded private key>"
}
}
}
}
-
Encode your certificate and private key using https://www.base64encode.org/ or equivalent.
-
Paste your encoded certificate text into the
certificate_urlkey following the three slashes. That is to say, replace<base64 encoded certificate>with your encoded certificate text. -
Repeat the process for the private key. You will be replacing
<base64 encoded private key>with your encoded private key text.
Blindfolded certificate and private key Instructions
- If you have a blindfolded certificate and private key, paste the following JSON template into the JSON editor.
{
"metadata": {
"name": "certificate-name",
"namespace": "my-namespace"
},
"spec": {
"disable_ocsp_stapling": {},
"certificate_url": "string:///<blindfolded certificate>",
"private_key": {
"blindfold_secret_info": {
"location": "string:///<blindfolded private key>"
}
}
}
}
-
Paste your blindfolded certificate into the
certificate_urlkey following the three slashes. That is to say, replace<blindfolded certificate>with your blindfolded certificate text. -
Repeat the process for the private key. You will be replacing
<blindfolded private key>with your blindfolded private key text.
-
Once your certificate and key are in the
specsection, ensure that thenameandnamespacevalues are correct in themetadatasection. Thenamespacevalue must match your selected namespace. -
Click the
Formtab to return to theTLS Certificateform.
Figure: TLS Certificate Added
-
Select an
OCSP Staplingoption. Then clickContinueto save the certificate. -
Click
Save and Exitto create your certificate. -
Your new certificate will now be in your certificates list. Make sure it is selected in the
Certificatesdrop-down menu and then clickApplyto save your TLS parameters.
Step 4: Complete the modifications to your HTTP Load Balancer.
-
In the
TLS Parametersform, you can useAdd Itemto add more TLS certificates, if required. -
Click
Applyto save your TLS parameters. -
Click
Save and Exitto complete the modifications to your HTTP load balancer.