Distribute and Secure a Web Application
Objective
This guide provides instructions on how to globally distribute and secure your web application with F5® Distributed Cloud Services (F5XC) utilizing F5XC's Load Balancing, Content Delivery Network (CDN), and Web App and API Protection (WAAP) services.
Important: Multiple certificates in a single CDN distribution are not supported.

Figure: Web Application Security and Performance Steps
The following visual provides an overview of how traffic flows through CDN service to WAAP service on the RE.
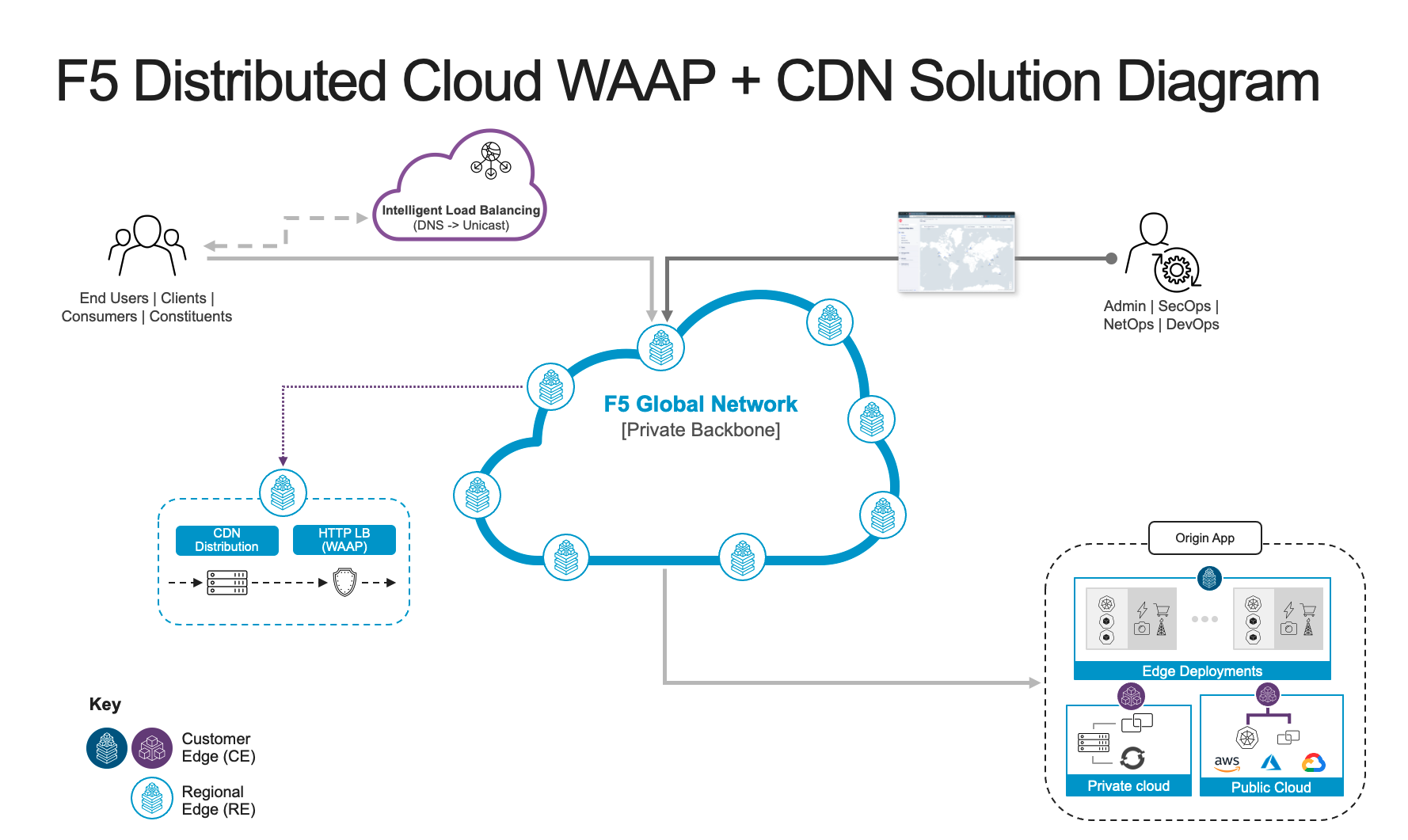
Figure: F5 Distributed Cloud CDN Reference Architecture
Prerequisites
-
F5 Distributed Cloud Console SaaS account. If you do not have an account, see Getting Started with Console.
-
Google Domains account.
Note: This quickstart guide assumes you have a domain in Google Domains, and you will use this to delegate your domain to F5XC. You can perform the same function using a different domain hosting service. However, the specific steps to delegate a domain will vary from vendor to vendor.
Configuration
The use case provided in this guide demonstrates enabling a domain for an application hosted on a public website and secures it using Distributed Cloud's JavaScript challenge, WAF/WAAP, and a CDN. The following actions outline the activities in domain setup and securing the web app:
-
The domain for the application is delegated to F5 Distributed Cloud Services for handling the queries towards the subdomain for the application and management of the SSL certificates for the subdomain.
-
An HTTP load balancer is created for the subdomain with automatic certificate management. As part of this step, an origin pool is created with the origin server as the public website. This use case demonstrates securing the
cloud.f5.comwebsite. -
The load balancer is secured with the JavaScript challenge and WAF for its ingress traffic.
-
A CDN Distribution is created to improve the performance of the website. The CDN will be service chained to the HTTP load balancer.
Step 1: Create Primary Zone
Note: Previous versions of this quick start instructed you to delegate your domain to the F5 Distributed Cloud Platform. The Delegate Domain capability has since been deprecated. Now you will configure your domain to use F5 Distributed Cloud DNS instead.
Log into Console and perform the following:
Step 1.1: Navigate to zone management and start adding a zone.
- Click
DNS Managementservice on the Console home page.
Figure: Navigate to DNS Management
-
Select
DNS Managementoption in the primary navigation menu located on the left side of the page. -
Click
Add Zone.
Figure: Add Zone
-
Enter domain or subdomain name in the
Domain Namefield in the metadata section. -
Optionally, set labels and add a description for your zone.
Step 1.2: Start configuring primary zone.
Select Primary DNS Configuration for the Zone Type field in the DNS Zone Configuration section. Click Edit Configuration under the Primary DNS Configuration field. Do the following in the zone configuration form:
- In the
SOA Record Parameterssection, theUse Default Parametersis populated by default. To customize this, selectSOA Record Parametersoption, clickView Configuration, and set the SOA parameters such as refresh interval, retry interval, TTL, etc.
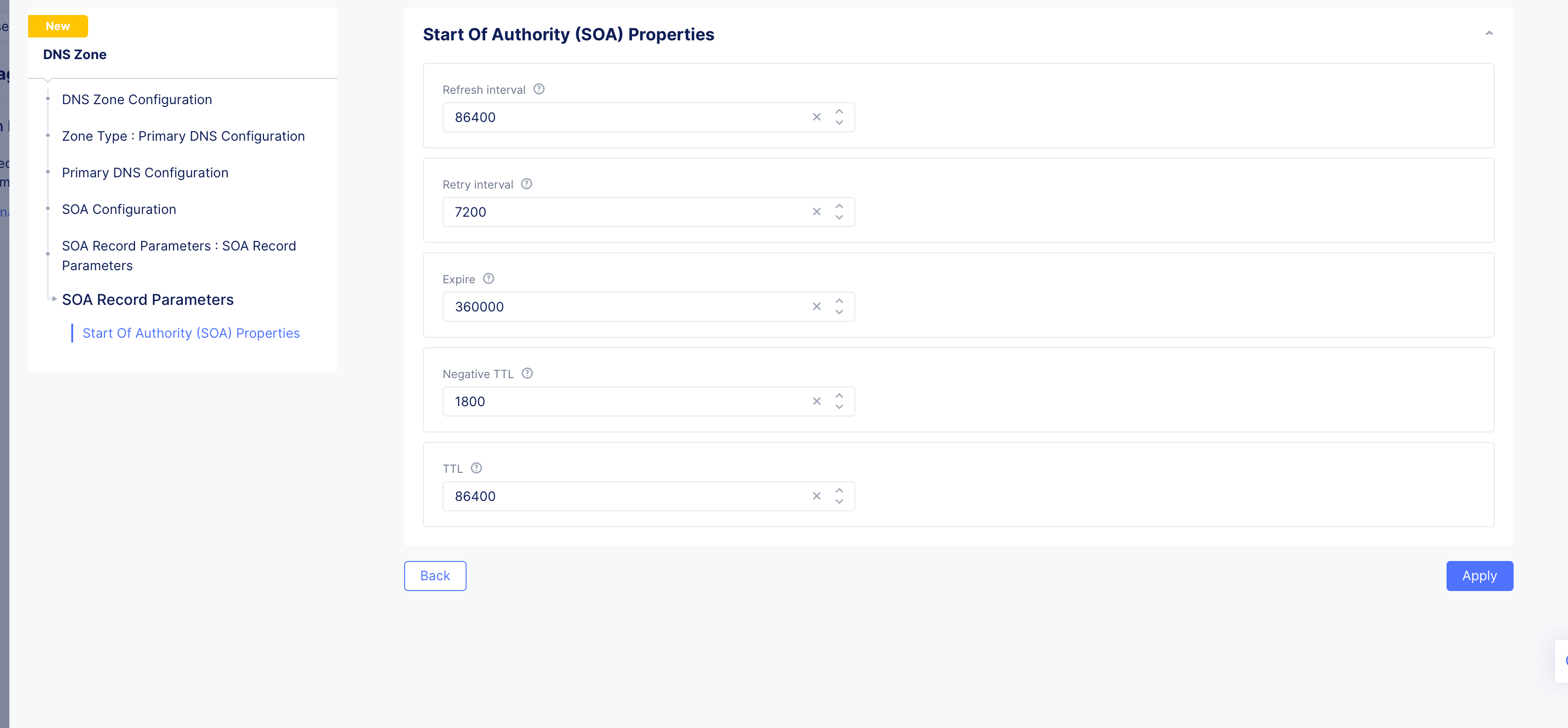
Figure: SOA Custom Configuration
Step 1.3: Configure resource record sets for the default group.
-
Go to
Resource Record Setssection and clickAdd Item. The resource record sets configuration form opens. -
Enter a value for the
Time to livefield. -
Select a record type for the
Record Setfield, enter a name for your record name in theRecord Namefield, and set the fields as per your record type selection. Refer to the following table for the record type and field mapping:
| Record Type | Fields | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| A | List of IPv4 Addresses | Enter IPv4 addresses. |
| AAAA | List of IPv6 Addresses | Enter IPv6 addresses. |
| ALIAS | Domain | Enter alias domain name. |
| CAA | Tags and Value | Enter a tag and its value. |
| CNAME | Domain | Enter domain name. |
| MX | Domain and Priority | Enter domain and priority in the MX Record Value section. |
| NS | List of Name servers | Enter the FQDN for the name servers. |
| PTR | List of Name servers | Enter the FQDN for the name servers. |
| SRV | Priority, Weight, Port, Target | Click Add Item in the SRV Value section and set the parameters. |
| TXT | List of Text | Add the TXT record. |
| DNS Load Balancer | DNS Load Balancer Records | Add the DNS Load Balancer record. |
| NAPTR | Naming Authority Pointer | Enter regex based domain names used in URIs. |
| DS | Delegation signer | Enter the signer to identify DNSSEC signing key of a delegated zone. |
| CDS | Child DS | Enter Child copy of DS record, for transfer to parent. |
| EUI48 | MAC address (EUI-48) | Add uniquely identified MAC address as per the EUI-48 specification. |
| EUI64 | MAC address (EUI-64) | Add uniquely identified MAC address as per the EUI-48 specification. |
| AFS | AFS record | Enter the AFS record. |
| DNSKEY | DNS Key | Enter the type, protocol, algorithm, and public key. |
| CDNSKEY | Child DNS Key | Enter the type, protocol, algorithm, and public key. |
| LOC | Location information | Enter geographical details such as latitude, longitude, hemispheres, etc. |
| SSHFP | SSH Key Fingerprint | Enter the fingerprint algorithm, type, and hexadecimal hash result of the ssh key. |
| TLSA | TLS Certificate Association | Enter the usage, selector, matching type, and association data. |
| CERT | Public Key Certificate | Enter the type, key tag, algorithm, and certificate. |
Note: Use the
Add itembutton available in each record type configuration to add more than one record for that record. See DNS Load Balancer for instructions on how to configure DNS load balancer for your zone.
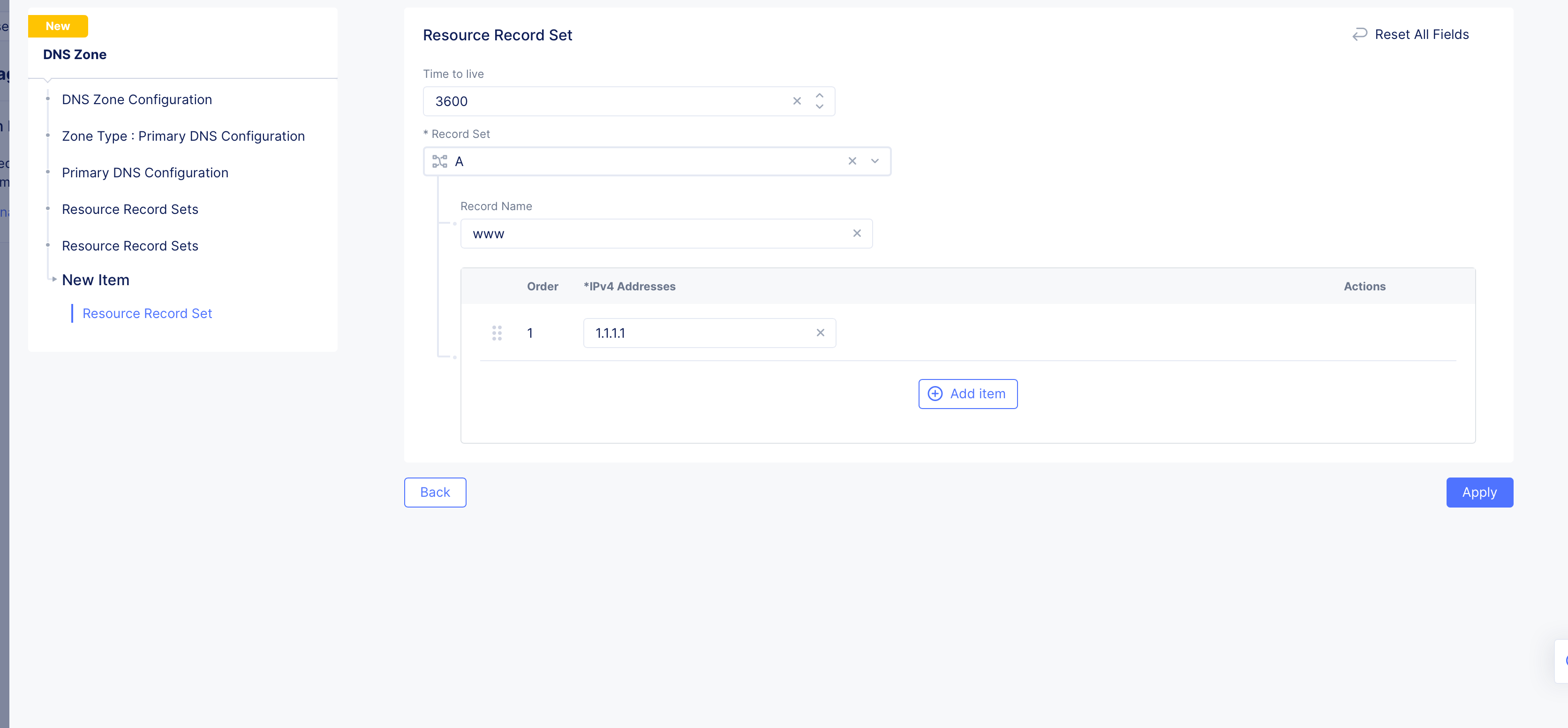
Figure: Resource Record Set
- Click
Add Itemto add the resource record set to the list of resource record sets. Use theAdd Itembutton to add more than one resource record step.
Step 1.4: Configure specific resource record sets group.
This step configures specific groups for resource record sets. A resource record sets group allows grouping of DNS records to make it easier to manage them. For example, you can group DNS records that belong to the same application.
-
Enable
Show Advanced Fieldsin theResource Record Setssection. -
Click
Add Itemin the appearedAdditional Resource Record Setssection. This opens new resource record sets form. -
Enter a
Namein the metadata section. -
Click
Add Itemin theResource Record Setssection. This opens the resource record sets configuration form. -
Configure the records in the same way as mentioned in previous step.
-
Click
Add Itemto add the resource record set to the group. Use theAdd Itembutton to add more than one resource record set. -
Click
Add Itemin theResource Record Setsform to add the group to theAdditional Resource Record Setssection. Use theAdd Itembutton to add more than one group.
Step 1.5: Optionally, enable DNSSEC and load balancer management.
- In the
DNSSEC Modesection, selectEnablefor theDNSSEC Modefield if you want to use DNS security extensions (DNSSEC) to authenticate DNS response data.
Note:
DNSSEC Modeis disabled by default.
- Check the
Allow HTTP Load Balancer Managed Records. This is only optional for a legacy delegated domain.
Note:
Allow HTTP Load Balancer Managed Recordsis unchecked by default, which might have made sense for a delegated domain. However, Distributed Cloud Services has deprecated the Delegated Domain capability, which means that new domains will need to be setup as a Primary DNS zone corresponding to your HTTP Load Balancer (which is what you created in these steps), and you must check theAllow HTTP Load Balancer Managed Recordscheckbox for the HTTP Load Balancer to work properly.
Step 1.6: Complete creating the primary zone.
- Click
Applyin the primary zone configuration form.
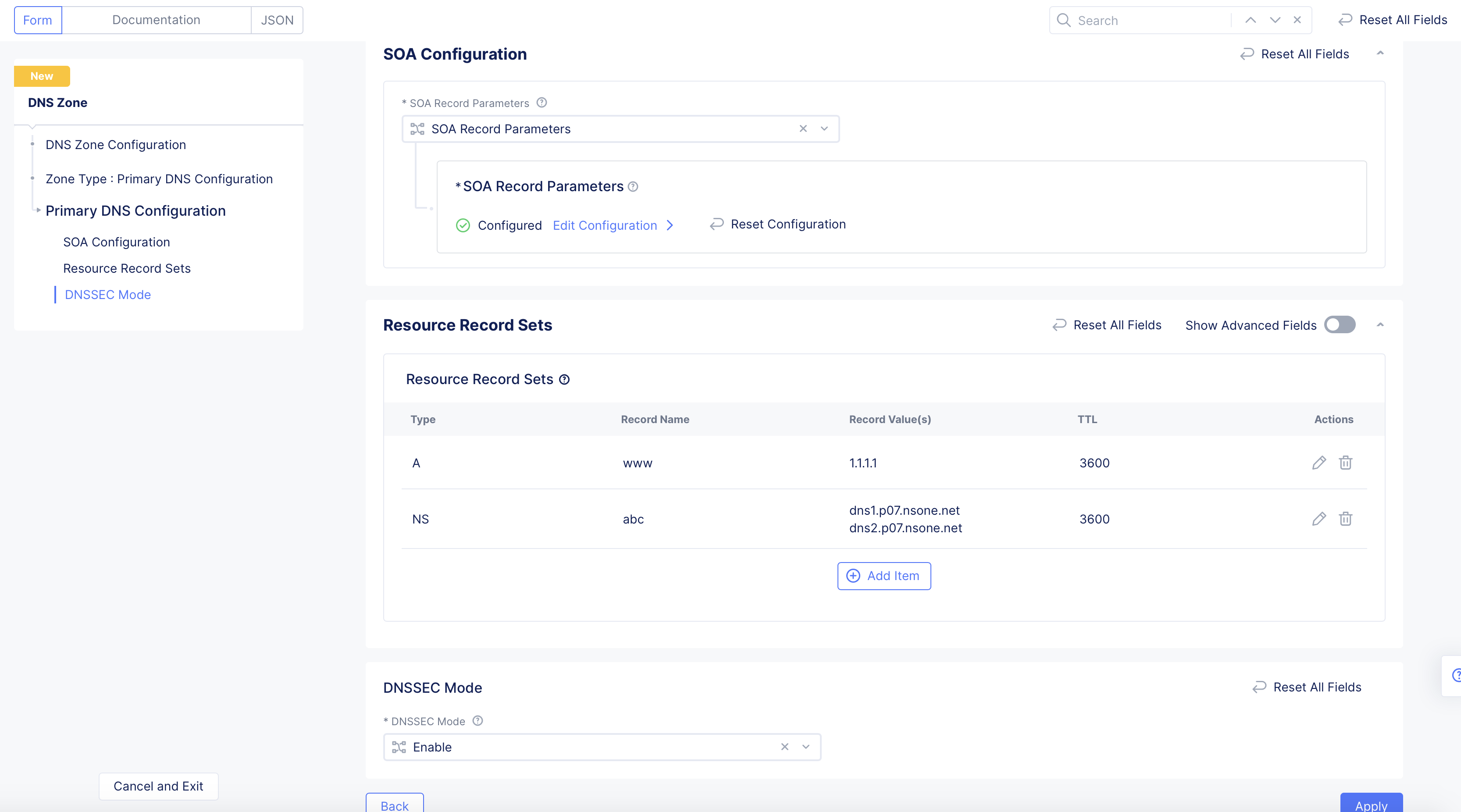
Figure: Primary Zone Configuration
- Click
Save and Exitin the main zone configuration form to complete creating the primary zone.
Note: In case you enabled the DNSSEC, the system generates a DS record and displays it in the
DNSSEC DS Recordcolumn. Click on the displayed value, clickCopy DS Recordon the displayed window, add the DS record to your parent zone. After primary zone is created, you can use thedig ds <domain name>command to verify that the DS record digest is displayed in the output. This indicates that DNSSEC is functional.
Step 2: Create HTTP Load Balancer with WAF
Perform the following steps for creating load balancers and WAF to enhance the application performance and security:
Step 2.1: Start creating an HTTP Load Balancer.
- Select the
Web App & API Protectionservice. - Verify that the namespace you created in step 1.4 is selected.
- Navigate to
Manage>Load Balancers>HTTP Load Balancersand then selectAdd HTTP Load Balancer. - Enter a name for your load balancer in the
Metadatasection. - Enter your domain name, corresponding to the delegated sub-domain (step 1.1), in the
Domainslist within theDomains and LB Typesection. - Select
HTTPS with Automatic Certificatein theLoad Balancer Typefield. - Check the
HTTP Redirect to HTTPScheckbox. - Ensure the
HTTPS Portis set to 443 and theTLS Security Levelis set toHigh.
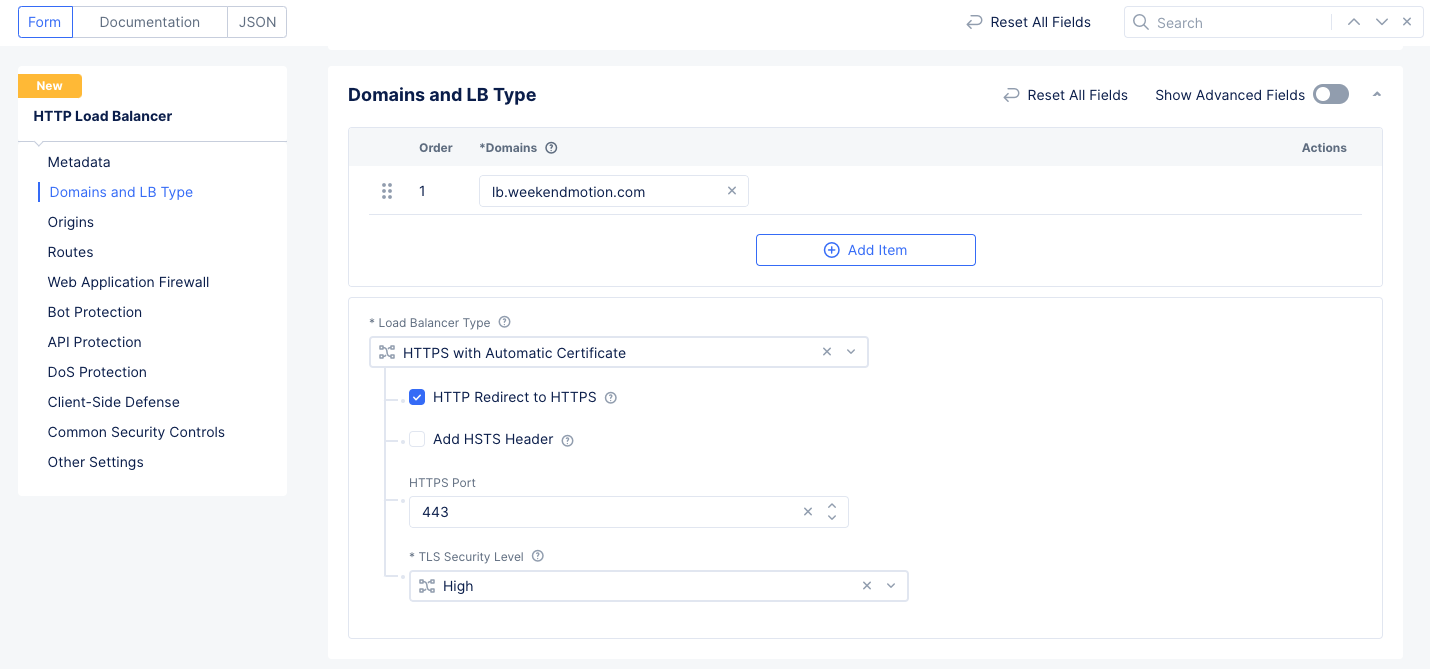
Figure: Load Balancer Setup
Step 2.2: Create origin pool.
-
In the
Originssection, selectAdd Itemto add a new entry in the list of origin pools. This will bring up theOrigin Pool with Weight and Prioritysetup form. -
If you already have an origin pool setup, you could select it from the
Origin Pooldrop-down menu; however, for this example, use the drop-down menu to selectAdd Itemto create a new origin pool. -
Enter a name for your origin pool in the metadata section.
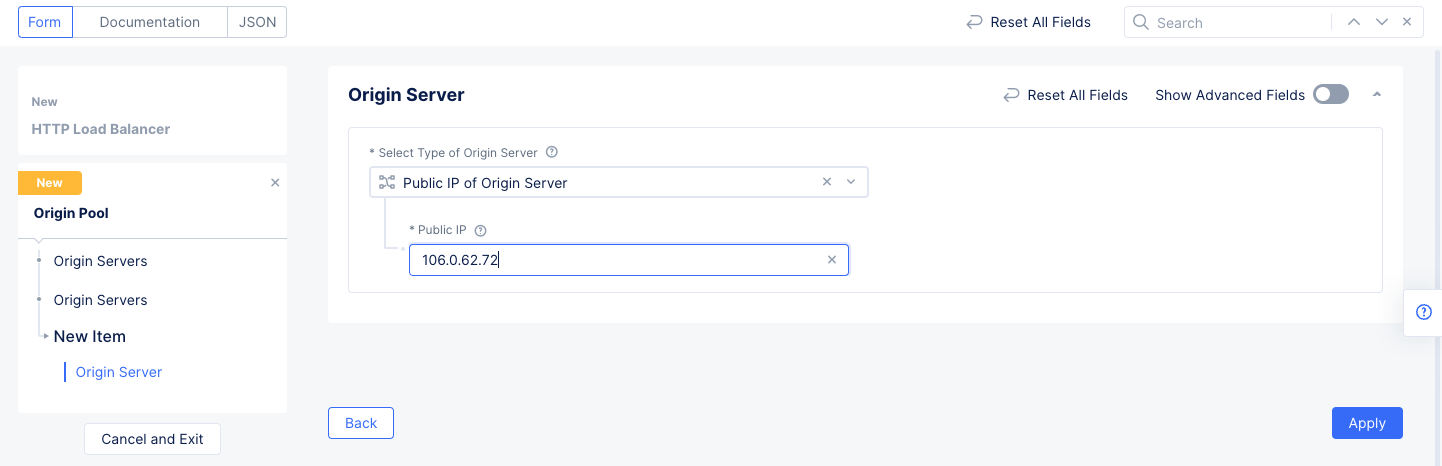
-
The
Origin Serverssection contains the list of servers that make up this pool. SelectAdd Itemto add a new server.- Select the type of origin server in the
Select Type of Origin Serverfield and then enter the appropriate server identification. For this example, selectPublic IP of Origin Serverand enter13.56.168.147in thePublic IPfield. - Select
Applyto save the origin server information and return to theOrigin Pool with Weight and Prioritysetup form.
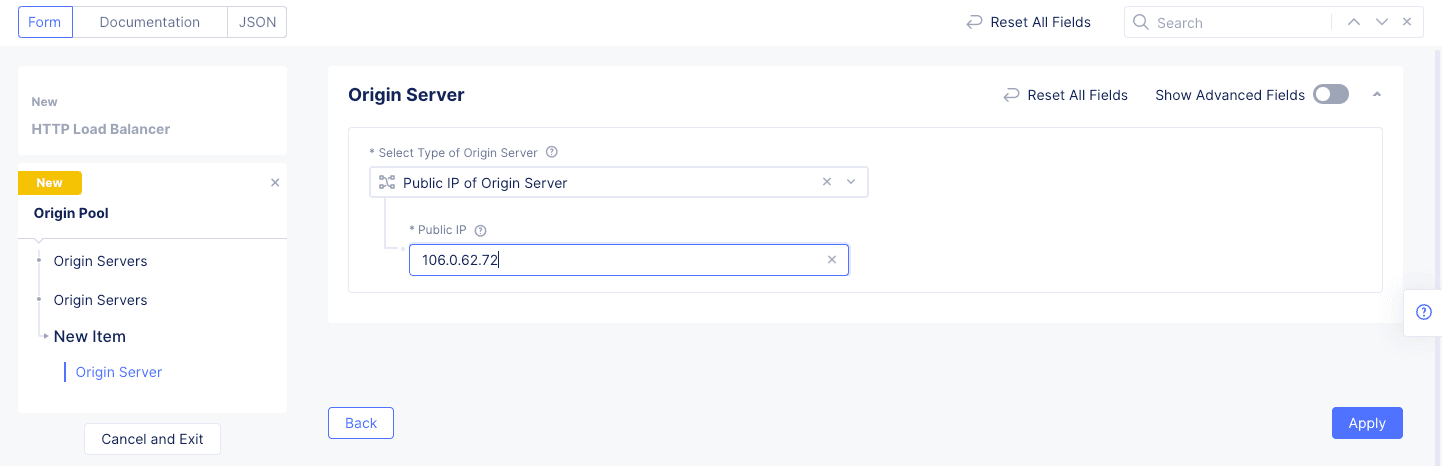
Figure: Origin Server Basic Configuration
- Select the type of origin server in the
-
In the
Origin servers Portsection, enter80for thePortfield. -
Optionally scroll down to the TLS port to set up TLS security.
-
Select
Continueat the bottom of the form to save the origin pool.
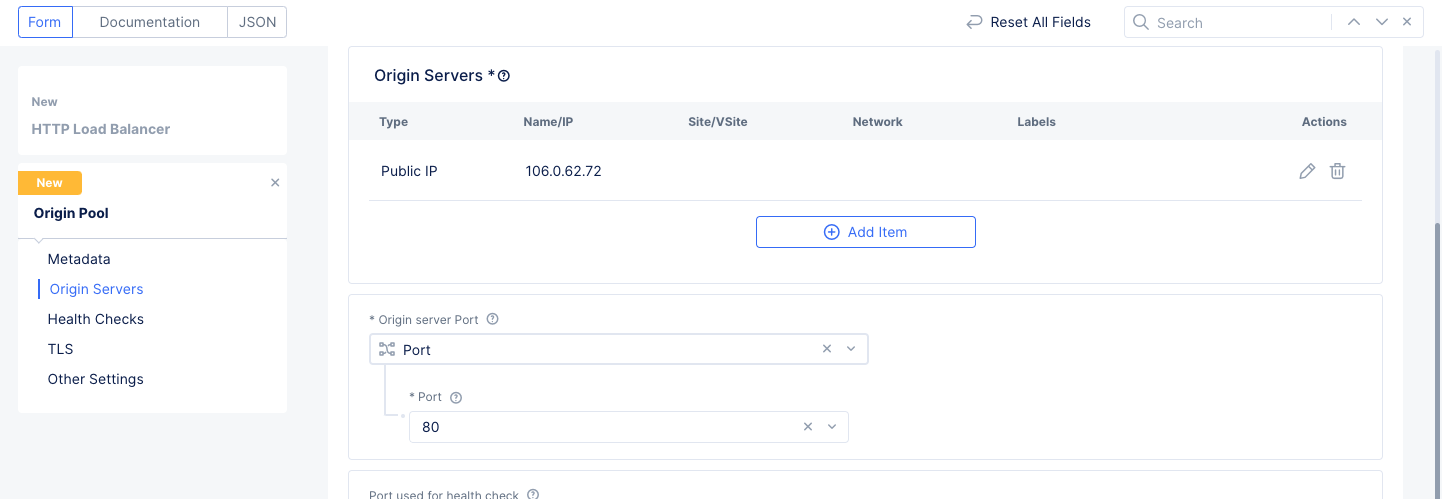
Figure: Origin Server List
- Complete the origin pool by entering
WeightandPriorityvalues. These will only be used if you have multiple origin pools in your load balancer.
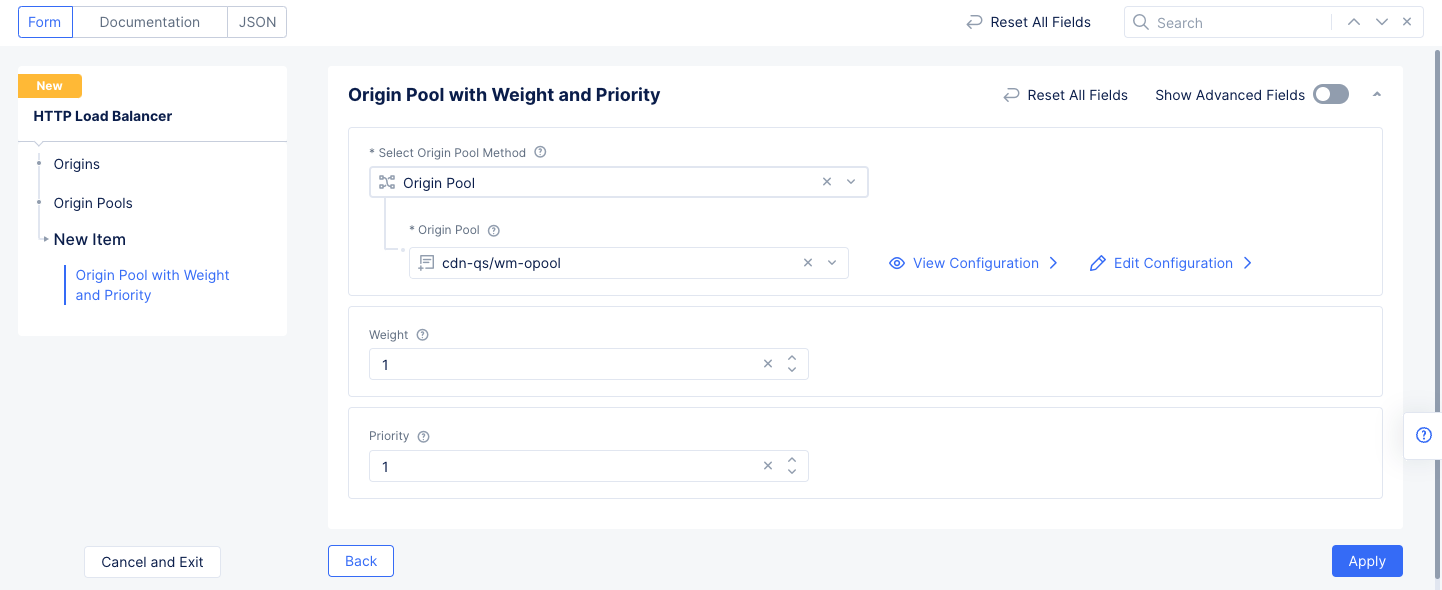
Figure: Origin Pool
- Select
Applyto save the origin pool to your load balancer.
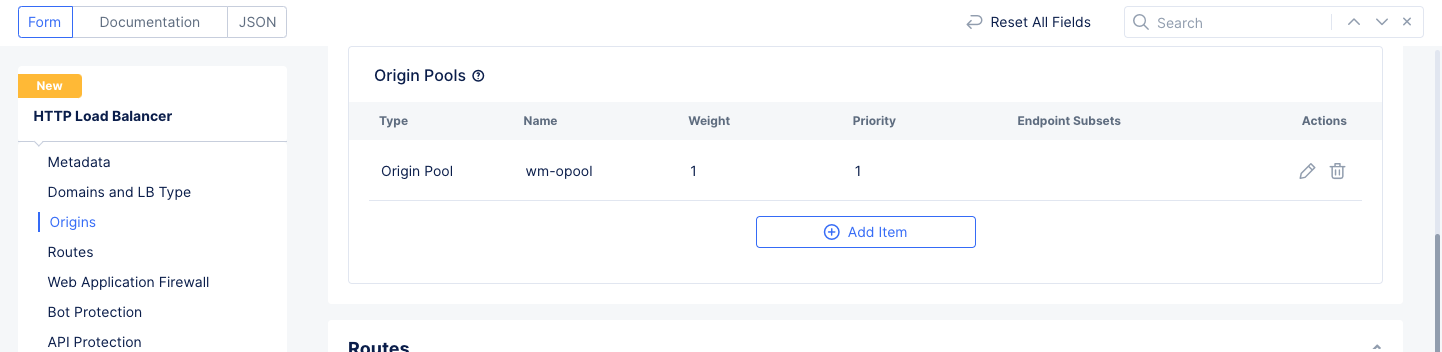
Figure: Load Balancer Origins
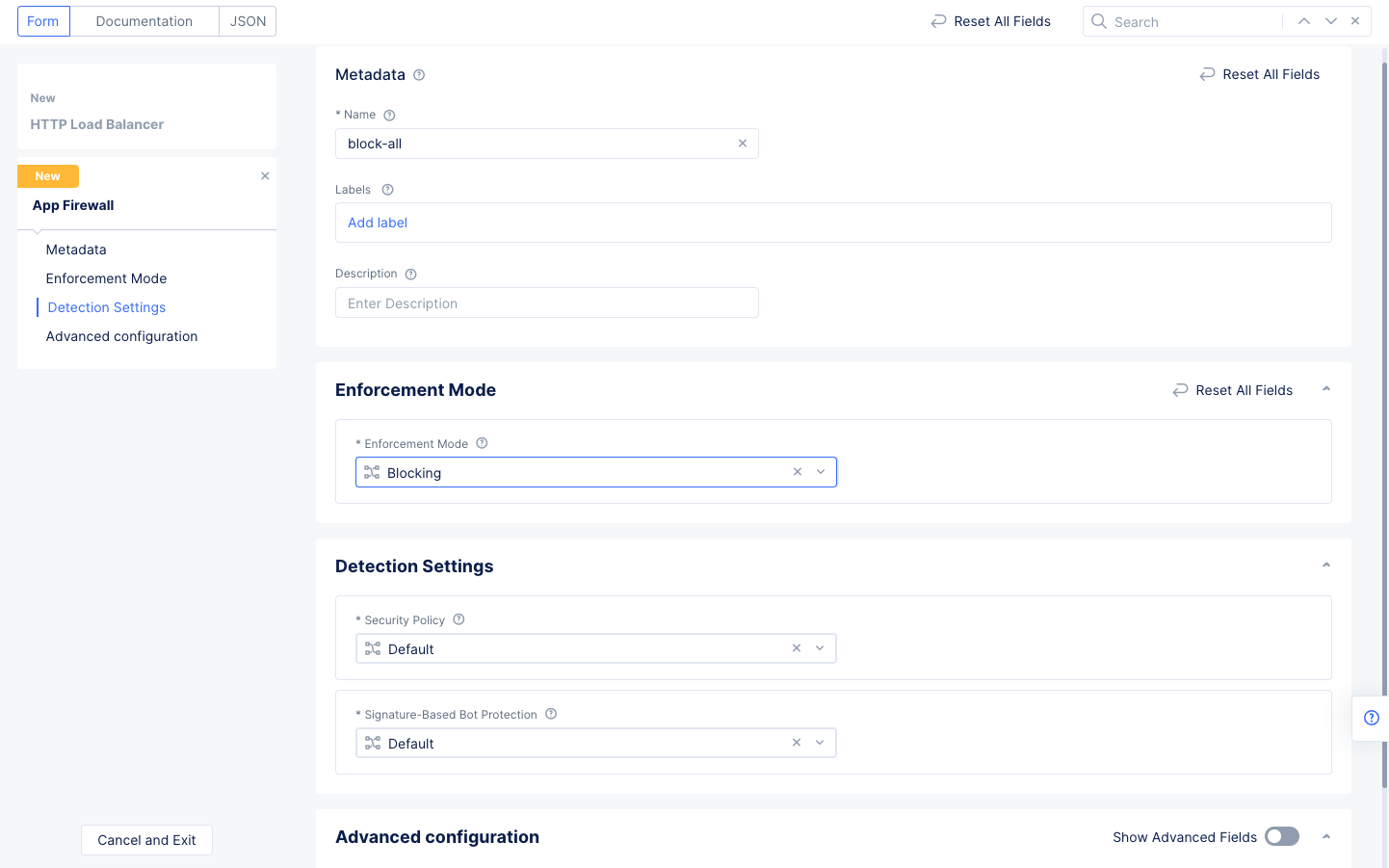
Step 2.3: Setup WAF.
-
Select
Enablein theWeb Application Firewall (WAF)field. -
Use the
Enabledrop-down menu to selectAdd Itemto configure a new firewall. This example will block all threats using default values.- Enter a name for your firewall configuration.
- Select
Blockingin theEnforcement Modefield. - Select
Defaultfor all fields in theDetection Settingssection.
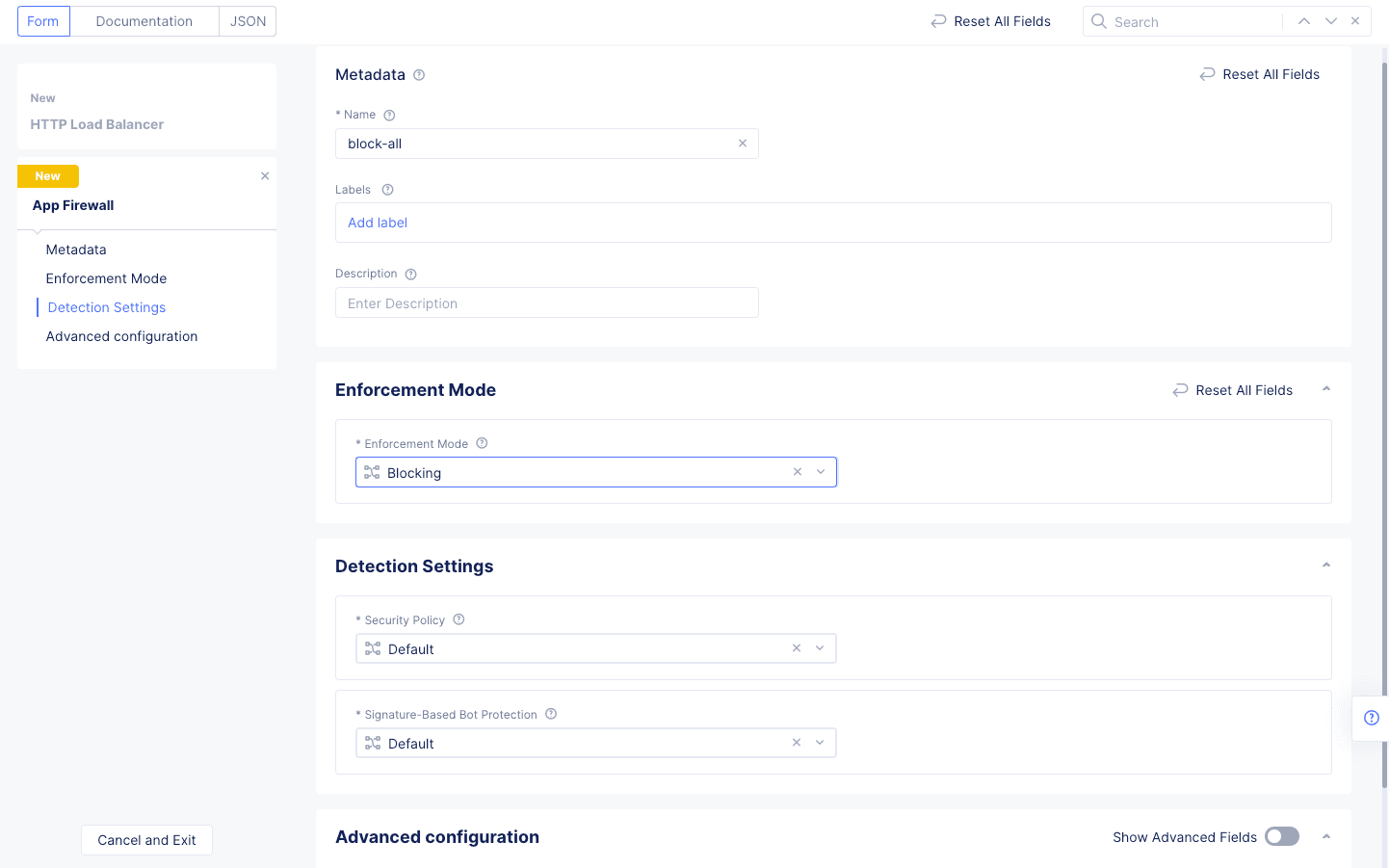
Figure: Default Blocking WAF
- Select
Continueat the bottom of the form to complete your WAF.
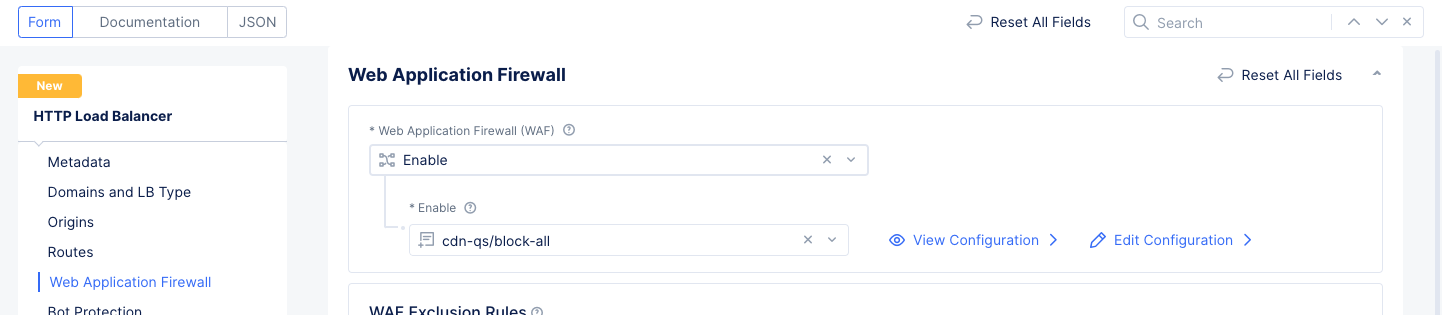
Figure: Load Balancer WAF
Step 2.4: Complete the load balancer setup.
- Scroll down to the
Common Security Controlssection and selectDo Not Apply Service Policiesin theService Policiesfield. - In the
Other Settingssection, selectInternetin theVIP Advertisementfield. - Verify that
Round Robinis selected for theLoad Balancing Algorithmfield. - Select
Save and Exitat the bottom of the form to save the load balancer configuration.
Step 3: Create CDN Distribution
Perform the following to create your CDN distribution:
Step 3.1: Create a new CDN distribution.
-
Select the
Content Delivery Networkservice. The CDN distribution configuration page opens. -
Go to
Manage>Distributions. -
Verify that the namespace you created in step 1.4 is selected.
Figure: CDN Distributions Page
- Select
Add Distribution.
Step 3.2: Configure metadata, domains, and distribution type.
-
In the
Namefield, enter a name for the distribution. -
Optionally, select a label and enter a description.
-
Go to
Basic Configurationand enter a domain name in theDomainsfield. This should match the delegated domain name you entered in step 1. -
Select
Add itemto add more domains, if needed. -
Select an option for the
Select Type of CDN Distribution. The following options are supported:- Select
HTTPto create the CDN Distribution. Select theAutomatically Manage DNS Recordscheckbox if your domain is delegated to F5 Distributed Cloud. Otherwise, ensure in your DNS provider configuration that your domain is resolved. - Select
HTTPS with Automatic Certificateto create the CDN Distribution with an automatic TLS certificate. Ensure that the domain is delegated to F5 Distributed Cloud. Optionally, selectHTTP Redirect to HTTPSand/orAdd HSTS Headercheckboxes to enable those functions. You can also select TLS security level to be high or medium. - Select
HTTPS with Custom Certificateto create the CDN Distribution with your custom TLS certificate.
- Select
-
If you are using the
HTTPS with Custom Certificateoption:- Set the TLS configuration using the
Configureoption under theTLS Parametersfield. - From the
TLS Security Leveldrop-down menu, select the desired level. - In the
TLS Certificatessection, SelectAdd Item. - For the certificate URL encoding, select
PEMorbase64(binary), and then enter the certificate URL. - To configure the private key, Select
Configure. - Under the
Secretsection, enter your private key inTexttype, SelectBlindfold, wait for the Blindfold operation to complete, and then SelectApply. - Select
Add Item. - In the
TLS Parameterssection, SelectApply.
- Set the TLS configuration using the
Note: You can add more than one certificate using the
Add Itemoption.
This example configures a CDN Distribution of type HTTPS with Automatic Certificates.
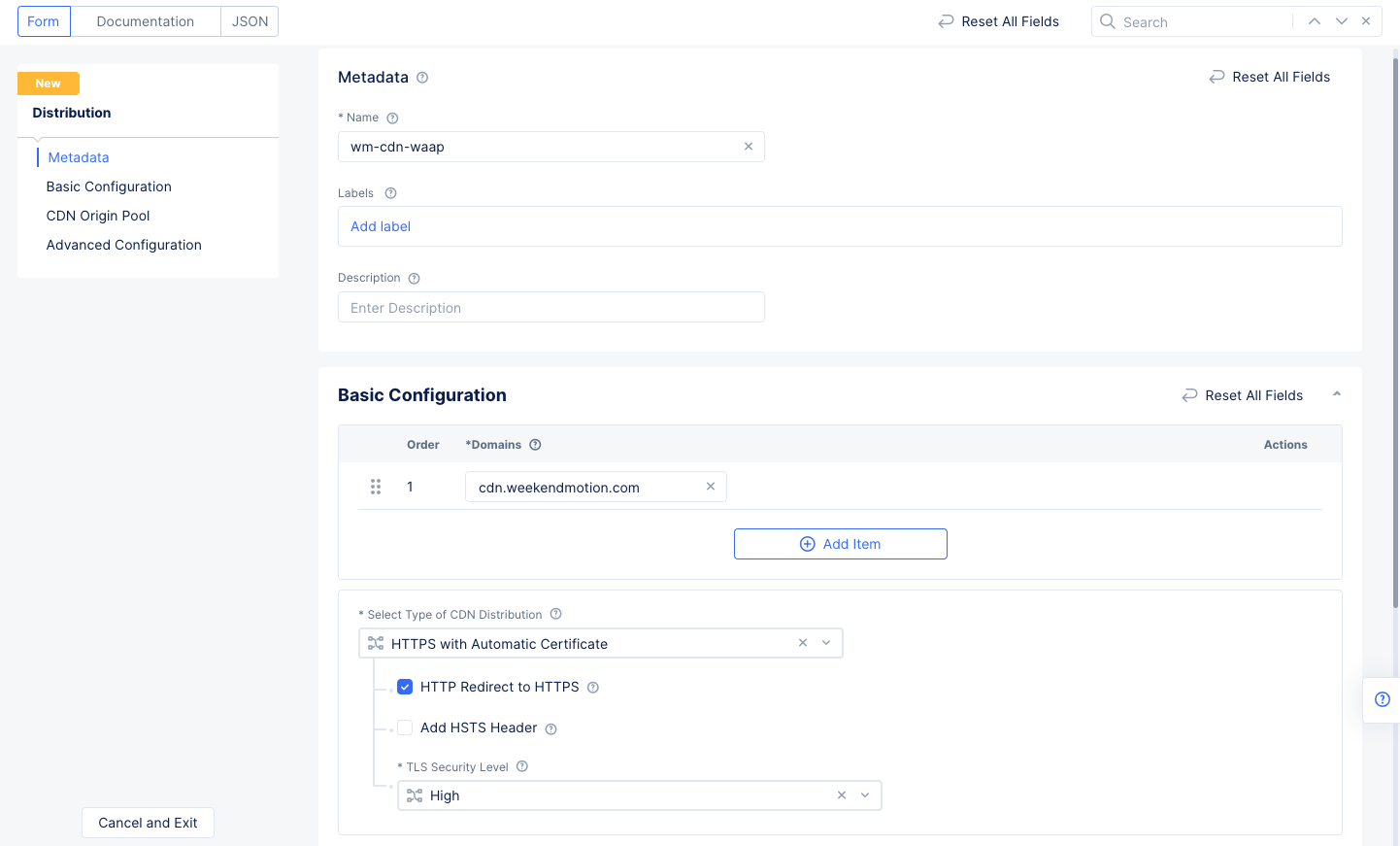
Figure: Distribution of Type HTTPS with Automatic Certficate
Step 3.3: Configure CDN origin pool.
- Select
Configurein theCDN Origin Poolsection. The CDN origin pool configuration page opens. - Enter the CDN origin domain name in the
DNS Namefield. The domain name must be the same domain name you entered for the delegated domain in step 1.1 and the HTTP load balancer in step 2.1. The requests to origin servers use this name in the host header. - Select a TLS choice in the
Enable TLS for Origin Serversfield. Ensure that this matches your origin server configuration. - Select
Add Itemin theList of Origin Serverssection. In the origin servers page, enter public DNS name or public IP of your origin server. SelectApply. - Enter a time value in the
Origin Request Timeout Durationfield. The default is 60s (sixty seconds). - Select
Applyin the CDN origin pool configuration page.
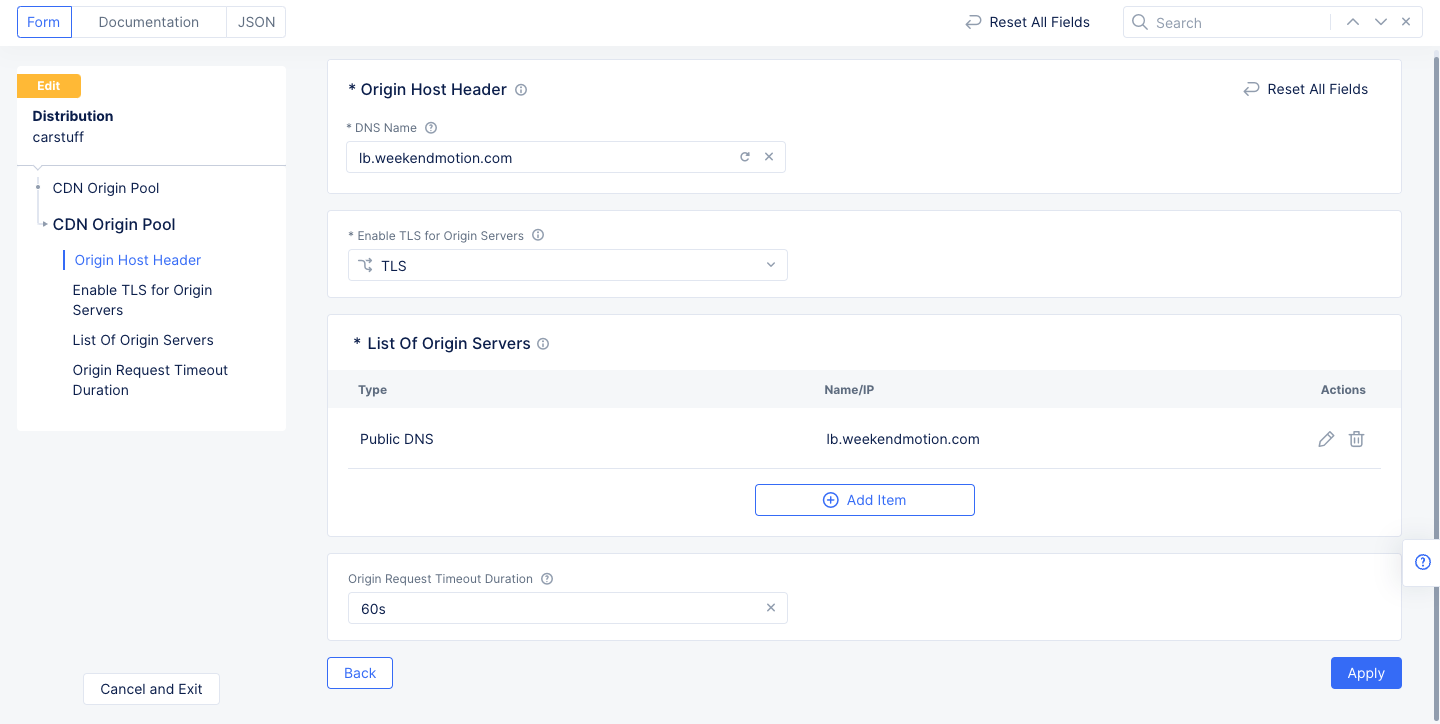
Figure: Origin Pool Configuration
Step 3.4: Optionally, configure advanced options to control your content delivery operation.
Advanced configuration consists of options such as header control, security, cache control, etc. Go to Advanced Configuration section and perform the following:
-
Select
Show Advanced Fieldstoggle to display the advanced configuration options. -
Select
Add Locationcheckbox to append the location header in the response. Value for this header is the Regional Edge Site name that serves your request.
Step 3.4.1: Configure header control.
Select Configure in the Header Control field and do the following:
Add Request Headers
-
Select
ConfigureinAdd Origin Request Headers. SelectAdd Itemin the next screen, and enter a name for the header to be added. -
Select
ValueorSecretfor the header value.- If it is value, enter a string value for the header and then select
Applyto save the header. - For a secret value, select
Configurein theSecret Valuefield, enter the secret using theTexttype, select the appropriateActionandPolicy Typesettings and then enter your secret in theSecret to Blindfoldfield. Select Apply to save the header.
- If it is value, enter a string value for the header and then select
-
Use the
Add Itembutton to add additional headers. -
Select
Applyto save the list of request headers.
Note: CDN sends the following headers with client IP values to upstream by default:
- X-F5-True-Client-IP
- X-Forwarded-For
Remove Request Headers
-
Select
ConfigureinRemove Origin Request Headers. -
Select
Add Itemand enter a name for the header to be removed. -
Select
Apply.
Note: Use the
Add Itemoption to specify more headers to be removed.
Add Response Headers
-
Select
ConfigureinAdd Response Headers. SelectAdd Itemin the next screen, and enter a name for the header to be added. -
Select
ValueorSecretfor the header value. If it is value, enter a string value for the header. In case of secret, selectConfigurein theSecret Valuefield, enter the secret using theTexttype, selectBlindfold, wait for the encryption to complete, and selectApply. -
Select
Applyin theHeaders to Addpage. -
Select
Applyin theAdd Response Headerspage.
Note: Use the
Add Itemoption to add more headers.
Remove Response Headers
-
Select
ConfigureinRemove Origin Request Headers. -
Select
Add Itemand enter a name for the header to be removed. -
Select
Apply.
Note: Use the
Add Itemoption to specify more headers to be removed.
Select Apply to apply header control settings.
Step 3.4.2: Configure security settings.
Select Configure in the Security Options field and do the following:
Client IP Filtering Options
-
Select
ConfigureinClient IP filtering Options. -
Select whether the IP filtering type is allowlist or denylist.
-
Enter IP prefix in the IP prefix list section.
-
Select
Add Itemto add more IP prefixes. -
Select
Apply.
Client Geo filtering Options
-
Select
ConfigureinClient Geo filtering Options. -
Select whether the Geo filtering type is allowlist or denylist.
-
Select countries from list in the
Country Codes Listfield. You can select more than one country. -
Select
Apply.
Authentication Options
-
Select
ConfigureinAuthentication Options. -
Select
JWT Token Authenticationfor authentication type. -
Enter the secret in the
Textbox of theSecretfield. SelectBlindfoldand wait for the operation to complete. -
Specify a source for the token. You can select header value or cookie name or query parameter name or set it as bearer-token.
-
Select
Apply.
Select Apply to apply security settings.
Step 3.4.3: Configure logging options.
Select Configure in the Logging Options field and do the following:
Client Request Headers to Log
-
Select
ConfigureinClient Request Headers to Log. -
Select
Add Itemand add headers for logging. -
Select
Apply.
Origin Response Headers to Log
-
Select
ConfigureinOrigin Response Headers to Log. -
Select
Add Itemand add headers for logging. -
Select
Apply.
Select Apply to apply logging option settings.
Step 3.4.4: Configure cache TTL.
-
Select
Configurein theCache TTLfield. -
Select an option for the
Cache TTL Settingsfield as per the following guidelines:- Select
Default Cache TTLif the origin server does not provide a TTL value. Set the value in theDefault Cache TTLfield. - Select
Override Cache TTLif the origin server provides a TTL in the response and you want to override it. Set the value in theOverride Cache TTLfield.
- Select
-
Select
Apply.
Step 3.5: Complete creating the distribution.
Select Save and Exit.
Step 3.6: Verify the distribution status.
It might take a few minutes for your CDN Distribution to be deployed and to be ready to cache and serve content at Regional Edges. During this time, the Status column will show Pending. Once deployment is complete, the status for your CDN distribution will show Active.
Note: To get a more detailed view of your site status, select
>against your distribution object and expand its JSON view. Verify that the service domain is created. Select...>Show Global Statusagainst your CDN object and ensure that theSite Statussection shows status asDEPLOYMENT_STATUS_DEPLOYED.
Delegated Domain with Automatic Certificates:
- Wait for the
DNS InfoandTLS Infocolumns to display theVIRTUAL_HOST_READYandCertificate Validvalues. This indicates that the virtual host and certificate is created successfully.
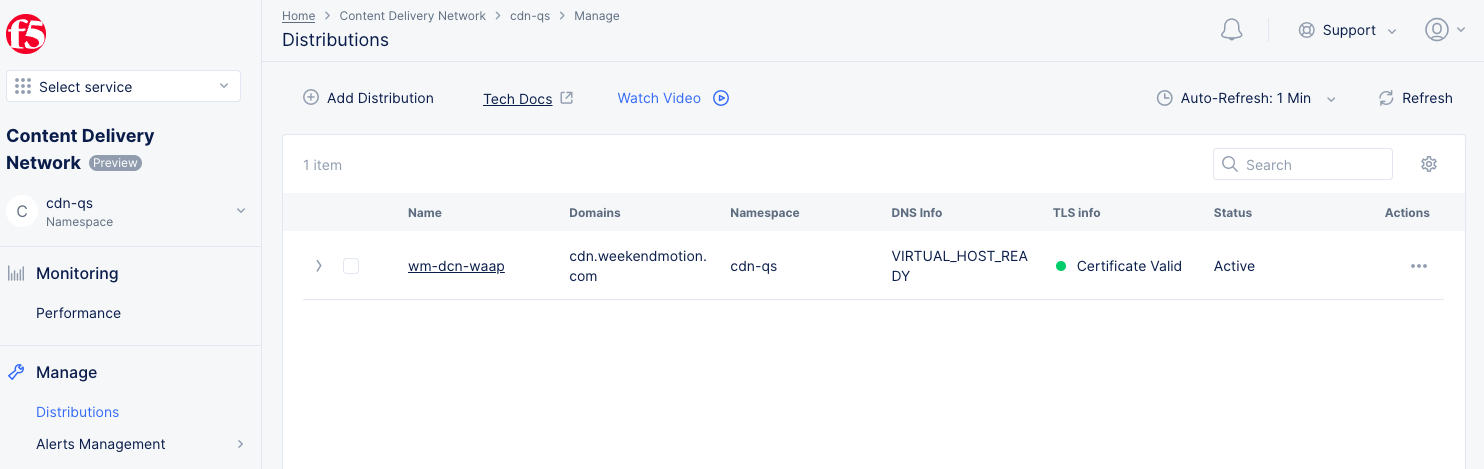
Figure: Distribution Created
-
In the
Statuscolumn, it showsActive, which indicates CDN distribution is up and running. -
Select ‘...’ in the
Actionscolumn for your distribution, and then selectShow Global Status.
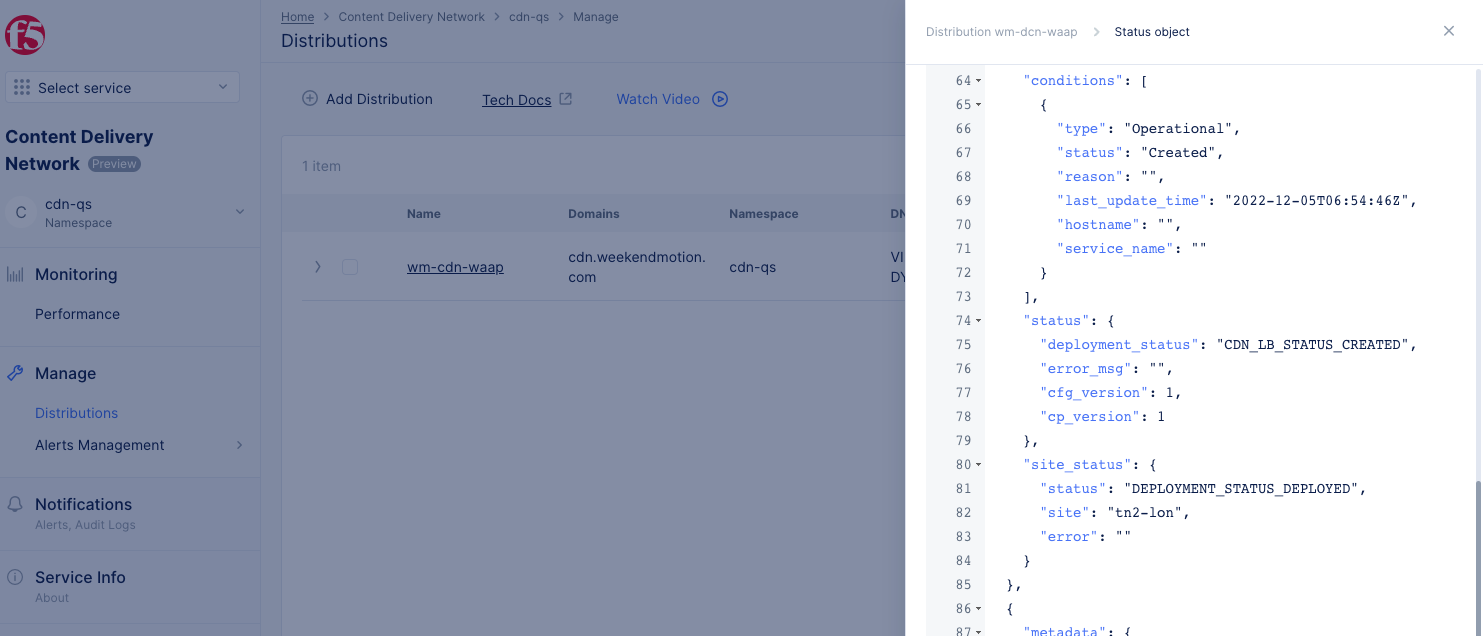
Figure: Distribution Global Status
-
Global status indicates two things: 1) whether the distribution has been pushed to the CDN back end, and 2) whether the distribution has been configured on the Edge sites.
-
CDN distribution is configured successfully, when at least one edge site is configured with
- Global status is updated to
OperationalandCreated. - Site Status is updated to
DEPLOYMENT_STATUS_DEPLOYED. - Site name is listed.
- There will be one global, and at minimum, one status object for each site.
- Global status is updated to
-
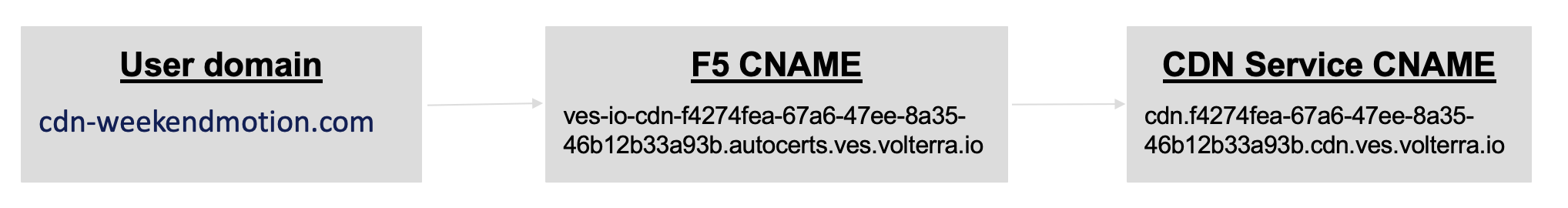
In this delegated domain scenario, verify that the CDN domain is mapped to the F5 CNAME, and the F5 CNAME is mapped to the CDN Internal service domain, automatically.
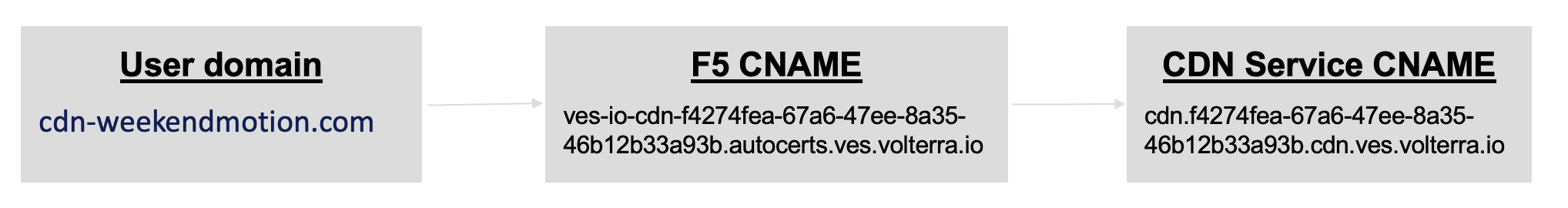
Figure: Distribution CNAME Mapping
-
The user domain and F5 CNAME can be found in the JSON for your tenant.

Figure: Distribution CNAME JSON
-
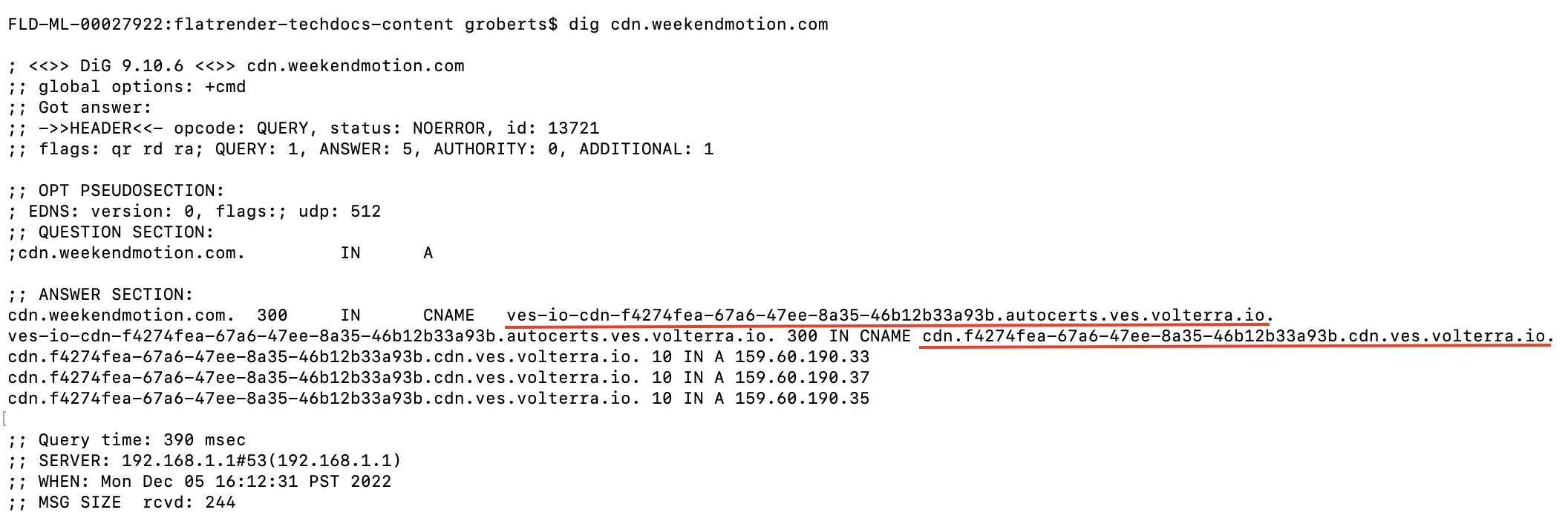
Verify CNAME mapping using
DIGcommand, and A records with unicast IP addresses of edge site, to indicate at least one edge site is configured for CDN distribution.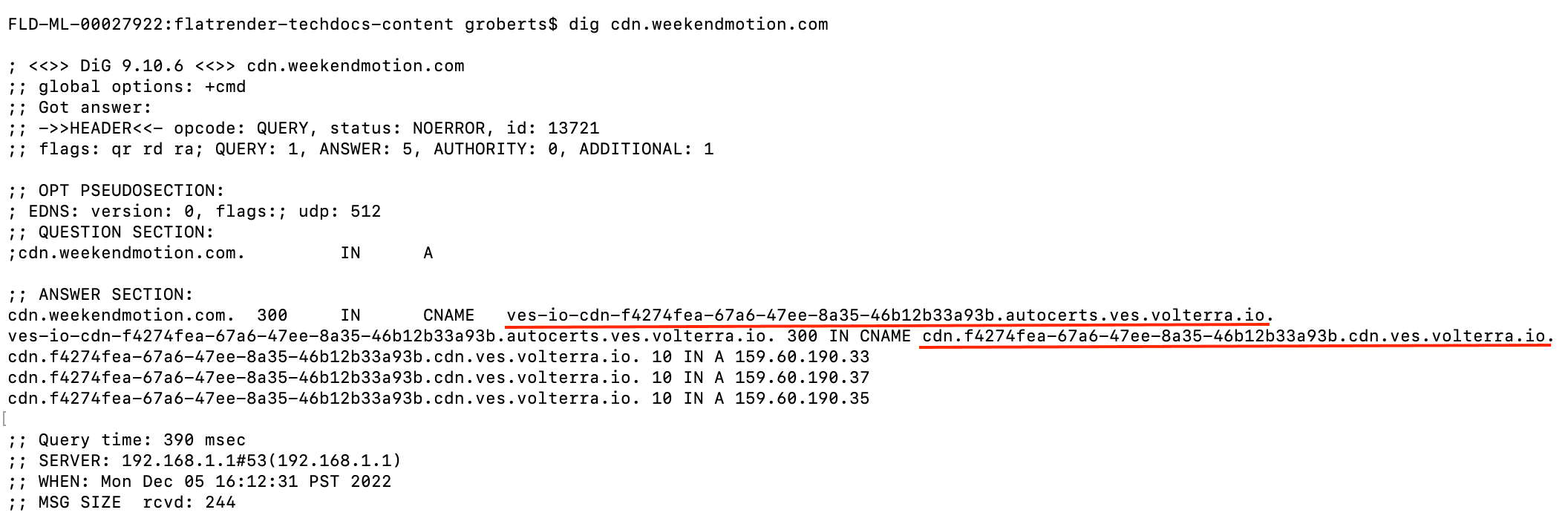
Figure: Distribution CNAME Mapping shown with dig
-
Verify that the requests to your CDN domain are processed, and the content is returned.
Delegated Domain with No Automatic Certificates:
Verify that the requests to your CDN domain are processed, and the content is returned.
Non-Delegated Domain:
Verify that the requests to your CDN domain are processed and the content is returned.
Note: In case of content updates in your origin servers, you can force the CDN servers to fetch the updated content using the purge option. Select
...>Purgefor your distribution object and the CDN service initiates purge for all the cache servers.
Step 4: CDN + WAAP Verification & Dashboard
Step 4.1: Check the load balancer and distribution with curl.
- Access the HTTP load balancer domain using a curl command,
curl -I -k lb.example.com, to make sure connection to the origin is fine. It should look something like this:
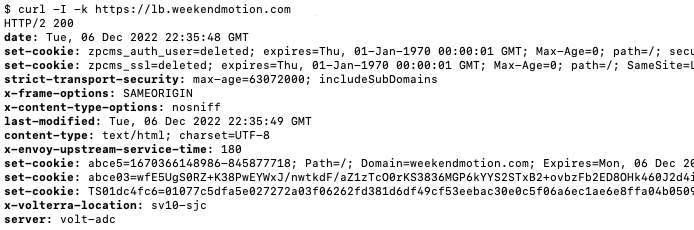
Figure: Verify Load Balancer with curl
- Access the CDN distribution domain to verify the end-to-end service chain is working correctly.
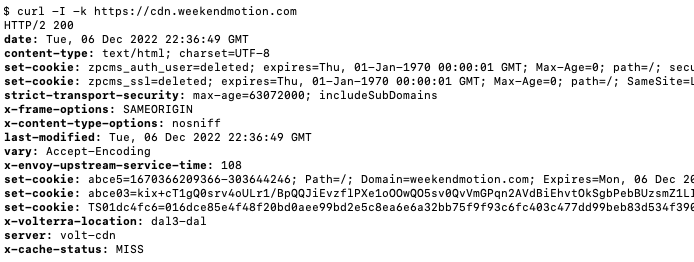
Figure: Verify Load Balancer with curl
- Because this is the first request to the CDN, the request will be redirected to the origin server causing the server to miss the cache (as shown at the bottom of the curl response:
x-cache-status: MISS). - Generate more requests to observe cached traffic (
Hits) and origin server traffic (Misses) as shown below.
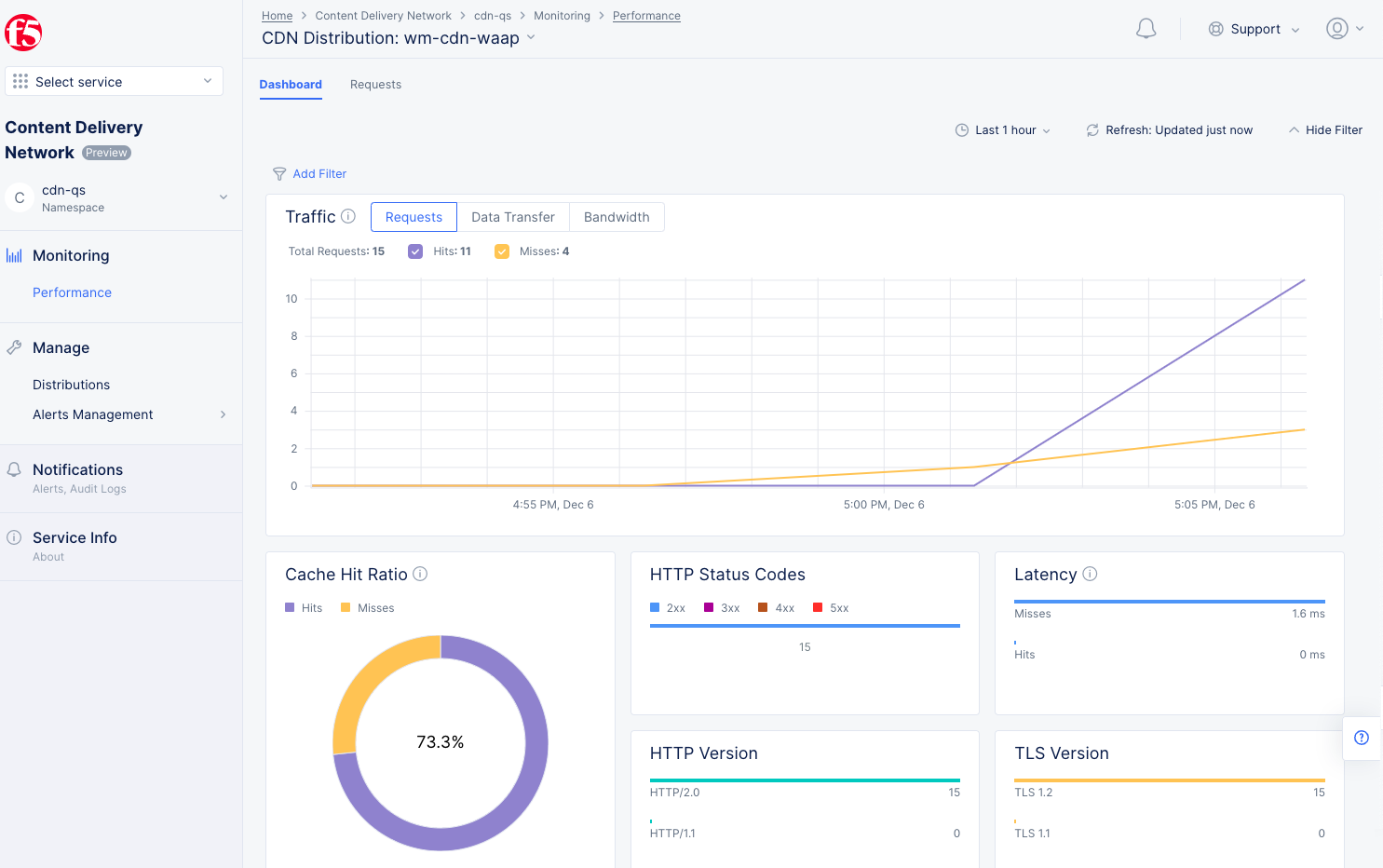
Figure: Verify CDN Hits and Misses
Step 4.2: View attack traffic in dashboards.
- Access the CDN domain with SQL injection or any other attack type sample.
- In Console, select the
Content Delivery Networkservice and navigate toMonitoring>Performance. - Select your distribution to see its dashboard.
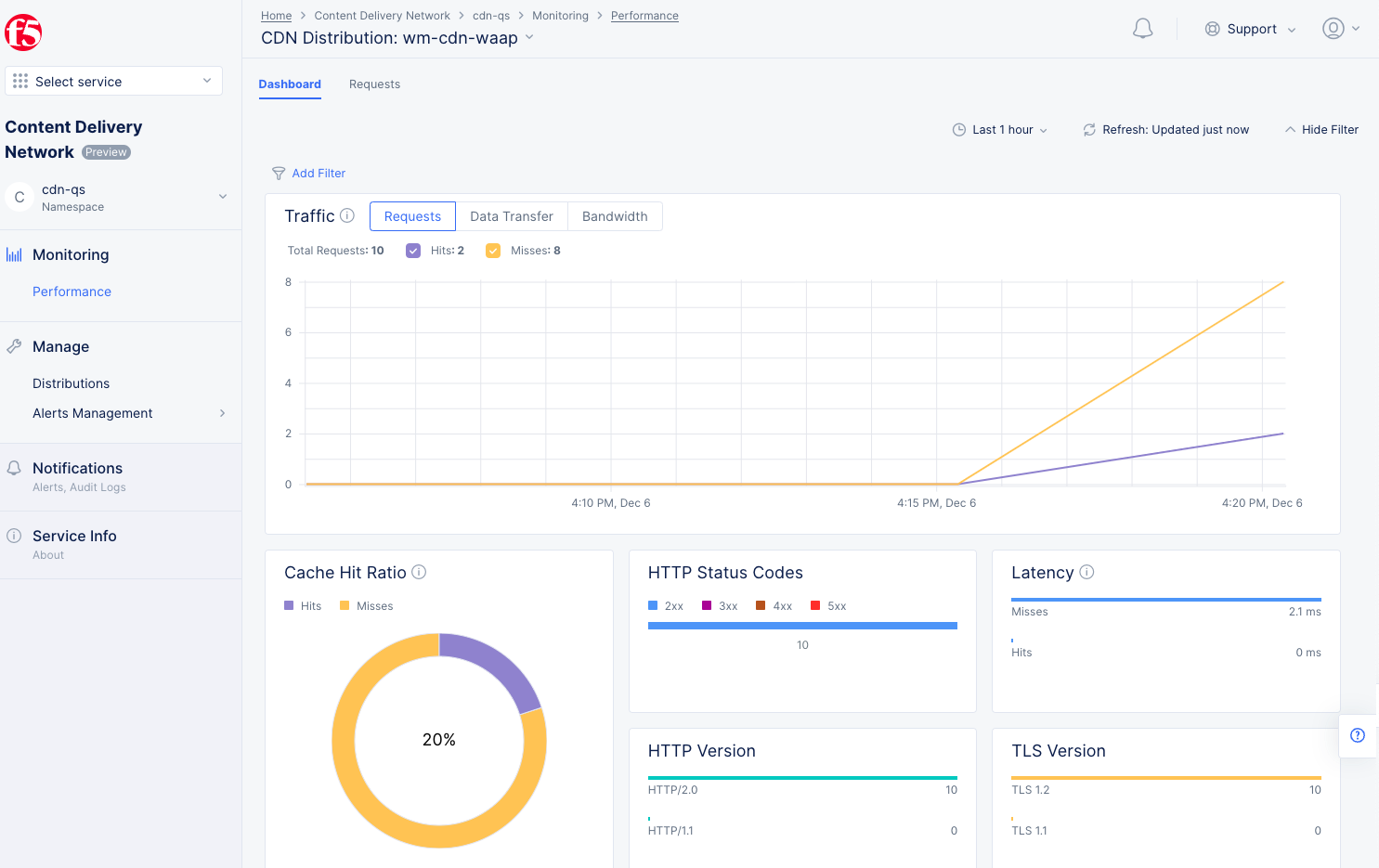
Figure: View Attack Traffic Cache Miss
- Observe the CDN dashboard is updated with cache misses.
- Switch to the
Web App & API Protectionservice and navigate toOverview>Security Dashboard.
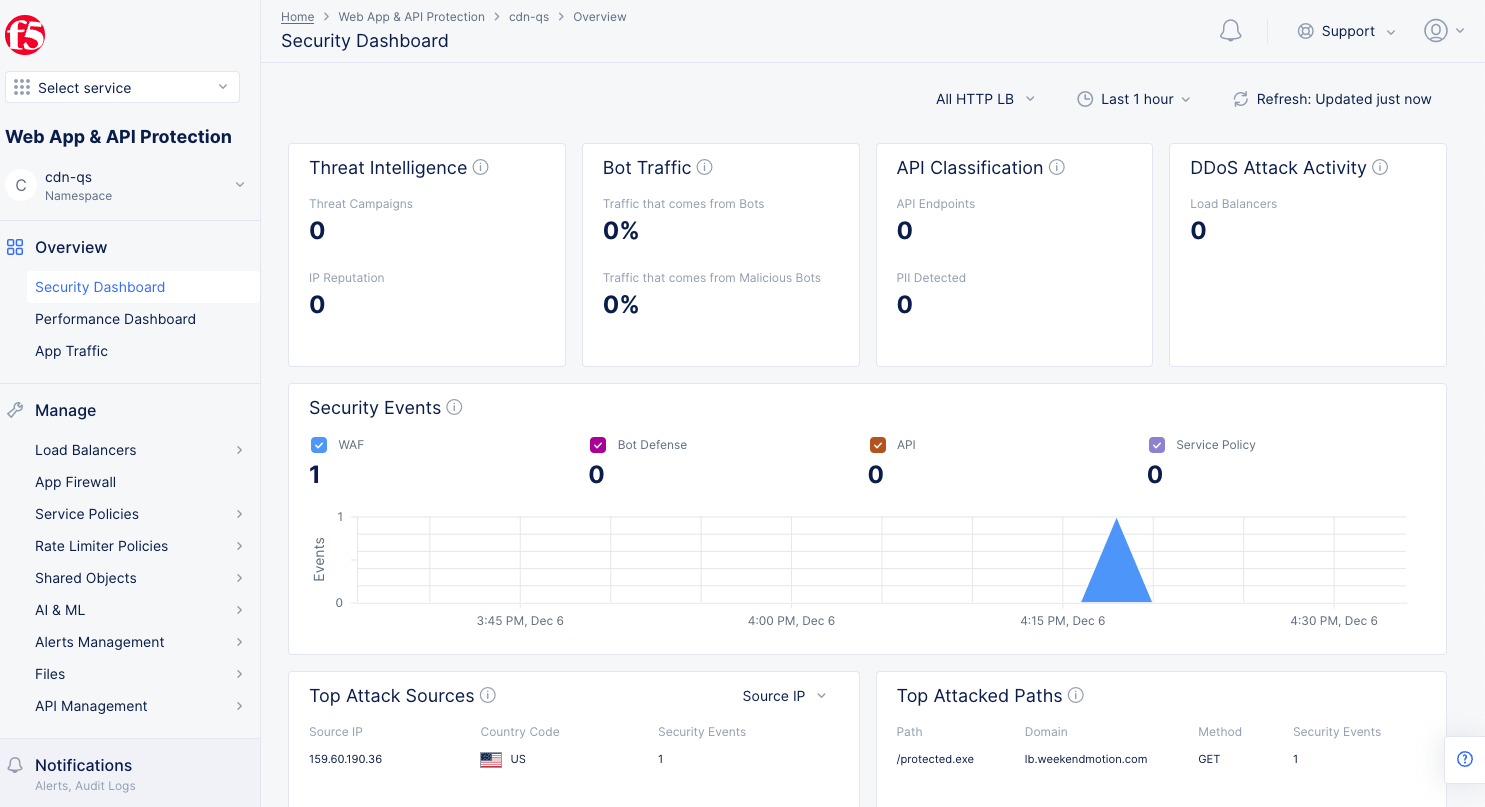
Figure: View Attack Traffic Details
- Observe the WAF security dashboard updated with security events.