F5 Customer Edge Deployment in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Reference
Objective
This reference provides information with load balancing techniques to help you deploy a CE Site on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
Single CE Deployed in Same VCN as Application
This topology diagram provides the standard deployment model.
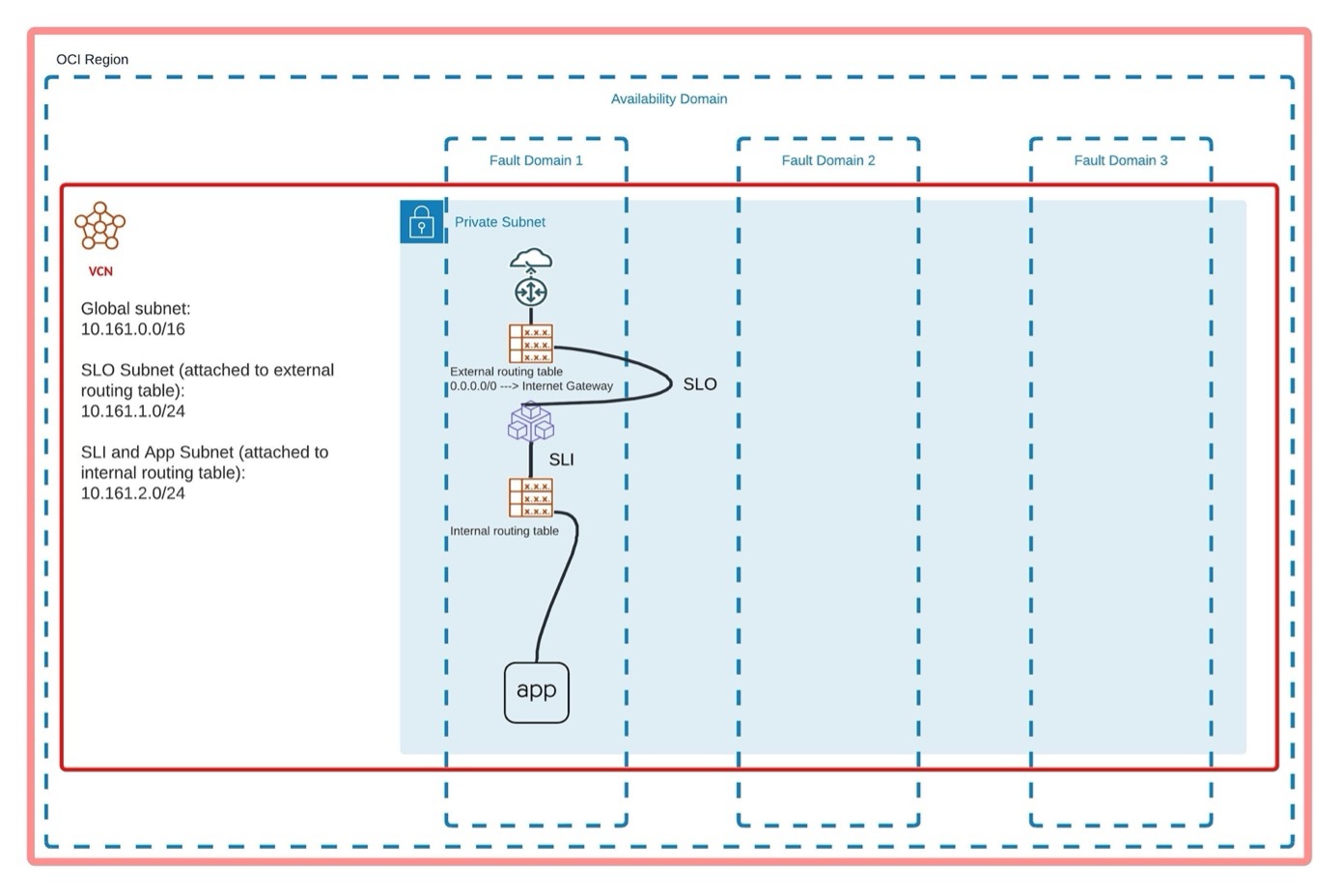
Figure: Global Topology
If you are exposing your application with any kind of Virtual Host object (such as TCP/UDP/HTTP/HTTPs) on the CE SLI interface, everything works as expected.
In this example, the CE IP address is 10.161.2.34.
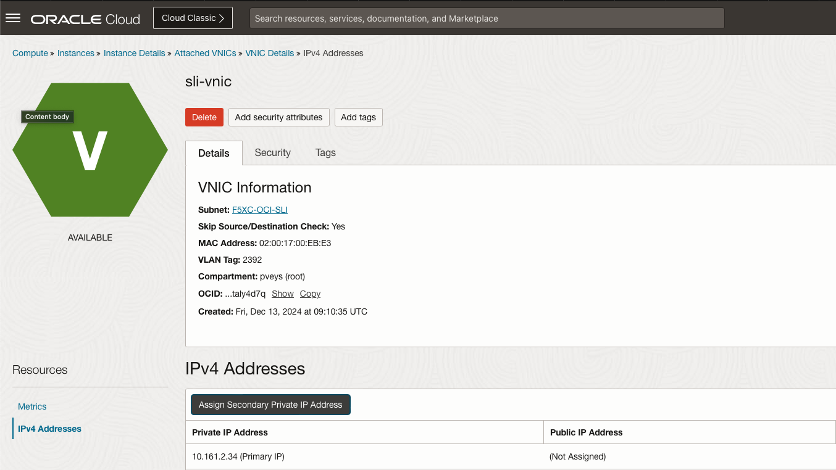
Figure: CE IP Address
If you use the curl command, from an OCI VM in the SLI subnet resolving the FQDN to the CE SLI, the IP address works as expected.
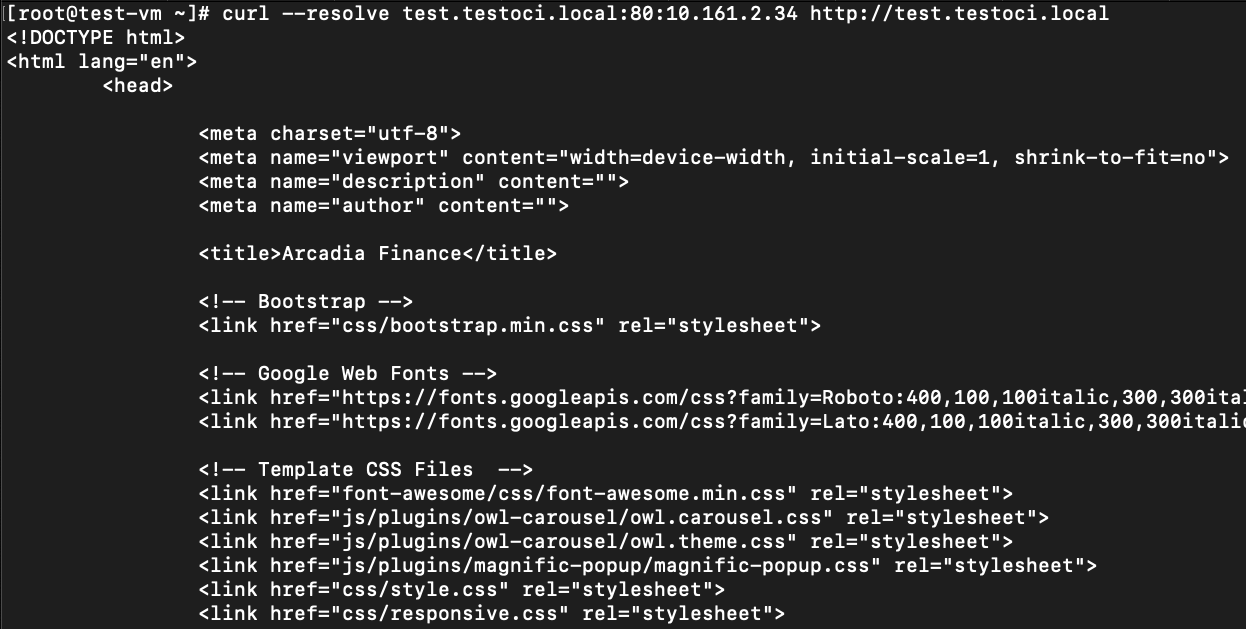
Figure: Curl Command
Problem
However, when you add a load balancer with a virtual IP address (VIP), then the configuration no longer works.
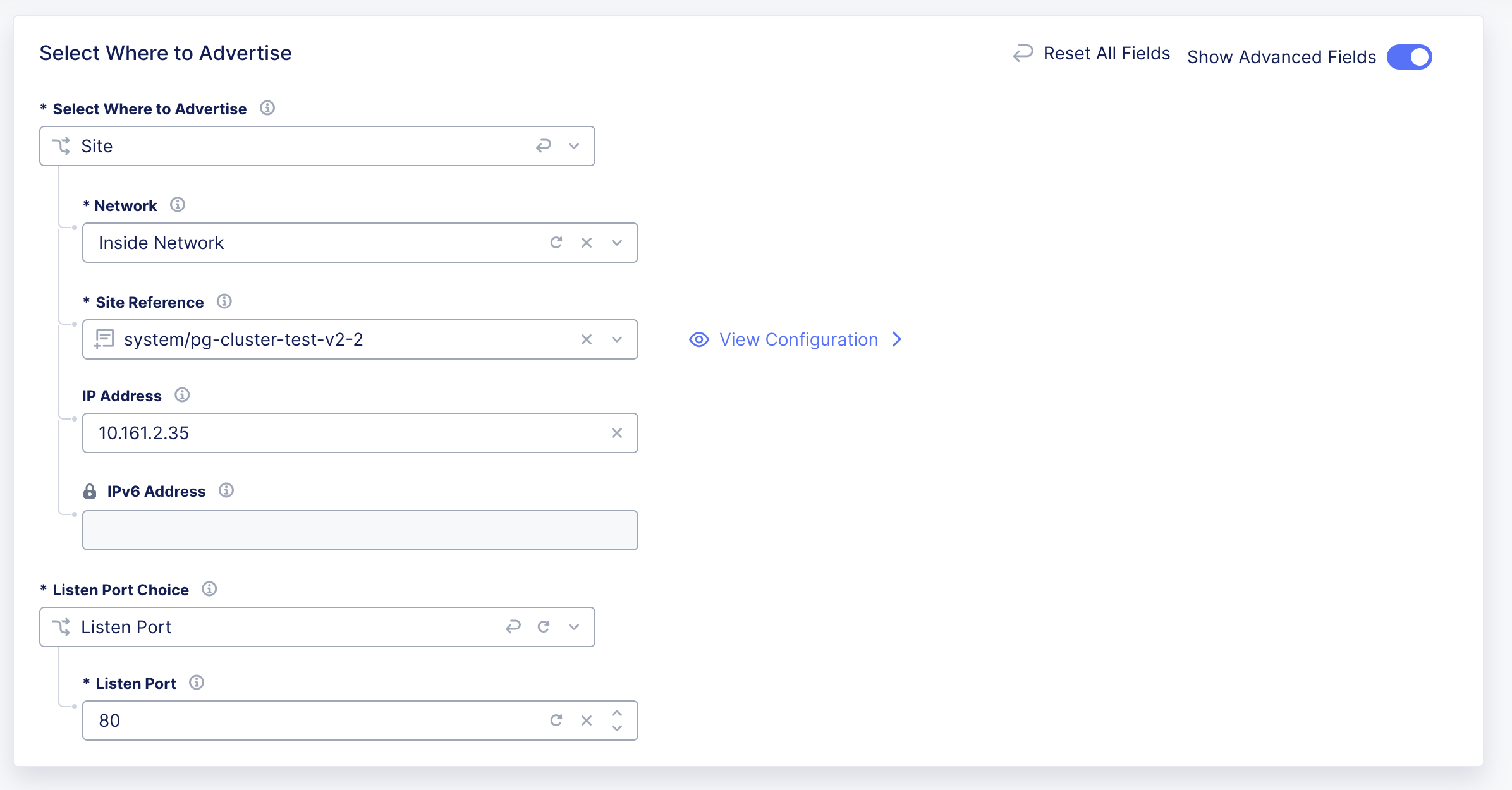
Figure: Add Load Balancer with VIP
The curl command demonstrates this.
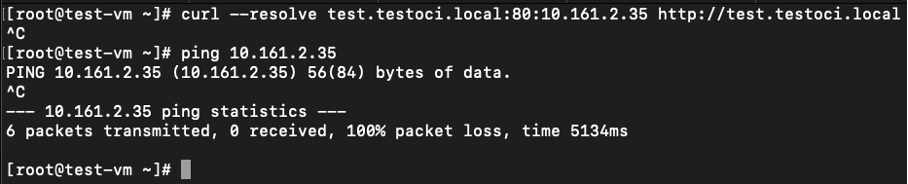
Figure: Curl Command
After you add the VIP IP address as an additional IP address to the OCI CE VM, then the configuration works correctly.
Figure: Added to the CE VM
Confirm with the curl command.
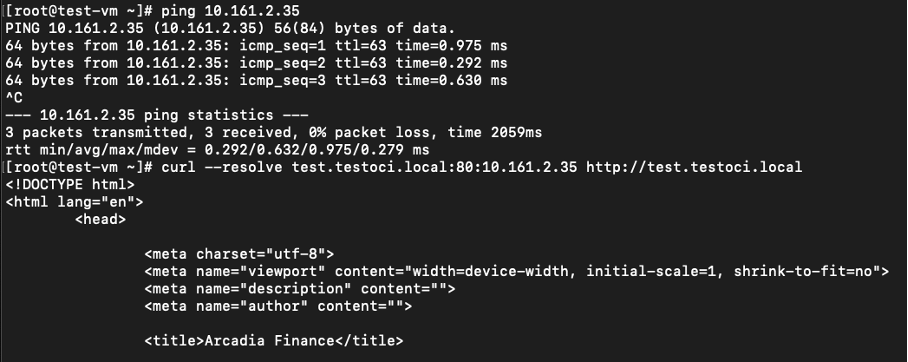
Figure: Added to the CE VM
Important: This is not a scalable solution for these reasons:
Deploying a multi-node CE Site
Using more than one VIP
Proposed Solution
Configure a dedicated VIP subnet and an OCI Network Load Balancer (NLB) with header preservation. This proposed solution provides the benefit of scaling your resources if the number of VIPs exceeds one.
This topology diagram provides the proposed solution.
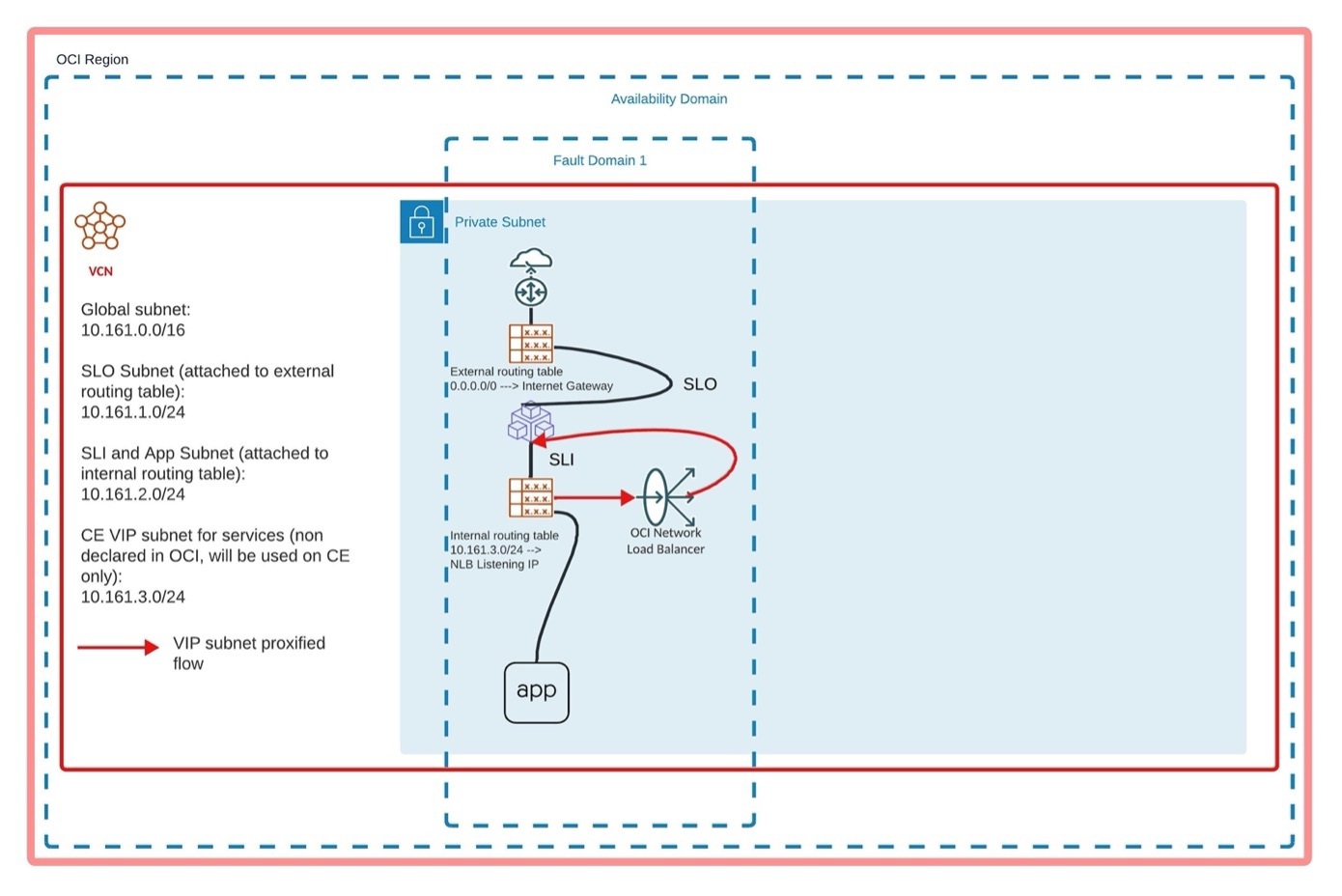
Figure: Solution Topology
Configure health check in Distributed Cloud Console
A simple HTTP load balancer is needed. First, a health check load balancer must be created on the CE on the default SLI IP address. This load balancer will be used by the OCI NLB health check to see if the CE is available or not.
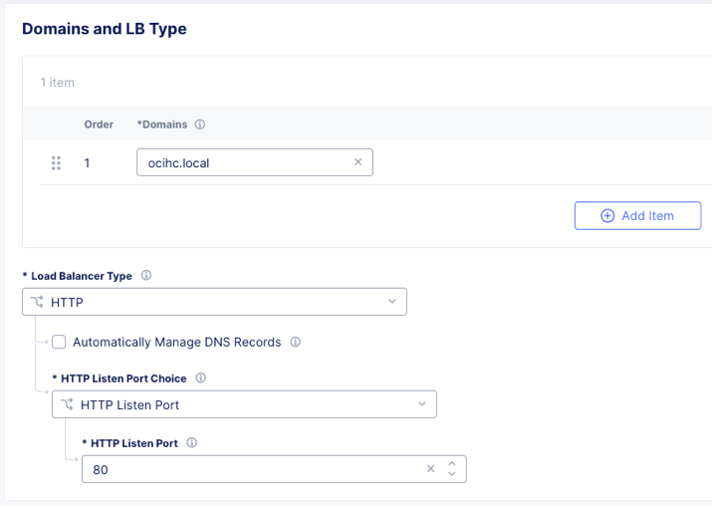
Figure: Health Check in Load Balancer
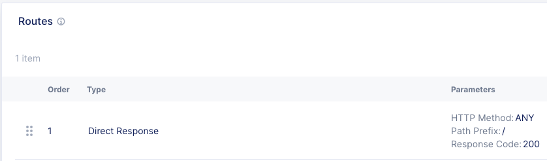
Figure: Health Check in Load Balancer
Configure NLB in OCI
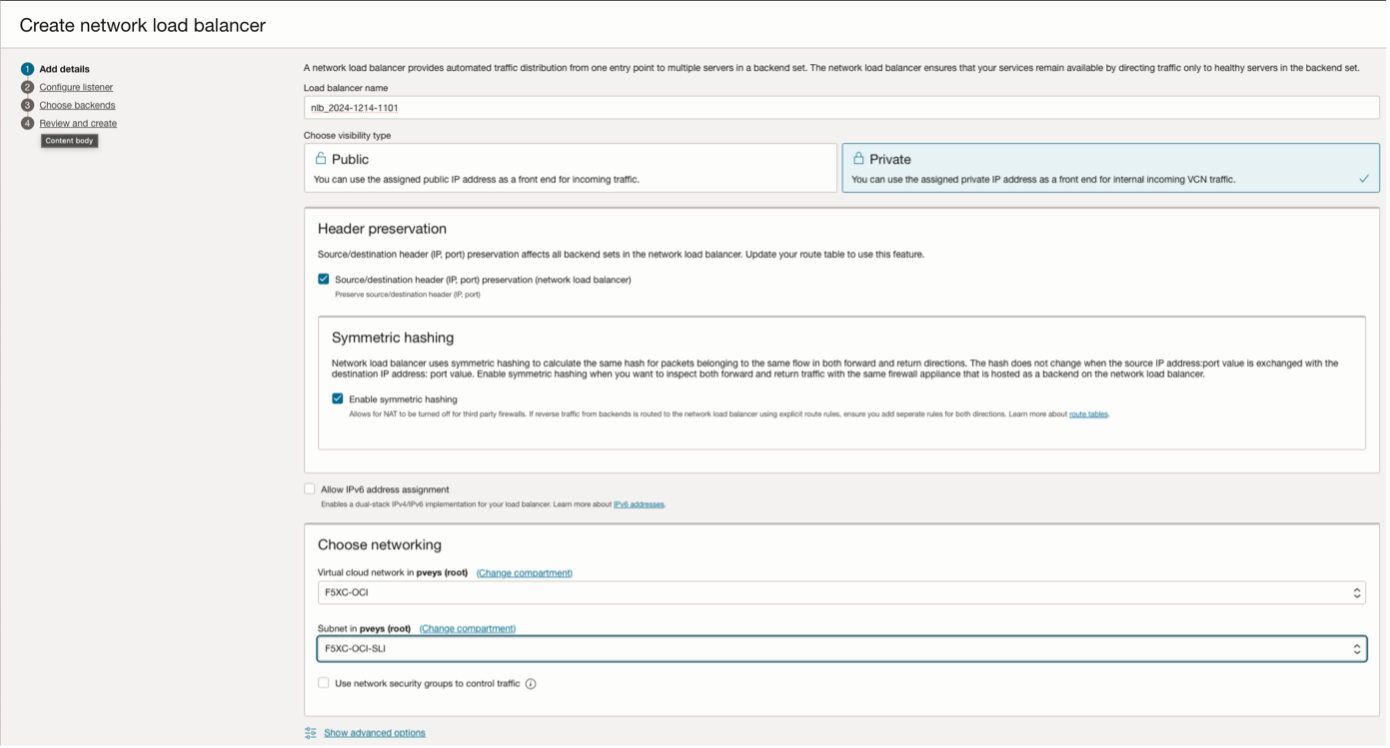
Figure: NLB Configuration
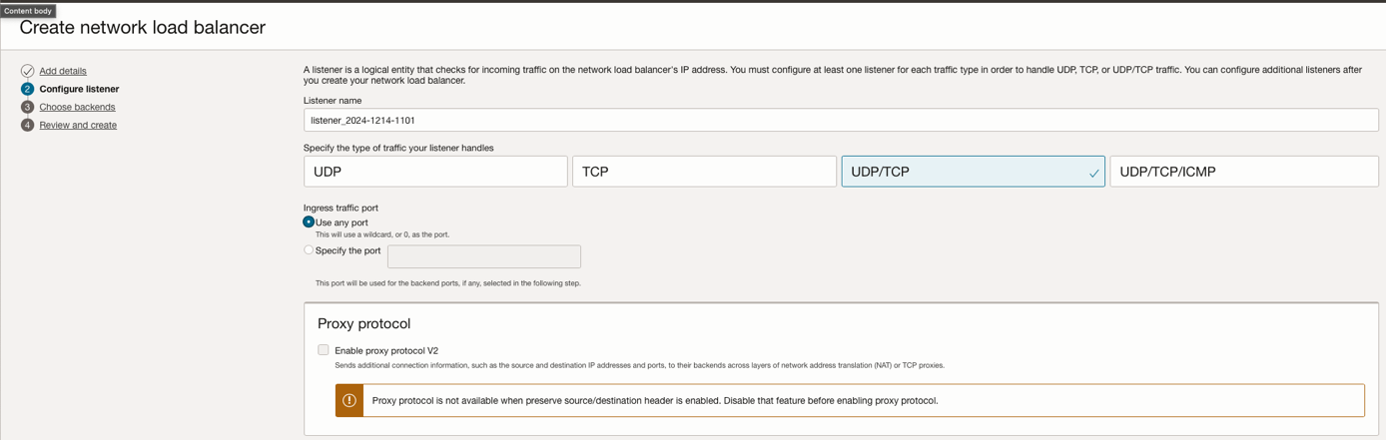
Figure: NLB Configuration
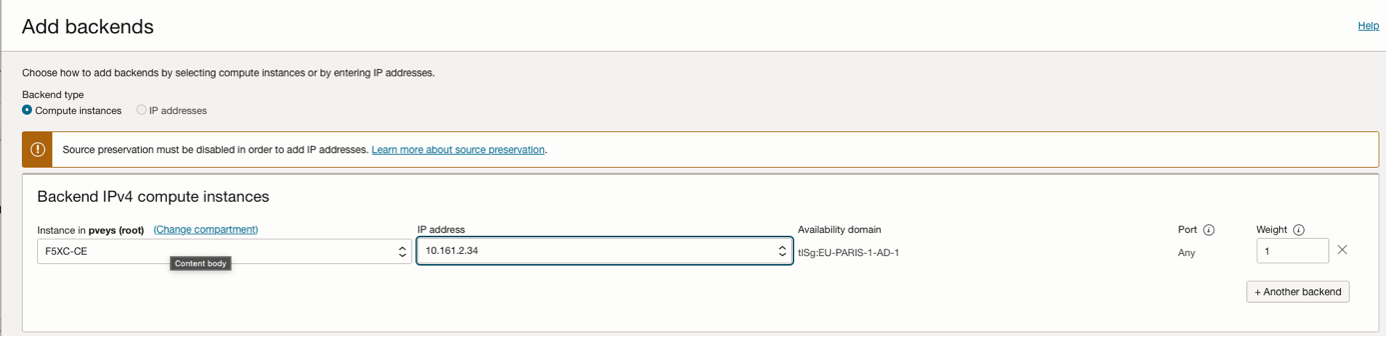
Figure: NLB Configuration
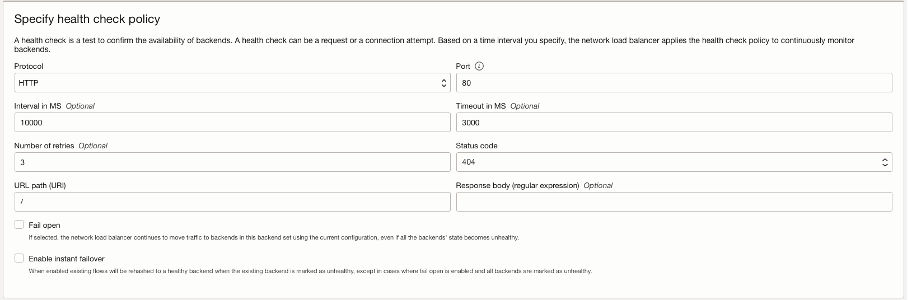
Figure: NLB Configuration
As the OCI NLB health check cannot pass the HTTP Header, a 404 error code is returned by the CE HTTP load balancer listening on the SLI.
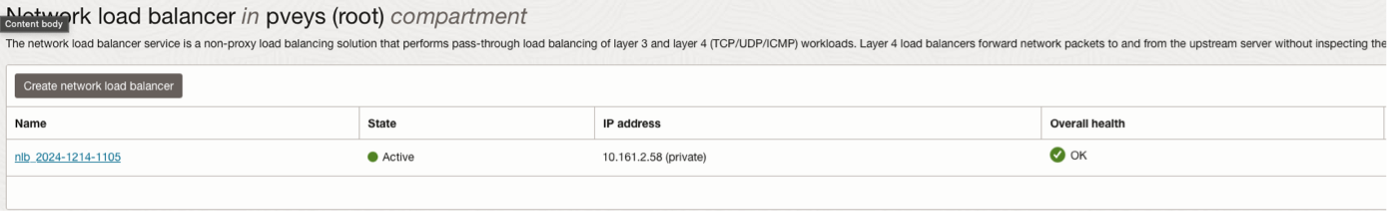
Figure: Listener Is Ready
Modify the OCI routing table and have the VIP subnet pointing to the NLB listener IP address.
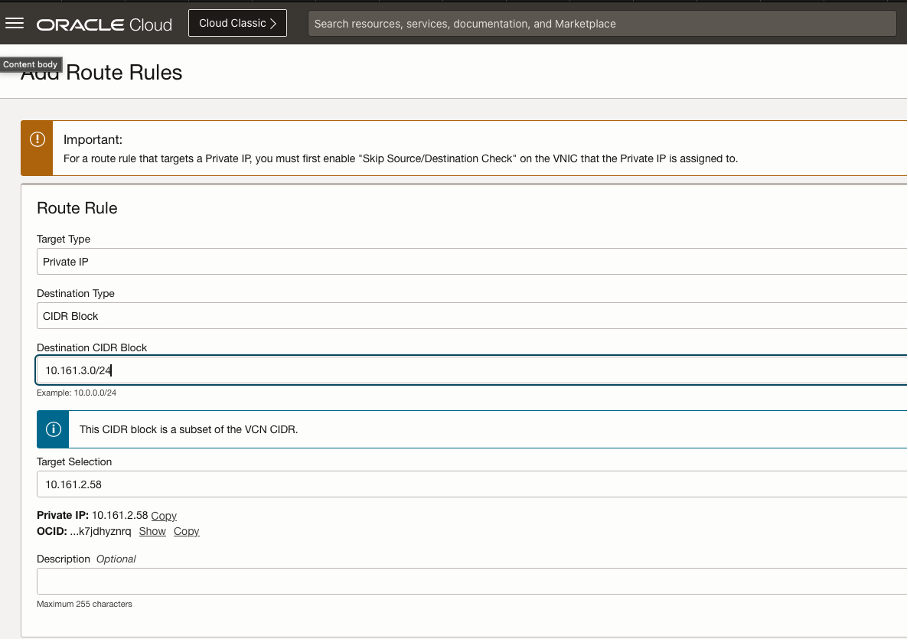
Figure: Modify Routing Table
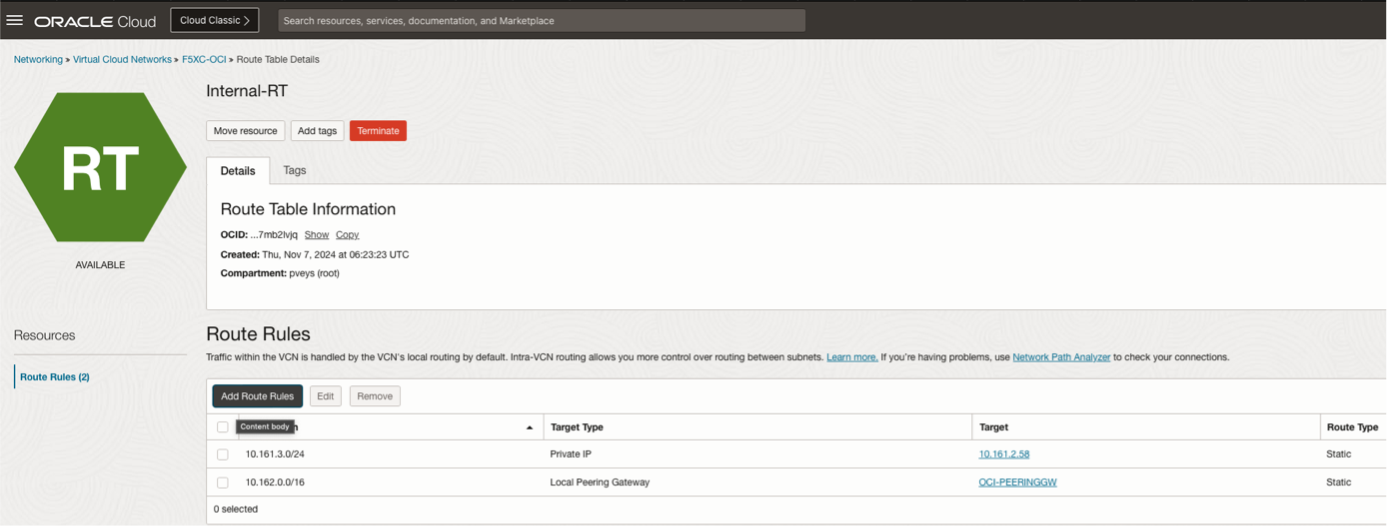
Figure: Modify Routing Table
Test the connections by adding two load balancers (TCP and HTTP) on the CEs in the VIP subnet.
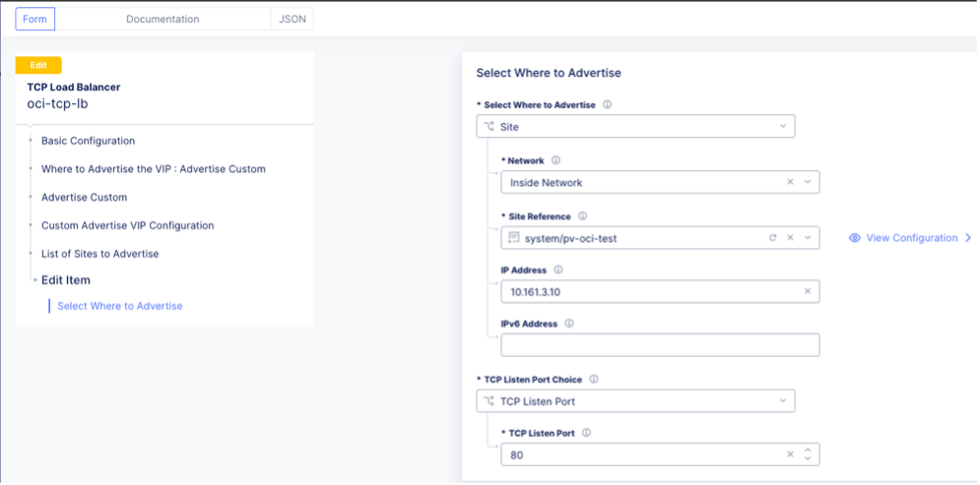
Figure: New Load Balancer
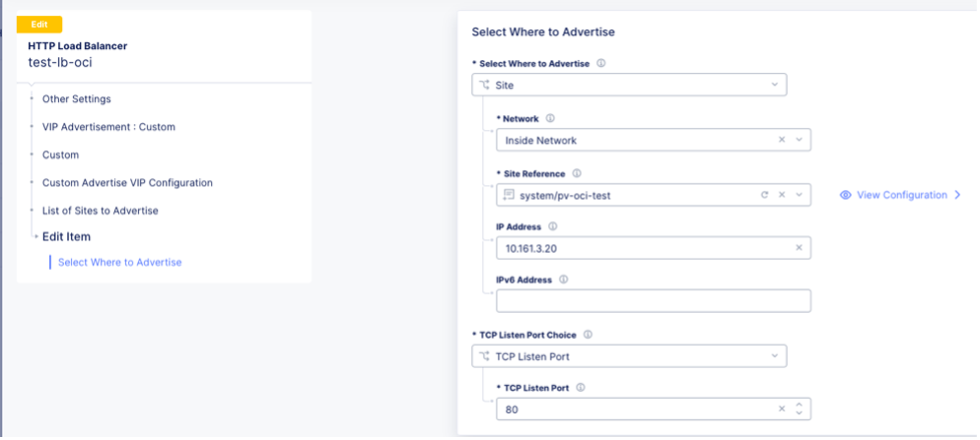
Figure: New Load Balancer
Confirm connectivity using curl command.
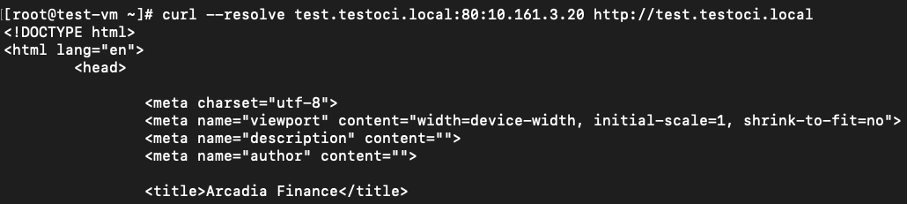
Figure: New Load Balancer
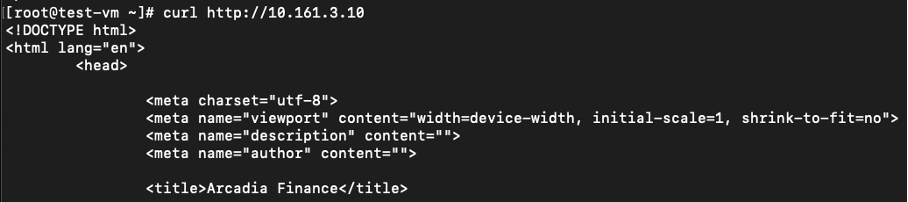
Figure: New Load Balancer
Multiple CEs Deployed in Same VCN as Application
The solution is the same to solve the VIP problem as for single CE deployed in the same VCN as the application. The only difference is that there will at least be three CE sites as members of the backend pool in the OCI NLB.
Multiple CEs Deployed in Different VCN than the Application
This diagram displays the topology.
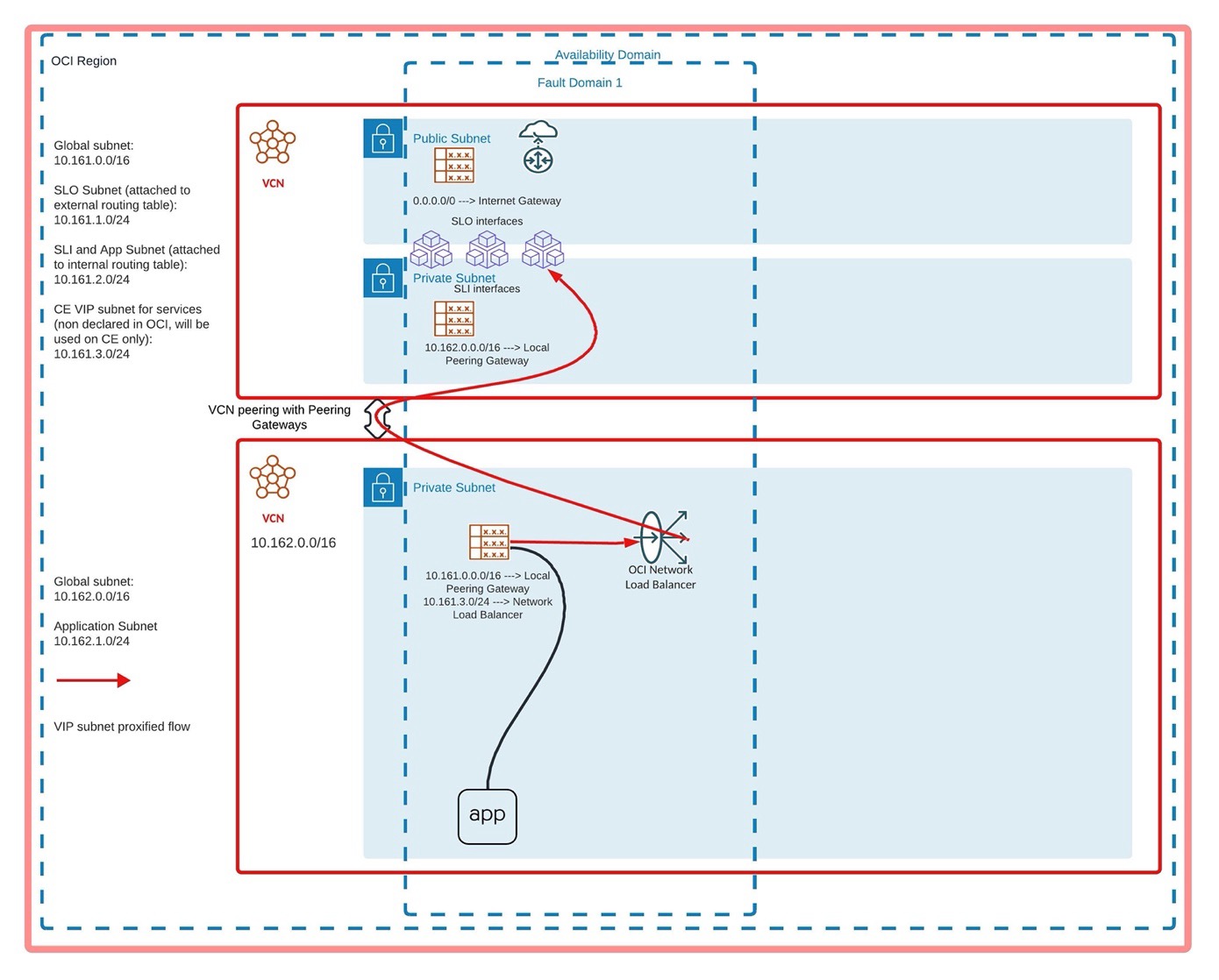
Figure: Multiple CEs in Different VCN Topology
Assigning SLI IP Address to CEs in OCI
From an infrastructure perspective, it is more relevant to fix IP addresses when assigning SLI IP addresses to CEs.
By doing so, you can plan in a better way your services' implementation. For example, the first twenty IP address of the subnet are reserved for network services.
For a cluster of CEs, an example can be:
- 10.161.2.10 CE1
- 10.162.2.11 CE2
- 10.162.2.12 CE3
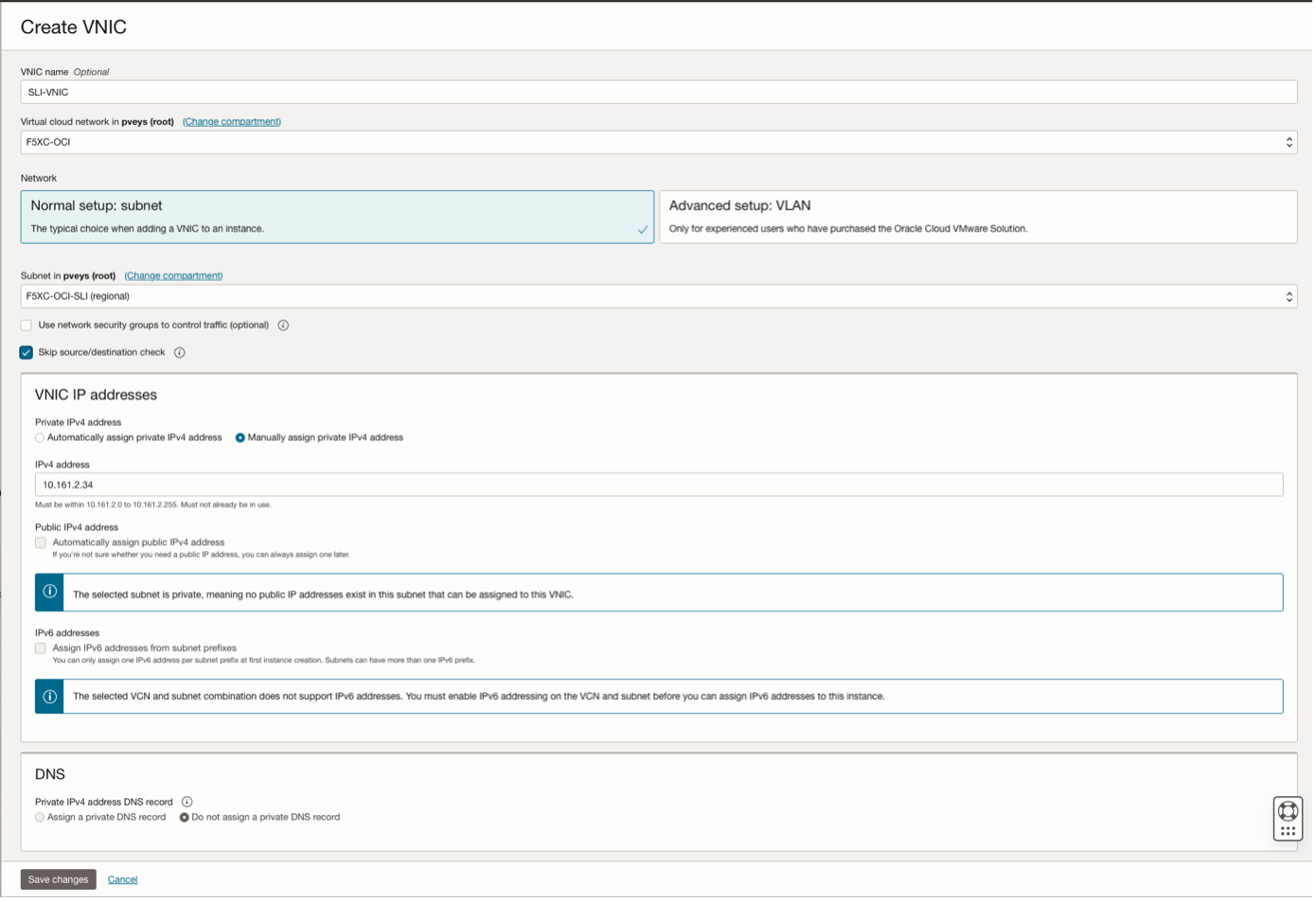
Figure: Assign Fixed IP Addresses