Encrypt and Decrypt Application Secrets
Objective
This document provides instructions on how to encrypt your application secrets using the F5® Distributed Cloud Services Blindfold and how to decrypt from your vK8s application. To learn more about Blindfold and secrets management, see Blindfold.
The following image illustrates the sequence of actions performed by Distributed Cloud Services in securing the secrets:
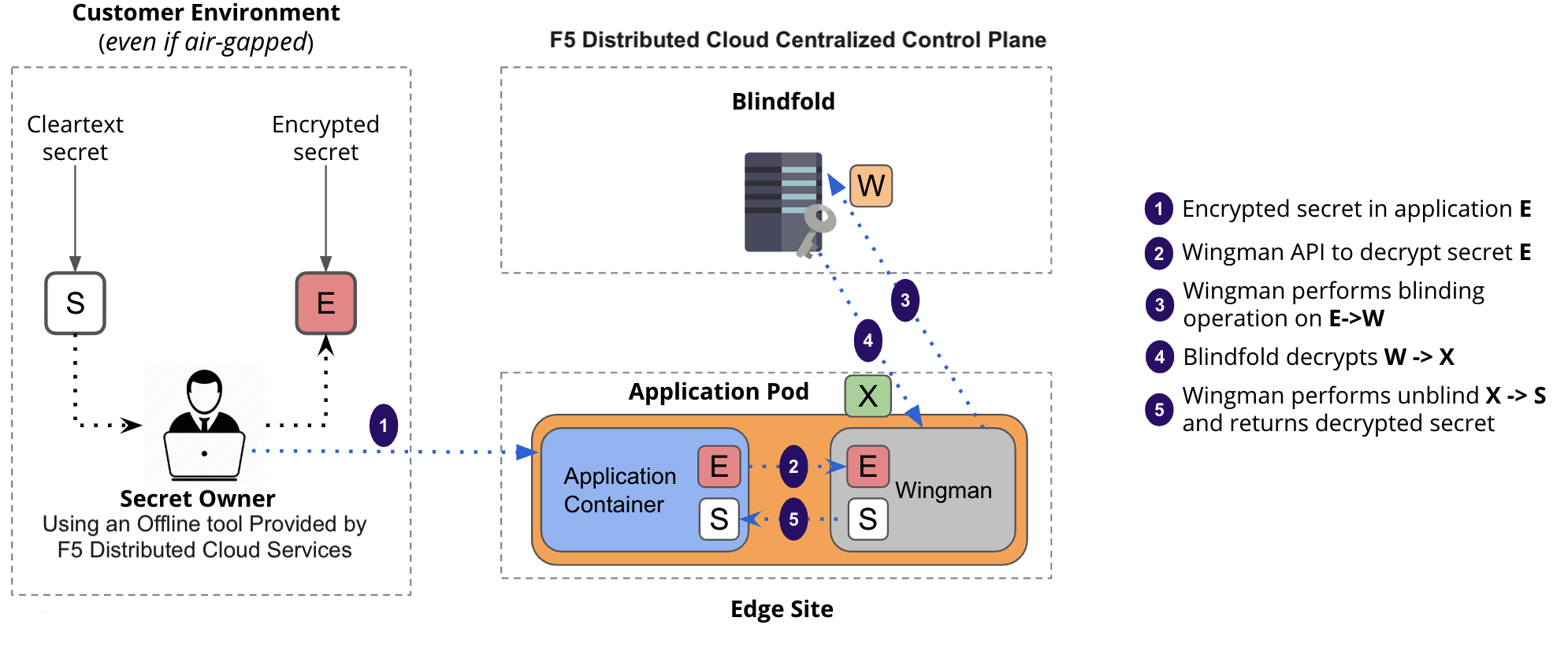
Figure: Distributed Cloud Services Blindfold
Using the instructions provided in this guide, you can encrypt application secrets and store them in code or configmap.
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites apply:
-
An F5 Distributed Cloud Account. If you do not have an account, see Getting Started with Console.
-
An application running on vK8s. If you do not have an application running on vK8s enable Wingman, see Deploy Application.
-
The vesctl tool. Download
vesctlon your local machine, as it is used to apply the Blindfold to the TLS certificate. -
A minimum of
monitorrole in theSharednamespace is required.
Workflow
Applying Blindfold to the secret of your cloud application and decrypting using Wingman includes performing the following sequence of actions:
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Create a Secret Policy | Create a policy to permit your application to decrypt the secret. |
| Prepare Credentials and Policy | Retrieve API credentials from F5® Distributed Cloud Console (Console), derive certificates, derive keys, and obtain policy. |
| Encrypt application secret | Perform the encryption on a local computer. It is recommended to use an air-gapped computer. |
| Access decrypted secret from your application | Make a REST call to Distributed Cloud Services security sidecar (Wingman) to access decrypted secret. |
Note: You must download the API credentials in PKCS #12 file format.
Create a Secret Policy
The secret policy allows Wingman running as sidecar in your application access to the secret.
Create a secret policy using the instructions provided in the Secrets Policy document. This example assumes that a policy named demo-secret-policy is created.
Note: Wingman sidecar communicates with Distributed Cloud Services. Therefore, traffic flows from vK8s pods to Distributed Cloud Services.
Wingman sidecar container will not be injected automatically for workloads in non-F5 Distributed Cloud/customer namespaces on CE sites. Although existing workloads in non-F5 Distributed Cloud namespace will continue to run Wingman even after upgrade until there are some changes in workloads which triggers re-creation of pods. If such workloads have dependency on Wingman then they must include following annotation in pod template of the workload: ves.io/wingman-injection-mode": "enable".
Prepare Credentials and Policy
Step 1: Create an API certificate in Console.
Create an API certificate using the instructions provided in the Generate API Certificate for My Credentials procedure.
Step 2: Download API certificate.
Download the API certificate in PKCS #12 format.
Step 3: Derive a certificate from the downloaded PKCS #12 file.
This example shows how to derive the certificate using OpenSSL:
openssl pkcs12 -nokeys -in demo-api-credentials.p12 -out demo-api.crt
Note: This step prompts for password. Enter the password used in Step 1 to generate the certificate file in the
.crtfile.
Step 4: Derive a key from the PKCS #12 file.
Enter the following command:
openssl pkcs12 -nocerts -nodes -in demo-api-credentials.p12 -out demo-api.key
Note: This step prompts for a password. Enter the password used in Step 1 and a passphrase to generate the key file in the
.keyformat.
Step 5: Obtain a public key and store the output to a file.
This example stores the output to a file named demo-api-pubkey:
vesctl --cert file:///demo-api.crt --key file:///demo-api.key -u https://demo-api.console.ves.volterra.io/api request secrets get-public-key > demo-api-pubkey
Note: For the
--certand--keyoptions, specify the path to the certificate file and key file derived in Step 3 and Step 4, respectively.
The following output capture shows a sample public key:
data:
keyVersion: 1
modulusBase64: rc3DxZa69sWeIn9NRrHGcZlZaXLHWYjc57jIS76Z47AcU0jDmodz3lNEysVO2swNAUn8p6yiuvf8Vj4LUuWB++LdP2yYX5ftEHmMgnHVq4AdKFBp5zbrh15g7mS0lpdX/xG6h0+IdHyrWPoIg/hZwYyV9xmIOcFc1Jk5PZC554hchHbToQ==
publicExponentBase64: A6ur/Xk=
tenant: volterra-demo1
Step 6: Obtain a policy document and store the output to a file.
This example stores the output to a file named demo-api-policy:
vesctl --cert file:///demo-api.crt --key file:///demo-api.key -u https://demo-api.console.ves.volterra.io/api request secrets get-policy-document --namespace volterra-demo --name demo-secret-policy > demo-secret-policy
Note: For the
--certand--keyoptions, specify the path to the certificate file and key file derived in Step 3 and Step 4 respectively. For the--namefield, enter the API credentials object name.
The following output capture shows a sample policy document:
data:
name: demo-secret-policy
namespace: volterra-demo
policyId: "101"
policyInfo:
rules:
- action: ALLOW
clientSelector:
expressions:
- app = demo-tls-server
tenant: volterrra-demo1
Encrypt Application Secret Using Blindfold
Use vesctl to encrypt secret using Blindfold and store the returned encrypted secret for using it in the application.
This is secret data that should only be seen by the application pod:
cat secretfile.data
This example stores the output to a file named secret.enc:
vesctl --cert file:///demo-api.crt --key file:///demo-api.key -u https://demo-api.console.ves.volterra.io/api request secrets encrypt --policy-document demo-secret-policy --public-key demo-api-pubkey secretfile.data > secret.enc
Note: Provide the certificate, key, public key, and policy document obtained in the Prepare Credentials and Policy chapter.
The following output capture shows a sample encrypted key:
Encrypted Secret (Base64 encoded):
AAAACWN1c3RvbWVyMQAAAAEAAAAAAAAAaAIAAAAFA6ur/XkAAAEArc3DxZa69sWeIn9NRrHGcZlZaXLHWYjc57jIS76Z47AcU0jDmodz3lNEysVO2s
This encrypted secret can be provided to the application pod via several means - put the encrypted secret in code, provided via configmap, provided via Kubernetes secret, etc.
Decrypt Application Secret
The application needs to make a REST call to Wingman (running a REST server on localhost:8070) to decrypt the secret. API specifications are specified here.
cat input.json
{
"type": "blindfold",
"location": "string:///AAAACWN1c3RvbWVyMQAAAAEAAAAAAAAAaAIAAAAFA6ur/XkAAAEArc3DxZa69sWeIn9NRrHGcZlZaXLHWYjc57jIS76Z47AcU0jDmodz3lNEysVO2s"
}
The following is an example curl request and output:
curl -XPOST http://localhost:8070/secret/unseal -d @input.json
VGhpcyBpcyBzZWNyZXQgZGF0YSB0aGF0IHNob3VsZCBvbmx5IGJlIHNlZW4gYnkgYXBwbGljYXRpb24gcG9kLg==
The output of the REST call is a decrypted secret in Base64 encoding format. If we get the original secret back, perform Base64 decoding of the output string value.
This is secret data that should only be seen by the application pod:
echo "VGhpcyBpcyBzZWNyZXQgZGF0YSB0aGF0IHNob3VsZCBvbmx5IGJlIHNlZW4gYnkgYXBwbGljYXRpb24gcG9kLg==" | base64 -D
Enable Wingman
Wingman sidecar will not be available by default to customer pods. Wingman sidecar injection can be optionally enabled if Distributed Cloud secrets management services is needed.
The following is an example:
spec:
template:
metadata:
annotations:
ves.io/wingman-injection-mode: enable
Note: Wingman sidecar was previously available by default, and it will be available until an application restarts. If an application needs Wingman sidecar then above annotation is needed in pod template before an upgrade or pod restarts.