Create vK8s Resources
Objective
This document provides instructions on how to deploy resources on the F5® Distributed Cloud Services network cloud or edge cloud using Distributed Cloud virtual Kubernetes (vK8s). Distributed Cloud Services provide a mechanism to easily deploy applications across the Distributed Cloud global network and make them available closer to users in major metro markets. To learn more about how Distributed Cloud Services distribute application deployment, see Distributed Application Management.
The vK8s resources covered in this guide are:
- Service
- Job
- Config map
- Secret
- Daemon sets
- Cron Jobs
- Service Accounts
- Custom Resource (CR)/Custom Resource Definition (CRD)
CR and CRD
The CR is supported only for App Stack CE sites enabled with managed K8s. You can create a CRD using a manifest file for every managed K8s cluster and apply the CR per a namespace using F5 Distributed Cloud virtual Kubernetes (vK8s). Creating a CR object is supported only for vK8s applied to the virtual site containing the CE sites. This is not supported for vK8s on virtual sites containing REs. The CRD for the CR must be previously applied to all sites in virtual Kubernetes (vK8s) using their individually managed k8s API endpoints.
Note: The CRD needs to be created in the managed K8s and be observable in vK8s.
The current release only supports CRDs and CRs for Seldon (a platform to deploy AI/ML models) and Ambassador's Emissary ingress. Health check must be defined in the Ambassador Mapping CR for the health probe on /live path to mark the endpoint as up, when the k8s service or the AI model is added to the F5 Distributed Cloud Services origin pool.
To deploy vK8s resources, first create a vK8s object per the instructions in the Create Virtual K8s Object guide.
Using the instructions provided in this guide, you can deploy resources with the kubeconfig of the vK8s object.
Prerequisites
-
An F5 Distributed Cloud Account. If you do not have an account, see Getting Started with Console.
-
An application and associated Kubernetes deployment file.
-
A kubeconfig file of the vK8s object. See the Create Virtual K8s Object guide for more details.
Configuration
You can deploy the vK8s resource in one of the following methods:
-
Using the resource manifest directly in the F5 Distributed Cloud Console.
-
Using the resource manifest and kubeconfig file of vK8s cluster from CLI with the
kubectlcommand.
Perform the following steps:
Step 1: Navigate to your vK8s object and download its kubeconfig.
-
Select the
Distributed Appsworkspace. -
Select the desired namespace from the
Namespacedrop-down menu. -
Navigate to
Applications>Virtual K8s. -
Click
...>Kubeconfigfor the created vK8s object to download its kubeconfig file. -
Set environment variable for the downloaded kubeconfig in your local machine.
export KUBECONFIG=<vK8s-kubeconfig>
Note: In case of deployment using the
kubectlcommand, settingKUBECONFIGvariable deploys the resources to the vK8s.
Step 2: Prepare the manifest file for the resource.
Create a file in your local machine and enter the manifest content in JSON or YAML format. The following is the list of sample manifests:
- vK8s service manifest sample:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: emailservice
labels:
app: emailservice
annotations:
ves.io/proxy-type: HTTP_PROXY
ves.io/http2-enable: "true"
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: emailservice
ports:
- name: grpc
port: 5000
targetPort: 8080
- vK8s job manifest sample:
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: pi
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: pi
image: perl
command: ["perl", "-Mbignum=bpi", "-wle", "print bpi(2000)"]
restartPolicy: Never
backoffLimit: 4
- vK8s config map manifest sample:
apiVersion: v1
data:
mysqld.conf: "[mysqld]\npid-file\t = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid\nsocket\t\t
\ = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock\n# Where the database files are stored
inside the container\ndatadir\t\t = /var/lib/mysql\n\n# My application
special configuration\nmax_allowed_packet = 32M\nsql-mode =
'STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION'\n\n# Accept connections from any
IP address\nbind-address\t = 0.0.0.0\n"
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
name: mysql-conf
- vK8s secret - Generate the secret using the following command:
kubectl create secret docker-registry dock-secret --docker-server=docker.io --docker-username="<registry username>" --docker-password="<registry password>" --docker-email=<registry email>
Note: In case of generating the secret using above command, the secret is directly created on vK8s and there is no need of performing any action on Console.
- Daemon set manifest sample:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: fluentd-elasticsearch
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: fluentd-logging
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: fluentd-elasticsearch
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: fluentd-elasticsearch
spec:
tolerations:
# this toleration is to have the daemonset runnable on master nodes
# remove it if your masters can't run pods
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
effect: NoSchedule
containers:
- name: fluentd-elasticsearch
image: quay.io/fluentd_elasticsearch/fluentd:v2.5.2
resources:
limits:
memory: 200Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 200Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: varlog
mountPath: /var/log
- name: varlibdockercontainers
mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers
readOnly: true
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
volumes:
- name: varlog
hostPath:
path: /var/log
- name: varlibdockercontainers
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/docker/containers
- Cron job manifest sample:
apiVersion: batch/v1beta1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name: hello
spec:
schedule: "*/1 * * * *"
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: hello
image: busybox
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
args:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- date; echo Hello from the Kubernetes cluster
restartPolicy: OnFailure
Note: The
ConcurrencyPolicyis always set toForbidirrespective of what is specified in the manifest for any CronJob launched on the Regional Edge Sites.
- Service account manifest sample - Here the YAML for role, service account, and role-binding are shown.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-read-role
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: pod-read-sa
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: pod-read-rolebinding
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: pod-read-sa
apiGroup: ""
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: pod-read-role
apiGroup: ""
- vK8s service manifest sample with CR:
Important: The CR is supported only for App Stack CE sites enabled with managed K8s. You can create a CRD using a manifest file for every managed K8s cluster and apply the CR per a namespace using F5 Distributed Cloud virtual Kubernetes (vK8s).
apiVersion: machinelearning.seldon.io/v1
kind: SeldonDeployment
metadata:
name: iris-model
namespace: vk8s-namespace
spec:
name: iris
predictors:
- graph:
implementation: SKLEARN_SERVER
modelUri: gs://seldon-models/v1.18.0-dev/sklearn/iris
name: classifier
name: default
replicas: 1
Step 3: Deploy the resource.
Step 3.1: Deploy from Console.
-
With your desired namespace selected, select
Applications->Virtual K8s. -
Click on your vK8s object to open its dashboard.
-
Click
Servicestab. ClickAdd Serviceand enter the service manifest prepared in Step 2. ClickSave.

Figure: vK8s Services
- Click
Jobstab. ClickAdd Joband enter the job manifest prepared in Step 2. ClickSave.
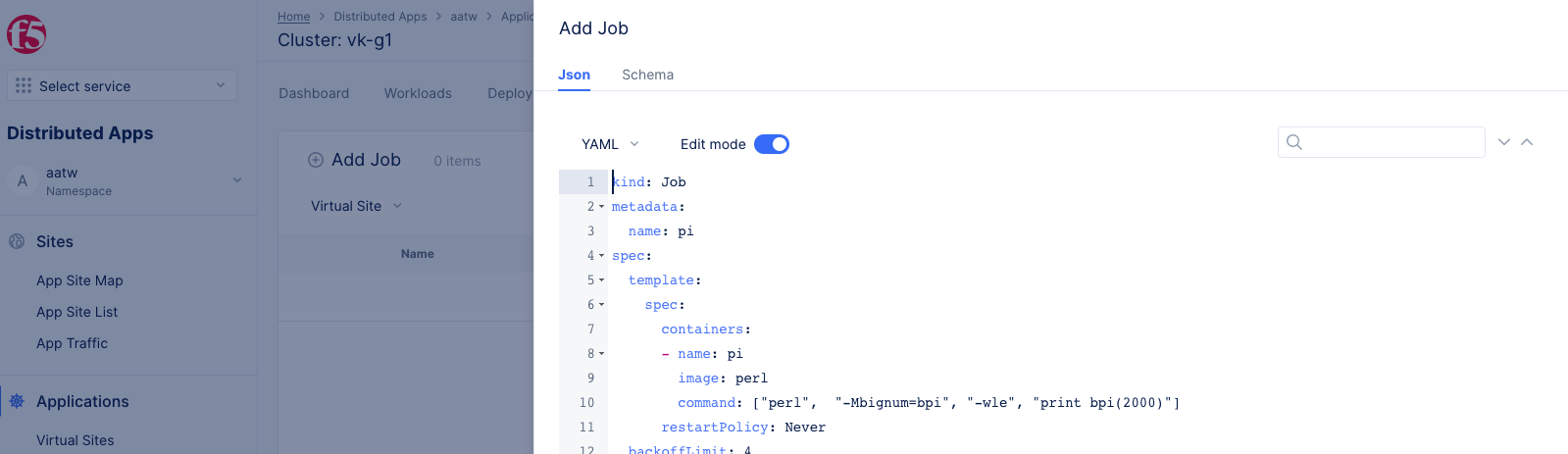
Figure: vK8s Jobs
- Click
Configmapstab. ClickAdd ConfigMapand enter the config map manifest prepared in Step 2. ClickSave.

Figure: vK8s ConfigMaps
- Click
Secretstab. ClickAdd Secretand enter the secret manifest prepared in Step 2. ClickSave.
Note: You can directly create secret on vK8s using
kubectlas shown in Step 2.

Figure: vK8s Secrets
Step 3.2: Deploy using kubectl command.
To deploy the web application in a K8s cluster, the following are required:
-
A kubeconfig file of the K8s cluster. For this, use the vK8s kubeconfig file downloaded in the previous step.
-
Manifest file of your web application. See Step 1.2 for sample manifests.
-
Enter the following command to deploy the resource. This sample deploys a vK8s service.
kubectl apply -f k8s-service-manifest.yaml --kubeconfig vk8s-kubecfg.yaml
Note: Pods created on a site via Deployment, StatefulSet, Job, and, CronJob in vK8s are configured with the site labels as environment variables. If the labels are changed on a site, the pods are restarted with the changed labels set as environment variables.